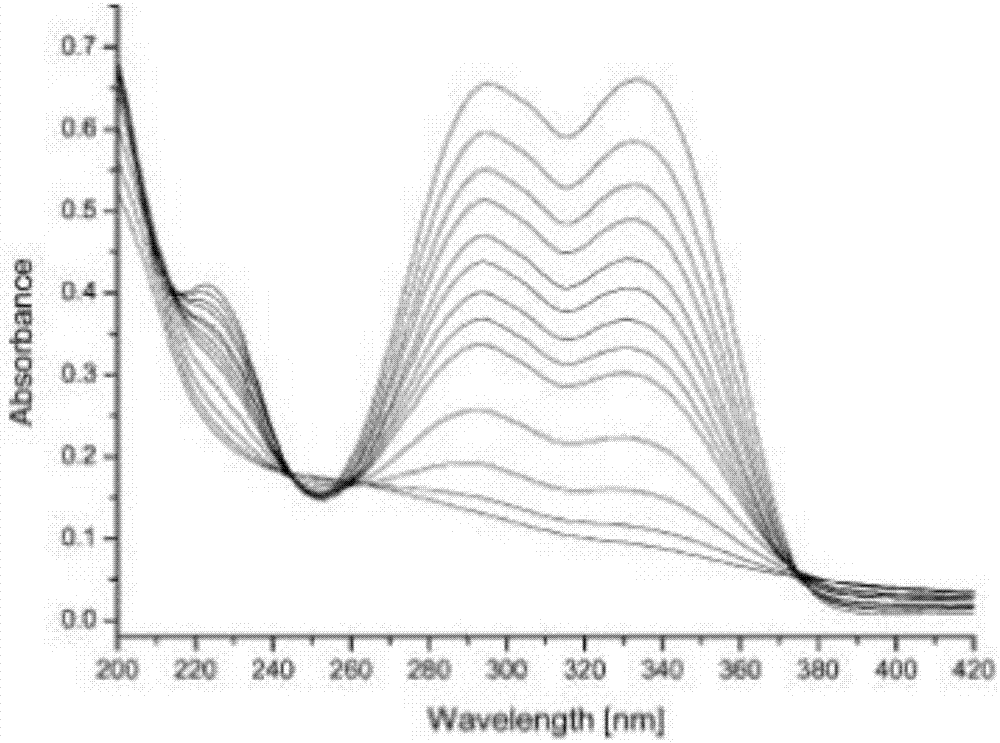
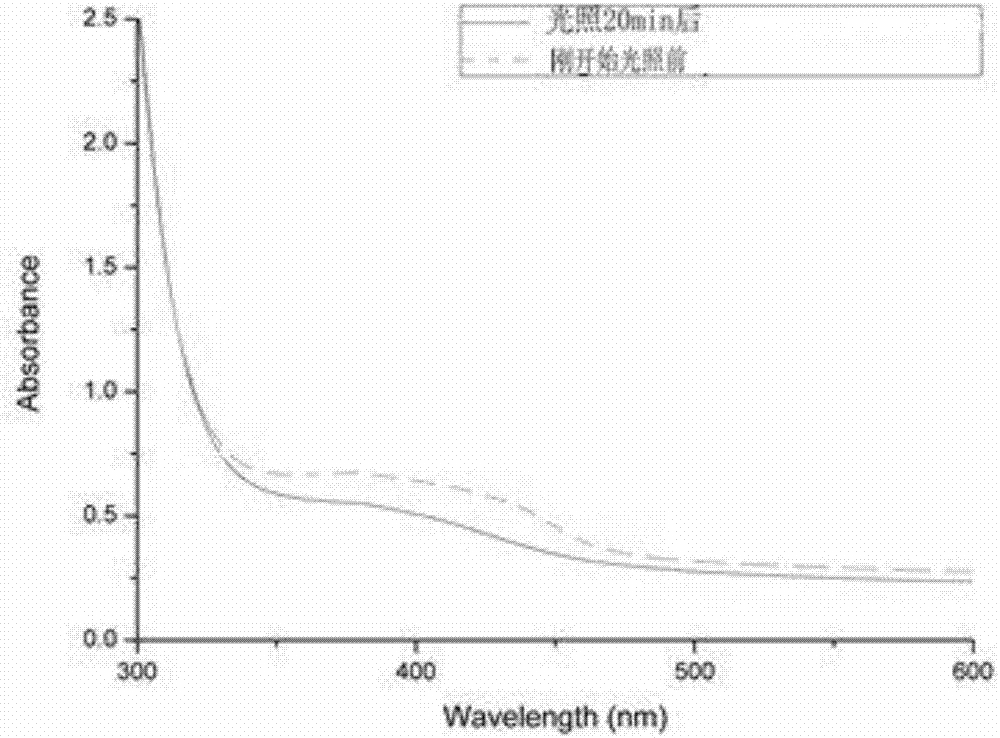
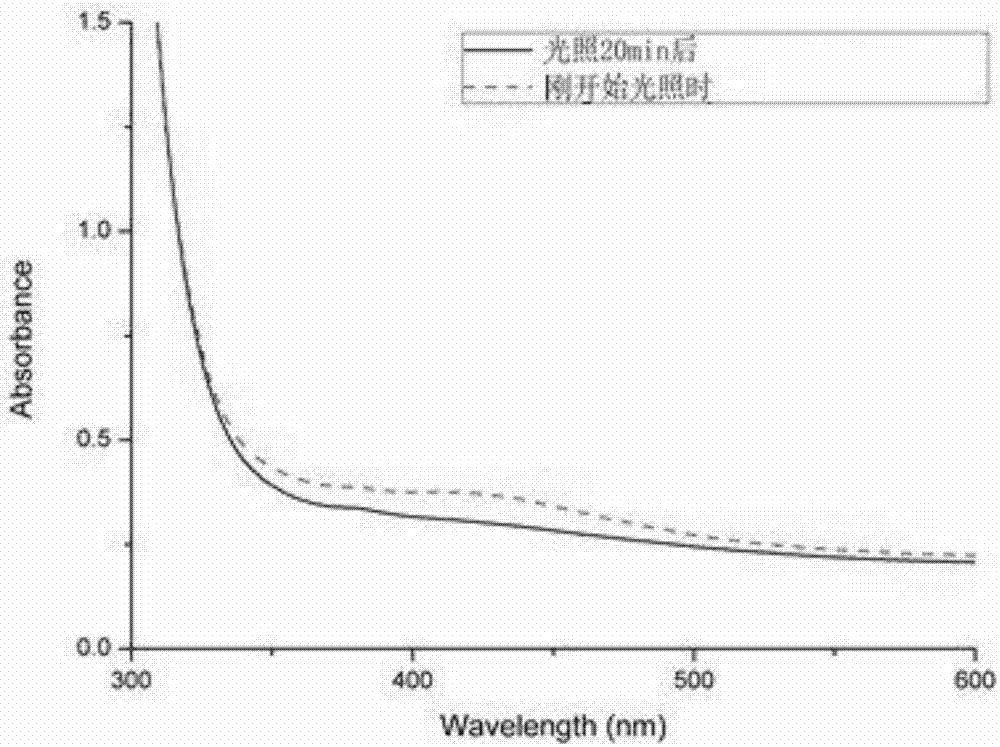
Novel photolytic triazene polymer
A technology of triazene and polymer, applied in the field of novel photolyzable triazene polymers, can solve the problems of decreased absorbance, poor transmission effect, easy viscosity of solution, etc., to avoid cell damage, novel structure, good solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031]
[0032] 1) Mix 0.015mol of diaminobenzophenone, 30mL of water and 7.5mL of 37% hydrochloric acid, stir slowly at room temperature for 2 hours and then cool to -5°C to obtain a mixed solution 1; add 0.03mol of sodium nitrite to 20mL of RO In water, a sodium nitrate solution was obtained, and after cooling to -5°C, the sodium nitrate solution was added dropwise to the mixed solution 1 to react for 1 hour, and the reaction temperature was -5°C to obtain the first type of solution 1;
[0033] 2) Mix and react 0.015mol of N,N'-diethyl-1,3-propylenediamine, 50mL of water and 3.5mL of 37% hydrochloric acid, and cool to -5°C to obtain the second type of solution;
[0034] 3) According to the mixing ratio of 1.5g / mL, add crushed ice into n-hexane and mix to obtain the third type of solution; then add the first type of solution 1 and the second type of solution dropwise into the third type of solution alternately , stirred and reacted for 0.5h to obtain intermediate product 1...
Embodiment 2
[0038]
[0039] 1) Mix 0.015mol of 2,6-diaminoanthraquinone, 30mL of water and 7.5mL of 37% hydrochloric acid, stir at room temperature for 1h, cool to -5°C to obtain mixed solution 2; add 0.03mol of sodium nitrite In 20mL of RO water, a sodium nitrate solution was obtained, and after cooling to -5°C, the sodium nitrate solution was added dropwise to the mixed solution 2 to react for 1 hour at a reaction temperature of -5°C to obtain the first type of solution 2;
[0040] 2) Mix and react 0.015mol of N,N'-diethyl-1,3-propylenediamine, 50mL of water and 3.5mL of 37% hydrochloric acid, and cool to -5°C to obtain the second type of solution;
[0041] 3) According to the mixing ratio of 1.5g / mL, add crushed ice into n-hexane and mix to obtain the third type of solution; then add the first type of solution 2 and the second type of solution dropwise into the third type of solution alternately , stirred and reacted for 1h to obtain the intermediate product 2;
[0042] 4) Add 60mL...
Embodiment 3
[0045]
[0046] 1) Mix 0.015mol of basic fuchsin, 30mL of water and 7.5mL of 37% hydrochloric acid, stir at room temperature for 2h, cool to -5°C to obtain mixed solution 3; add 0.03mol of sodium nitrite to 20mL of RO water , to obtain a sodium nitrate solution, and after cooling to -5°C, add the sodium nitrate solution dropwise to the mixed solution 3 to react for 1 hour at a reaction temperature of -5°C to obtain the first type of solution 3;
[0047]2) 0.015 mol of diethylamine, 50 mL of water and 3.5 mL of 37% hydrochloric acid were mixed and reacted, and cooled to -5°C to obtain the second type of solution 3;
[0048] 3) According to the mixing ratio of 1.5g / mL, add crushed ice into n-hexane and mix to obtain the third type of solution; then add the first type of solution 3 and the second type of solution 3 into the third type of solution dropwise alternately , stirred and reacted for 1 h to obtain intermediate product 3;
[0049] 4) Add 60mL of 2mol / L K to the interm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com