Aptamer for detecting human renal clear cell carcinoma cells and application of aptamer in preparing detection preparation
A technology of clear cells and nucleic acid aptamers, applied in measuring devices, biochemical equipment and methods, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of lack of early recognition or judgment of symptoms, no targeted therapy of renal cancer cells, insensitivity to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, etc. Achieve high affinity and specificity, short cycle time, and good reproducibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
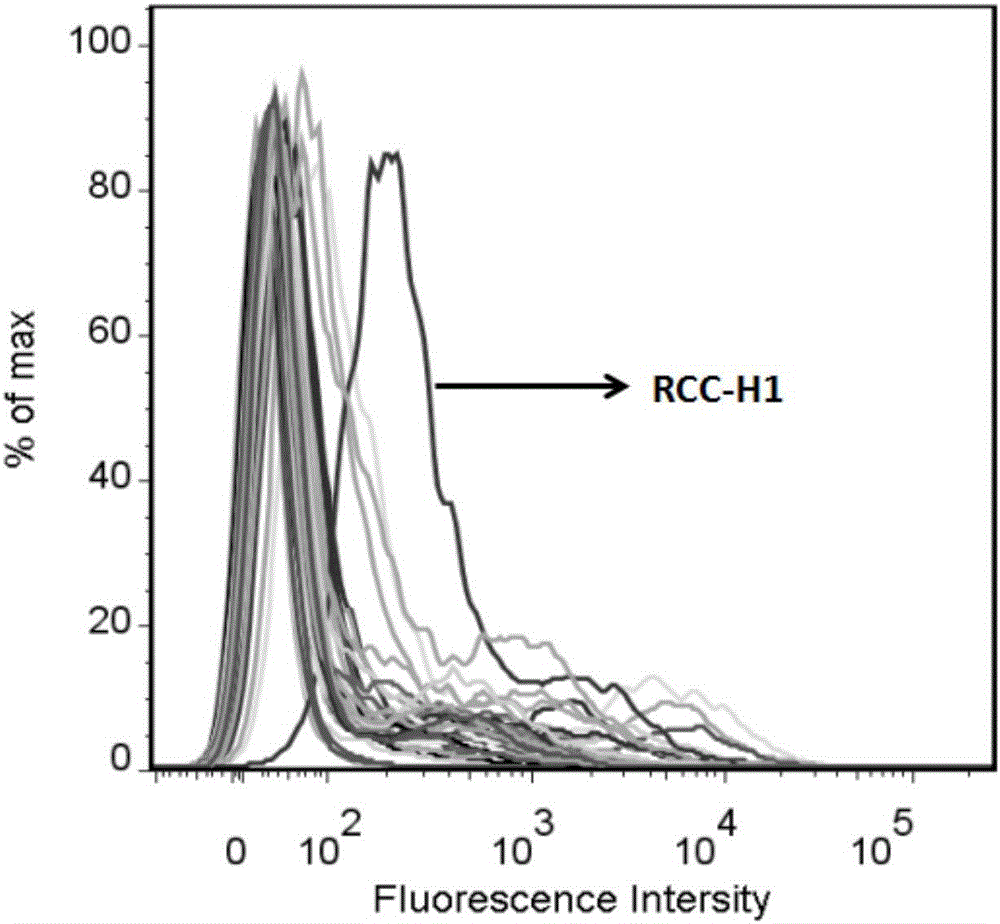
[0026] Example 1: Determination of the sequence with the strongest specific binding ability to the 786-O cell line
[0027] First, digest the 786-O cells in the adherent state from the culture dish with 0.2% EDTA, collect the cells into centrifuge tubes, and wash them by centrifugation with washing buffer (PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride) several times; secondly, all the sequences in the Swan Library with a final concentration of 250nM were added to the 786- O cells; then placed on a shaker at 4°C and incubated for 60 min; after the incubation was completed, they were centrifuged and washed twice with washing buffer (PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride), and fluorescence detection was performed by flow cytometry ( see results figure 1 ). The detection results are shown in the figure, the sequence with the largest displacement is the sequence with the strongest binding ability to 786-O cells, and we named it RCC-H1.
Embodiment 2
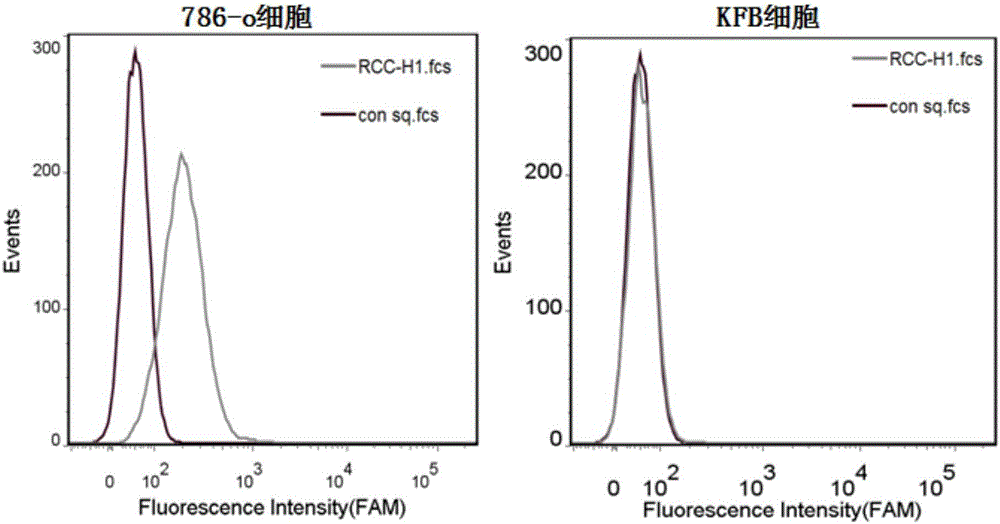
[0028] Embodiment 2: RCC-H1 specifically recognizes renal clear cell carcinoma cell 786-O
[0029] This experiment has similarities with some processing steps in Example 1. First, 786-O and KFB in the adherent state were digested from the culture dish with 0.2% EDTA, respectively, and the cells were collected into centrifuge tubes, and washed with washing buffer (PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride) Centrifuge and wash several times; add an equal amount of binding buffer (D-PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride, 100mg / L tRNA, 1g / L BSA) to 786-O and KFB respectively, and put into the final RCC-H1 and the control sequence at a concentration of 250nM; then placed on a shaker at 4°C and incubated for 60min; after the incubation was completed, they were centrifuged and washed twice with washing buffer (PBS, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride), and passed through flow cytometry Cytometer for fluorescence detection (results see fi...
Embodiment 3
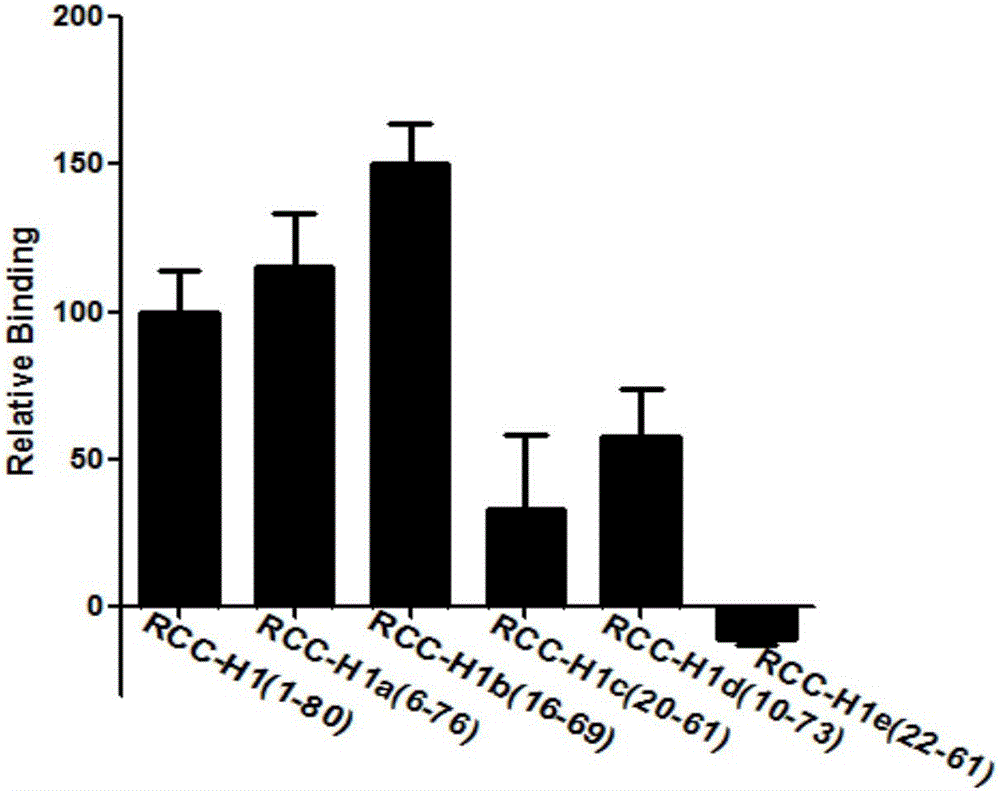
[0030] Embodiment 3: RCC-H1 sequence adds the deletion method of the primer complete sequence of both sides
[0031] Since we don't know which sequence in the whole sequence has a strong combination with 786-O, we optimize the sequence through the following deletion method:
[0032] (The underlined part is the conserved nucleotide sequence of RCC-H1)
[0033] The RCC-H1 sequence plus the full sequence of the primers on both sides is:
[0034] ACCGACCGTGCTGGACTCA TAGGGTTAGGGGCTGCTGGCCAGATATTCAGATGGTAGGGTT ACTATGAGCGAGCCTGGCG (SEQ ID NO. 1)
[0035] RCC-H1a: (Delete 5 bases in the left primer region, delete 4 bases in the right primer region)
[0036] CCGTGCTGGACTCA TAGGGTTAGGGGCTGCTGGCCAGATATTCAGATGGTAGGGTTACTATGAGCGAGCCT (SEQ ID NO. 2)
[0037] RCC-H1b: (Delete 15 bases in the left primer region, delete 11 bases in the right primer region)
[0038] ACTCA TAGGGTTAGGGGCTGCTGGCCAGATATTCAGATGGTAGGGTT ACTATGA (SEQ ID NO. 3)
[0039] RCC-H1c: (Delete 19 bases in the left pri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com