Crystalline form of ferric maltol
A technology of iron maltol and maltol, which is applied in the field of new polymorphs of compounds, and can solve the problems of not identifying or studying polymorphs and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
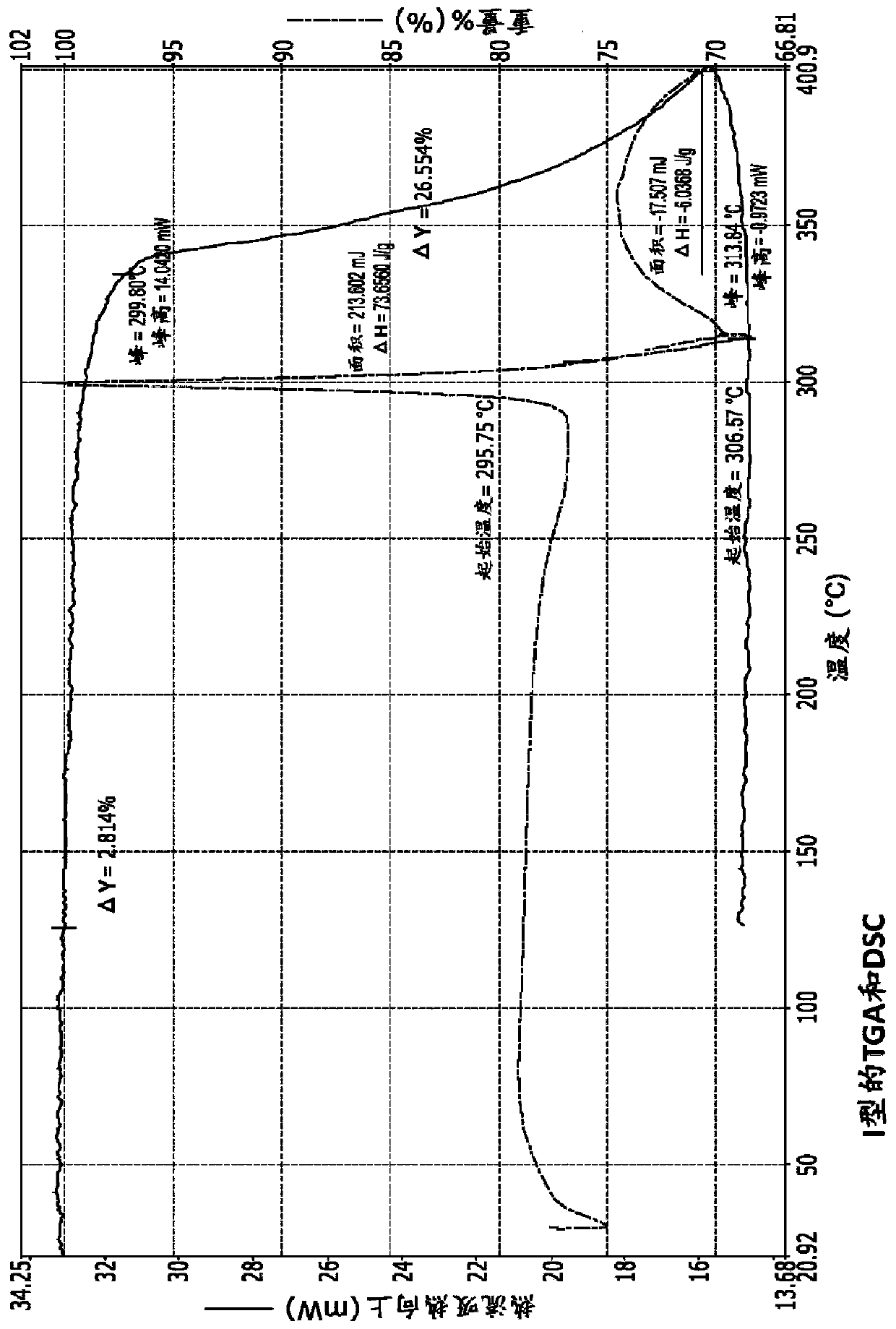
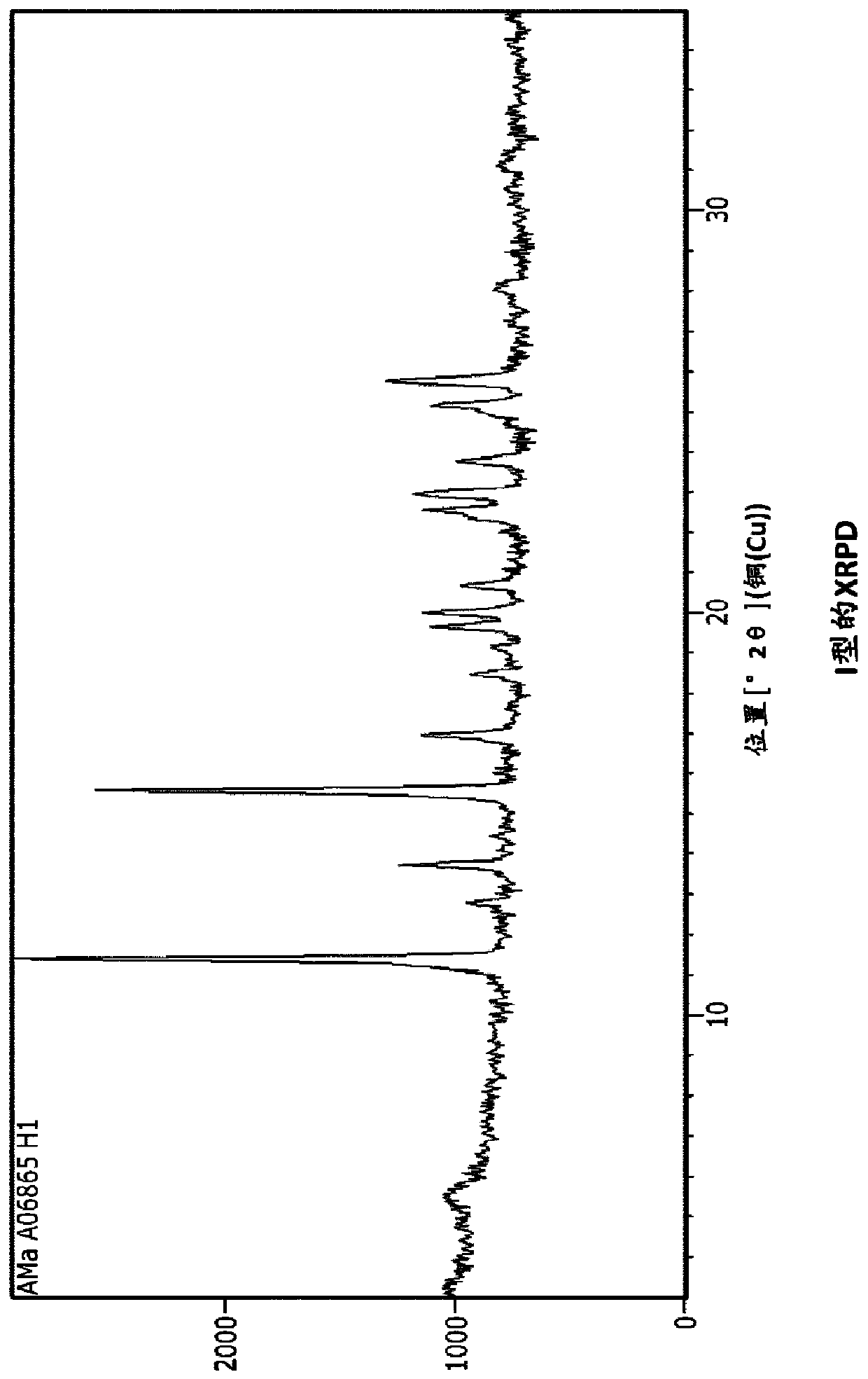
[0190] Example 1: Type I
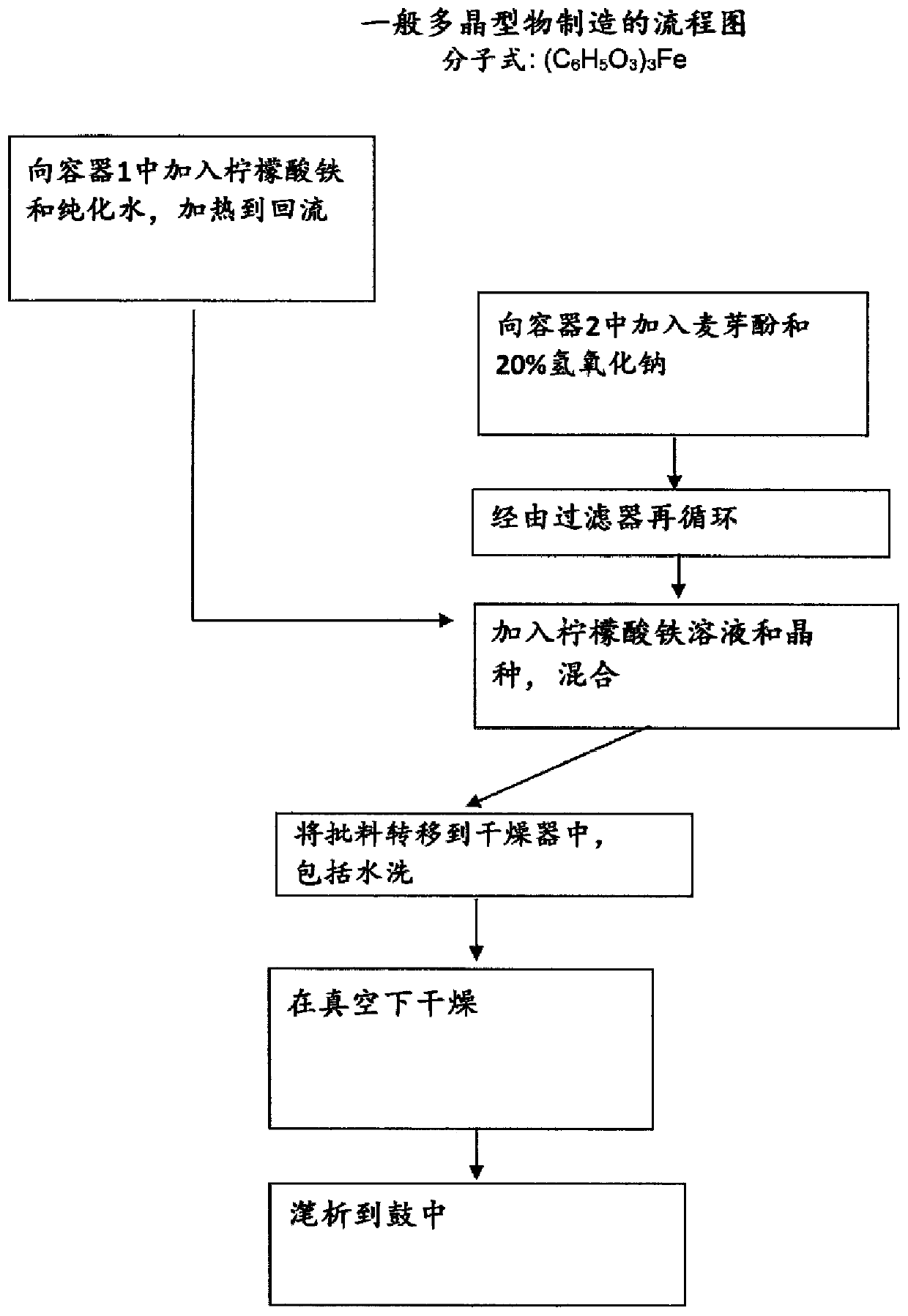
[0191] Combine 9.04 kg of ferric citrate with 29 liters of purified water. Separately 12.2 kg of maltol was combined with 15.2 liters of sodium hydroxide solution (20% w / w). Add ferric citrate and sodium hydroxide to the container, add 4 liters of water, and stir at 20°C to 25°C. Then add the seeds. The seed crystals were 65 g of ferric maltol polymorph in 12 liters of water. The seed crystals were prepared by the same method as described in Example 1, but no seed crystals were used. Add seeds to the vessel to aid consistent crystallization / precipitation. The mixture was kept in a suspension in a vessel to allow crystal growth, then filtered and washed three times with 13 liters of water each time. The resulting solid was dried below 80°C and yielded 13.25 kg dry ferric maltol.
[0192] The ferric maltol in Example 1 was produced in different batches on a scale of 12 kg to 15 kg. Analysis of the ferric maltol produced showed that the % w / w o...
Embodiment 1a
[0194] Production of ferric maltol via recrystallization with and without type II inoculation
[0195] Ferric citrate (15g, 6.12×10 -2 mol) was dissolved in water (60ml) and heated at reflux with stirring to aid dissolution. The solution was then cooled to room temperature. In a separate reaction vessel, maltol (19.17 g, 0.152 mol) was placed in 6M sodium hydroxide (27 ml) with stirring at room temperature until the solids were completely dissolved. The solution was then fine filtered.
[0196] The ferric citrate solution was added to the sodium maltate solution with stirring at room temperature. Precipitate formation was observed after about 15 minutes. The mixture was sampled after stirring for 2 hours and 4 hours. XRPD analysis showed a solid comparable to Form I. The slurry was then stirred overnight. The mixture was filtered under suction and most of the solids were dried in a vacuum oven (45°C). A small portion of solid (3 g) was removed and dried at 80°C without...
Embodiment 2
[0200] Example 2: Type II
[0201] Ferric maltol in Example 2 was produced using the general method as described in Example 1, but in larger batches of 24 kg to 33 kg.
[0202] Analysis of the ferric maltol produced showed that the % w / w of iron present was about 12.7% w / w and the % w / w of maltol present was about 88% w / w to 88.6% w / w.
[0203] The XRPD pattern of the type II polymorph obtained via Example 1a is shown in Figure 5 middle.
[0204] Analysis of the ferric maltol produced showed that in different batches the % w / w of iron present was about 12.7% w / w to 12.9% w / w and the % w / w of maltol present was about 86.7% w / w to 87.1% w / w. However, the ferric maltol seeds used in Example 2 were seeds of the Form I and Form II polymorphs.
[0205] Precipitated ferric maltol was also kept in the wet slurry for a longer time than Example 1.
[0206] The XRPD pattern of the type II polymorph obtained via Example 1a is shown in Figure 5 middle.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| solubility (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| solubility (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com