A method and system for improving soybean water use efficiency
A soybean and water technology, applied in the field of farmland management measures and systems, can solve the problems of crop growth, weak growth, crop yield reduction, etc., and achieve the effects of improving soil moisture and fertility, reducing damage and flow, and maintaining soil moisture and fertility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] This embodiment is a method for improving soybean water use efficiency. The steps of the method are as follows:
[0033] (1) Steps for assessing the degree of crop drought: first evaluate the degree of drought in different growth stages of crops under the long-term historical sequence, and evaluate the true degree of drought in the current growth period; if: the true degree of drought is greater than the historical degree of drought, and the historical degree of drought The evaluation shows that the drought is a strengthening trend, that is, the drought degree in the next growth period is greater than that in the current growth period, so the amount of root cutting needs to be determined according to the true drought degree in the current growth period.
[0034] Drought assessment: Calculations of Palmer's method and modified PDSI index can be used.
[0035] (1) Palmer method: Palmer (Palmer, translated as Palmer) believes that the drought period is a period of continu...
Embodiment 2
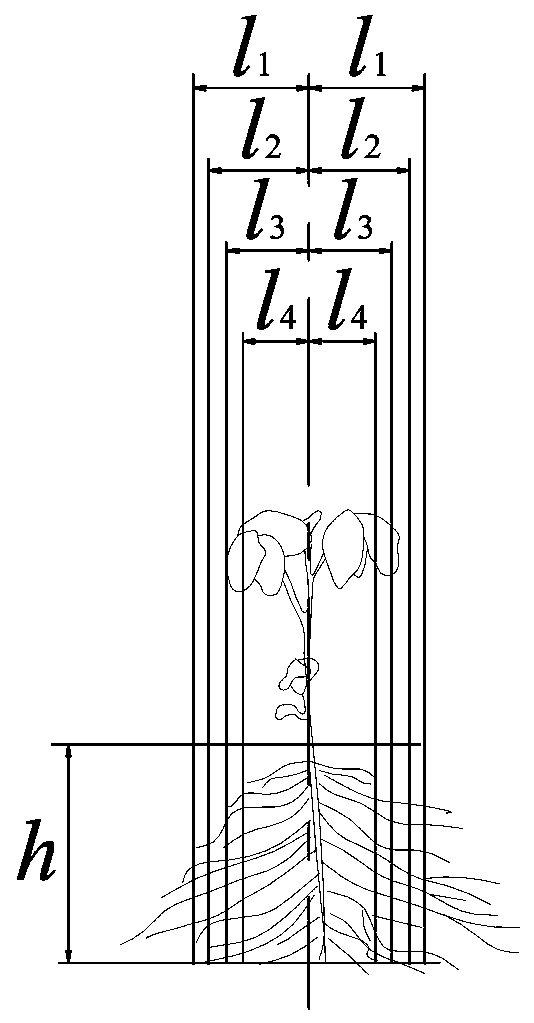
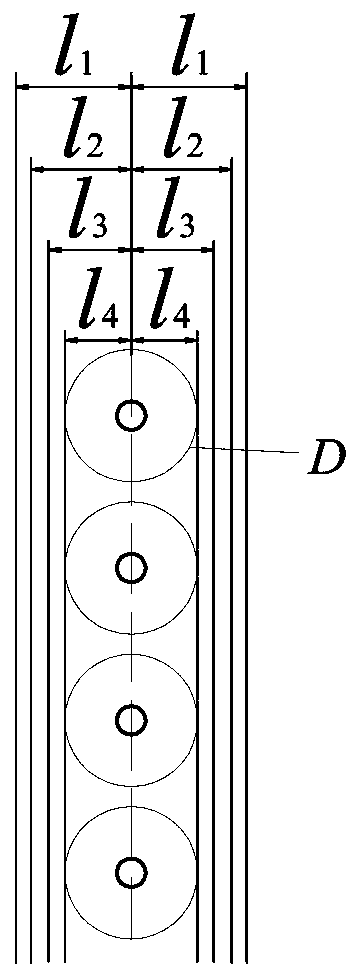
[0080] This embodiment is an improvement of the first embodiment, and it is a refinement of the first embodiment about the location of root removal. The root-cutting position described in this embodiment is from both sides of the main stem l 1 =3.8cm, l 2 =3.5cm, l 3 =3.0cm, l 4 = 2.5cm cm, see figure 1 , 2 , pruning depth h For: 20 cm vertical undercut, see figure 1 , the amount of cut root is 10%, 20%, 30%, 40% respectively.
[0081] The general distribution trend of soybean roots in the soil is: from the vertical direction, more than 90% of the roots are distributed in 0-20cm, while the roots below the bottom of Lili are less than 15%. And the branch roots are mainly branched from the main root at 5-20cm below the surface, and the branch roots branched from the main root below 20cm are few, and most of them are linear fine roots; 77.77%~82.88% are concentrated in the soil 0~5cm away from the plant.
Embodiment 3
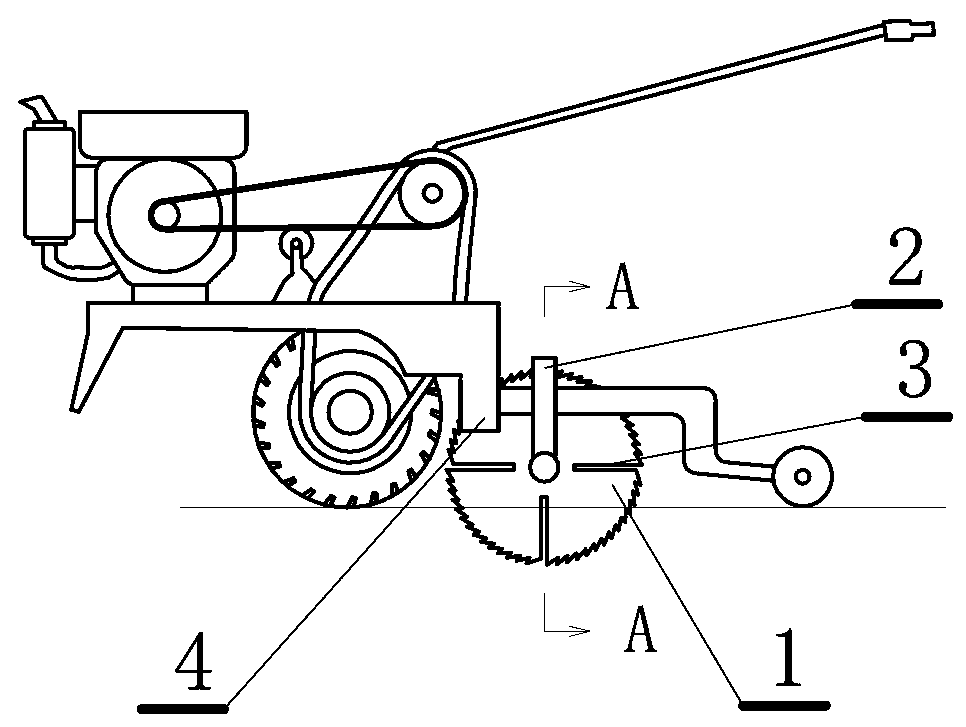
[0083] This embodiment is a system for improving the water use efficiency of soybeans that realizes the above method, and the system includes: at least one set of root-cutting knives 1 installed on the tractor frame and a knife holder 2 for installing the root-breaking knives, the root-cutting knife Or a condenser 3 is installed on the tool rest, and the condenser is connected with the condenser power supply 5 installed on the tractor 4, as image 3 , 4 shown.
[0084] This embodiment is a system for realizing the mechanized root-cutting operation of the above-mentioned root-cutting method. The system includes:
[0085] Ritual knife: It can be ultrasonic root knife or electric coagulation root knife.
[0086] A positioning device can be installed on the tool post: use laser rangefinder + carry stepping motor + tilting stepping motor to measure the distance between the central axis and the plant, and adjust the relative position and angle of the tool.
[0087] The console can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com