Epicoccum purpurascens and Aspergillus spp. coculture method, and compound obtained through method
A technology of Aspergillus and Epicoccus niger, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of limiting the discovery of new compounds and the difficulty of discovering new compounds
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] The medium used in the present invention for the activation of E. niger strain strains is a PDA medium, which is sterilized under high pressure at 121° C. for 20-30 minutes. Invert a 90mm petri dish, take E. niger mycelium and inoculate it, culture it statically at 25°C for 3 days to 7 days, store it at 4°C, and use it for cultivation and inoculation.
Embodiment 2
[0043] The used Aspergillus strain activation medium of the present invention is GMM medium, and the described solid medium of every 1L is prepared as follows: glucose 10g, nitrate mother liquor 50mL, trace element mother liquor 1mL, yeast extract 1g, agar 15-20g , add the above ingredients in sequence, and finally add distilled water to the final volume to 1L, adjust the pH value to 6.5, and sterilize at 121°C for 20-30 minutes. Invert a 90mm petri dish, streak and inoculate, and culture at 37°C for 3 to 4 days. Collect spores in sterile water, collect spores from each plate, make a spore suspension with a final volume of 2 mL, and store at 4°C for culture inoculation.
[0044] Wherein, the nitrate mother liquor preparation (1L) method is as follows: sodium nitrate NaNO 3 120g, potassium chloride KCl 10.4g, magnesium sulfate MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 10.4 g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 30.4g, add the above ingredients in order, and finally add distilled water...
Embodiment 3
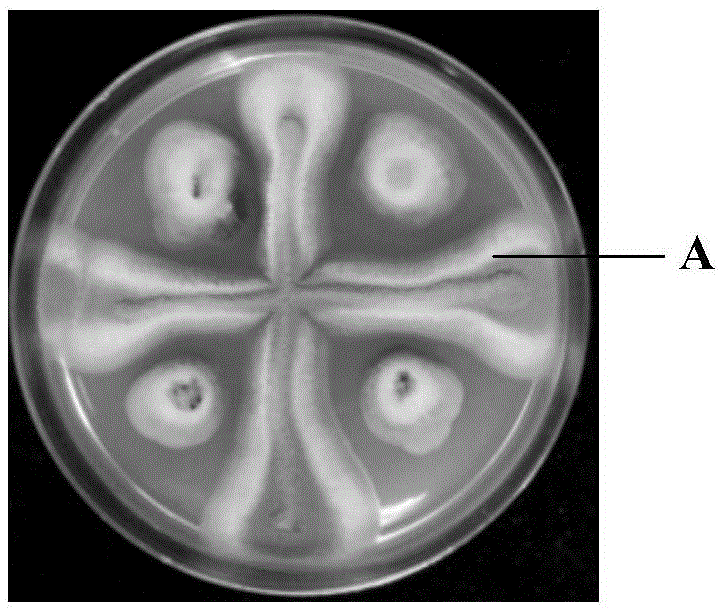
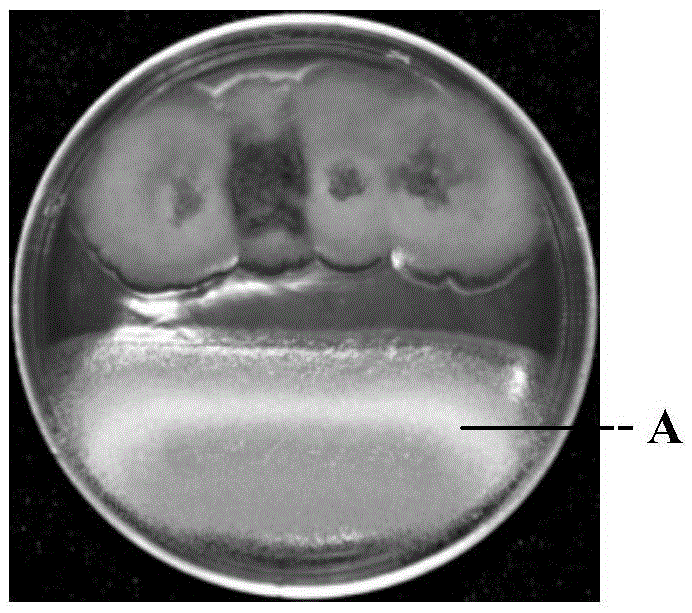
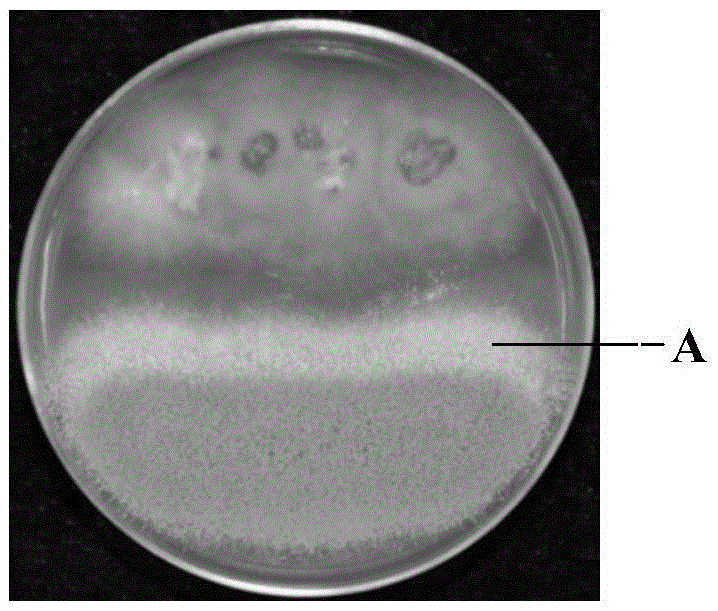
[0047] The used coccus niger and aspergillus co-cultivation method of the present invention are: coccus niger and aspergillus nidulans, aspergillus terreus and aspergillus oryzae are simultaneously inoculated onto the same petri dish that PDA medium is poured down respectively, co-cultivate. The cultivation temperature is 25° C. to 28° C., and the culture is static; after a period of cultivation, the growth of Aspergillus niger close to the side of E. niger is significantly inhibited, and the Aspergillus spores are obviously discolored; the cultivation time is 4 days to 7 days.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com