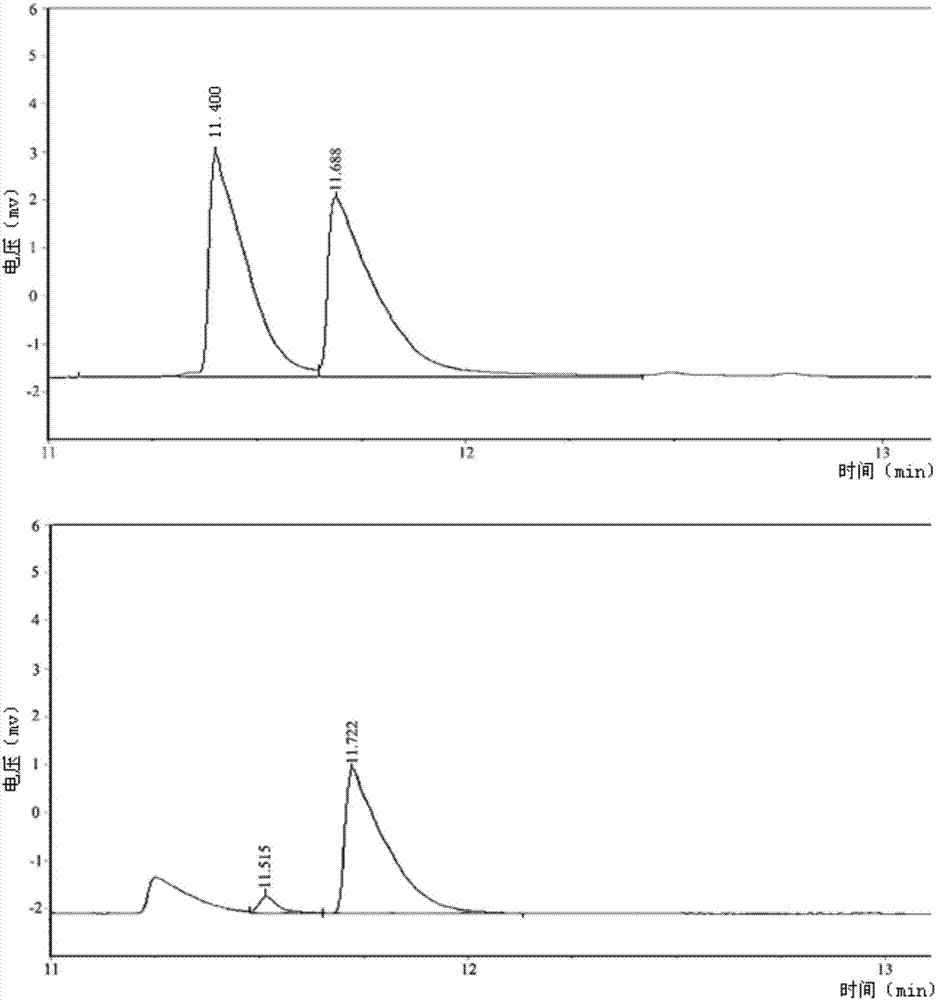
Method for generating L(+)-acetoin by in-vitro enzyme reaction
A technology of acetoin and in vitro enzyme, which is applied in the field of in vitro enzyme reaction to produce L-acetoin, can solve the problems of many by-products and affect downstream separation, and achieve effective regeneration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 Overexpression of 2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase (bdhA) using commercial protein expression vector pET28a
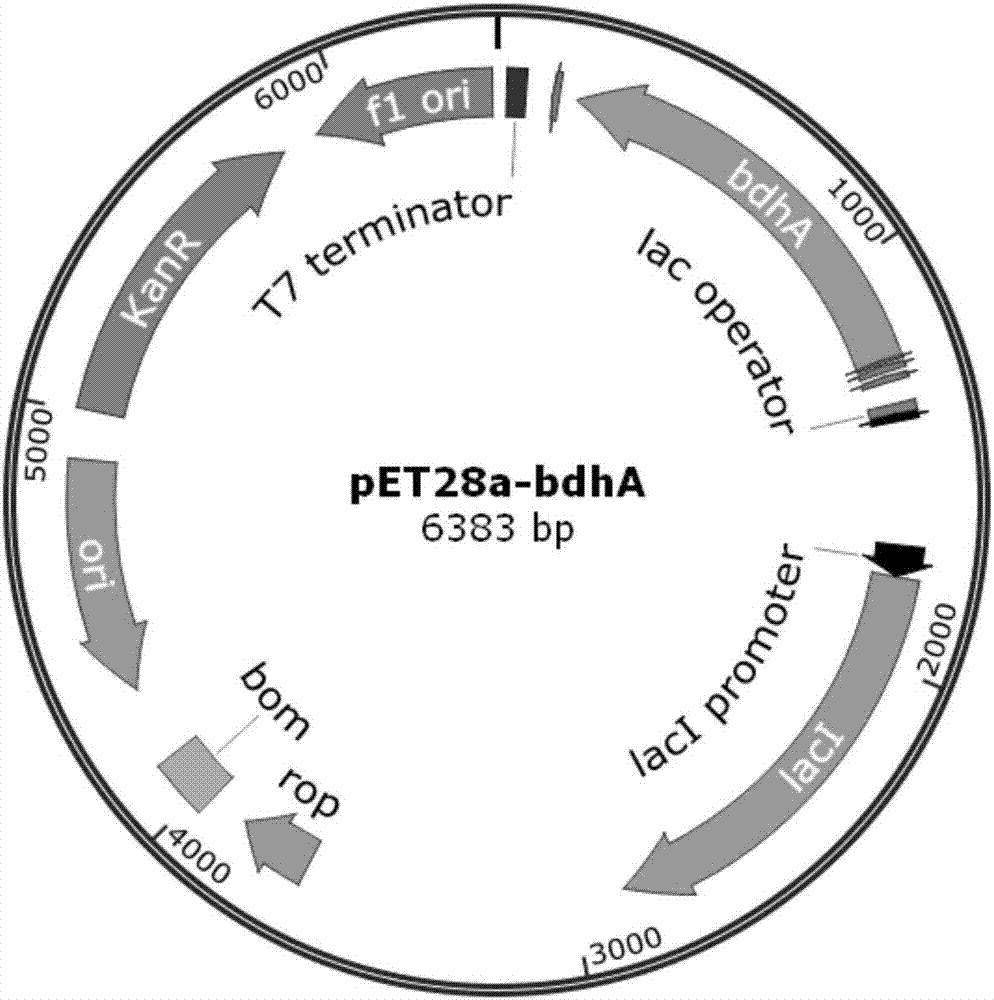
[0028] Using the Bacillus subtilis B. subtilis 168 genome as a template, primers p-bdhA1 and p-bdhA2 were used to amplify the gene bdhA fragment (about 1.0 kp). The bdhA fragment and the pET28A plasmid were digested with Thermo Fast digest NheI / BamHI, and after ligation and transformation, the expression vector pET28a-bdhA of the bdhA gene was obtained (see figure 1 ), and the sequence detection was correct. The plasmid with the correct sequencing result was transformed into commercially competent E. coli BL21(DE3) by the traditional calcium chloride method to obtain BL21-1 overexpressing 2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase (bdhA).
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2 Overexpression of NADH oxidase (yodC) using commercialized protein expression vector pET28a
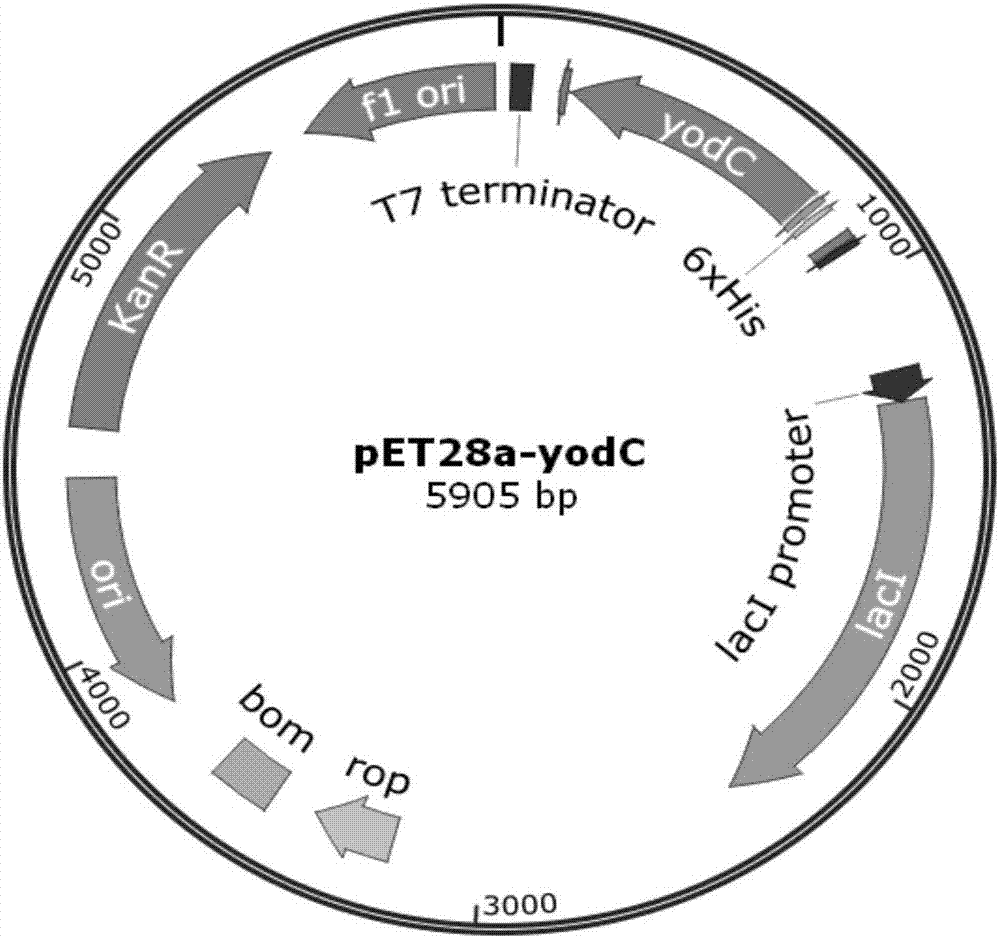
[0030] Using the Bacillus subtilis B. subtilis 168 genome as a template, primers p-yodC1 and p-yodC2 were used to amplify the gene yodC fragment (609bp). Then the yodC fragment and the pET28a plasmid were digested with Thermo Fast digest NdeI / XhoI, and after ligation and transformation, the expression vector pET28a-yodC of the yodC gene was obtained (see figure 2 ), and the sequence detection was correct. The plasmid with the correct sequencing result was transformed into commercially competent E. coli BL21(DE3) by the traditional calcium chloride method to obtain BL21-2 overexpressing NADH oxidase (yodC).
[0031] Table 1 Primer sequences used for strain construction
[0032]
Embodiment 3
[0033] Example 3 Purification and concentration of 2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase
[0034] 1. The specific steps for the purification and concentration of 2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase are:
[0035] 1) Inoculate Escherichia coli BL21-1 into 400mL LB medium, culture on a shaker at 37°C, 220rpm until the OD600 is 0.6, add the inducer IPTG to a final concentration of 0.5mM, culture at 16°C for 12h, centrifuge at 4°C, 4200rpm for 20min Collect the cells and suspend them with 20mL buffer A.
[0036] 2) Collect the suspension of BL21-1 obtained in step 1), break the cells under the action of a high-pressure cell breaker, at 4°C, 1200bar, oil pressure 18Kg / cm 3 Treated 3 times under the same conditions, centrifuged at 4°C and 8000rpm for 30min after crushing, and collected the supernatant to obtain the crude enzyme solution.
[0037] 3) Using the crude enzyme solution obtained in step 2) to purify the protein by using a gravity nickel column purification method. At 4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com