Porous biological ceramic scaffold and preparation method thereof
A technology for bioceramics and ceramic bodies, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of low connected pores, ineffective contact of porogens, and large differences in natural bones.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
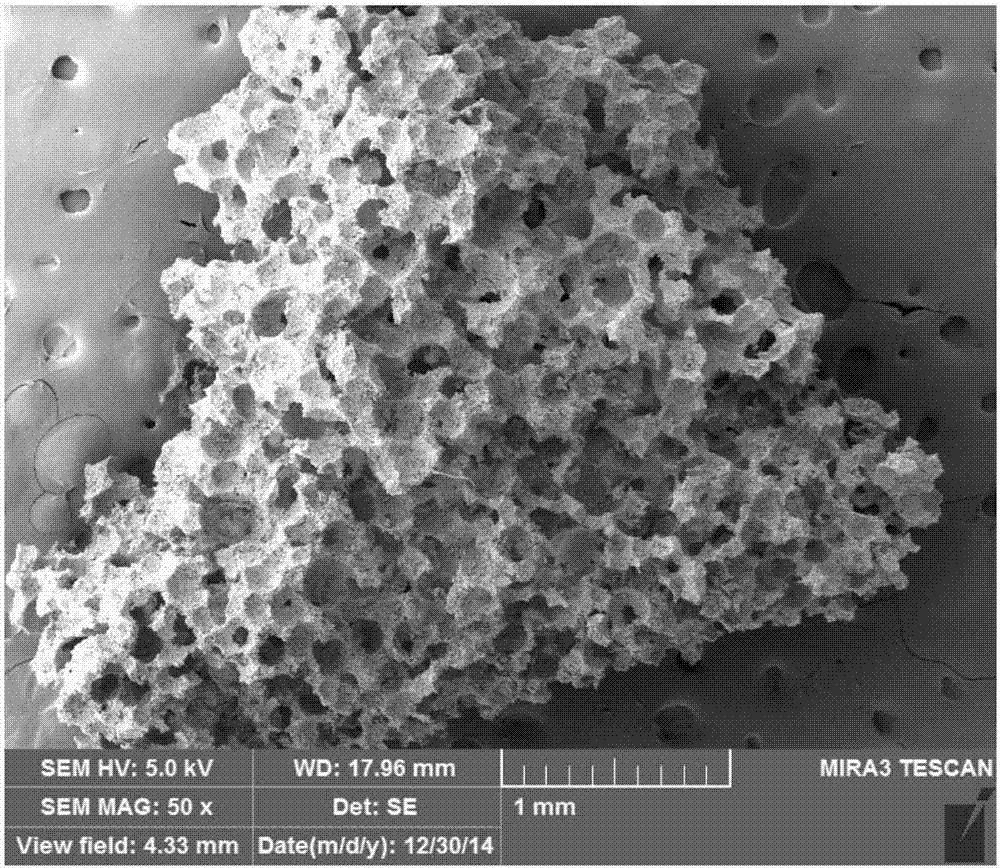
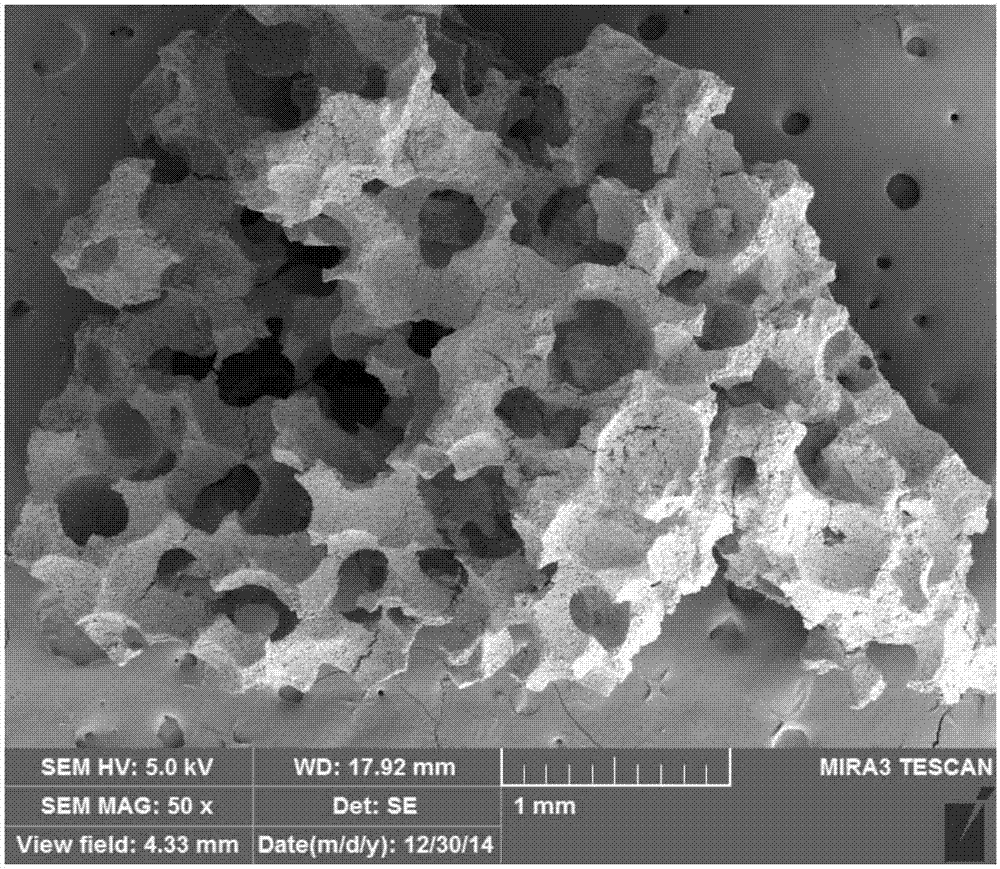
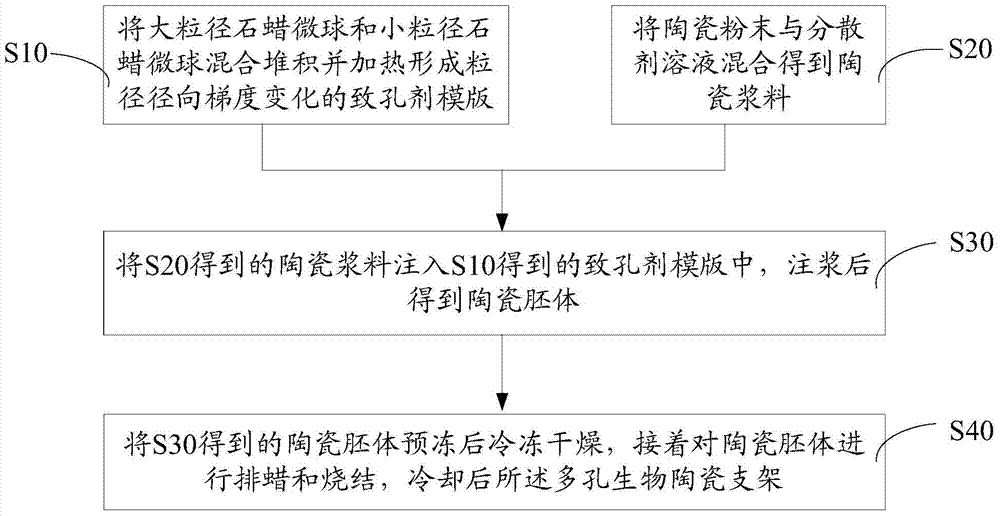
[0031] like figure 1 The preparation method of the porous bioceramic support of one embodiment shown, comprises the following steps:
[0032] S10, mixing and stacking the large-diameter paraffin microspheres and the small-diameter paraffin microspheres, and heating to form a porogen template with radial gradient changes in particle diameter.
[0033] The large-diameter paraffin microspheres can be spherical paraffin microspheres or ellipsoidal paraffin microspheres, and the small-diameter paraffin microspheres can be spherical paraffin microspheres or ellipsoidal paraffin microspheres.
[0034] The particle diameter of the paraffin wax microspheres with large particle diameter may be 600 μm-1200 μm, and the particle diameter of paraffin wax microspheres with small particle diameter may be 50 μm-600 μm.
[0035] In the porogen template, the mass ratio of large-diameter paraffin microspheres to small-diameter paraffin microspheres is 1:0.1-10.
[0036] The operation of mixing ...
Embodiment 1
[0054] 1. Screen out paraffin microspheres with a particle size ranging from 600 μm to 1200 μm as large paraffin microspheres, and paraffin microspheres with a particle size ranging from 50 μm to 600 μm as small paraffin microspheres.
[0055] 2. Large-diameter paraffin microspheres are accumulated inside the cylindrical mold, and heated at 45°C for 15 minutes after flattening, so that the large-diameter paraffin microspheres are bonded to each other, and large-diameter paraffin microspheres are formed after cooling Template: small-diameter paraffin microspheres are deposited on the outer periphery of the cylindrical mold, flattened and withdrawn from the cylindrical mold, then heated at 45°C for 15 minutes, and cooled to form a porogen template with radial gradients in particle size. Wherein, the mass ratio of large-diameter paraffin microspheres and small-diameter paraffin microspheres is 2:1.
[0056] 3. Prepare an ammonium polyacrylate dispersant solution with a mass perce...
Embodiment 2
[0063] 1. Screen out paraffin microspheres with a particle size ranging from 600 μm to 1200 μm as large paraffin microspheres, and paraffin microspheres with a particle size ranging from 50 μm to 600 μm as small paraffin microspheres.
[0064] 2. Large-diameter paraffin microspheres are deposited inside the cylindrical mold, and then small-diameter paraffin microspheres are deposited on the outer periphery of the cylindrical mold. After flattening, the cylindrical mold is withdrawn, and then heated at 40°C for 30 minutes. After cooling A porogen template with radial gradient changes in particle size is formed. Wherein, the mass ratio of large-diameter paraffin microspheres and small-diameter paraffin microspheres is 1:1.
[0065] 3. Prepare a sodium polyacrylate dispersant solution with a mass percentage concentration of 1%, mix hydroxyapatite and β-tricalcium phosphate in a mass ratio of 1:1 to form a ceramic powder, and then press the ceramic powder: ammonium polyacrylate di...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com