High-efficiency nondestructive identification method for edible oil doped with less illegal cooking oil
A technology for waste oil and edible oil, applied in Raman scattering, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of the need to improve the identification efficiency and persuasion, the limited space for illegal profit, the limited identification ability, etc., and achieve rich fingerprint information of samples. , Improve the efficiency of identification and persuasion, the effect of strong identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
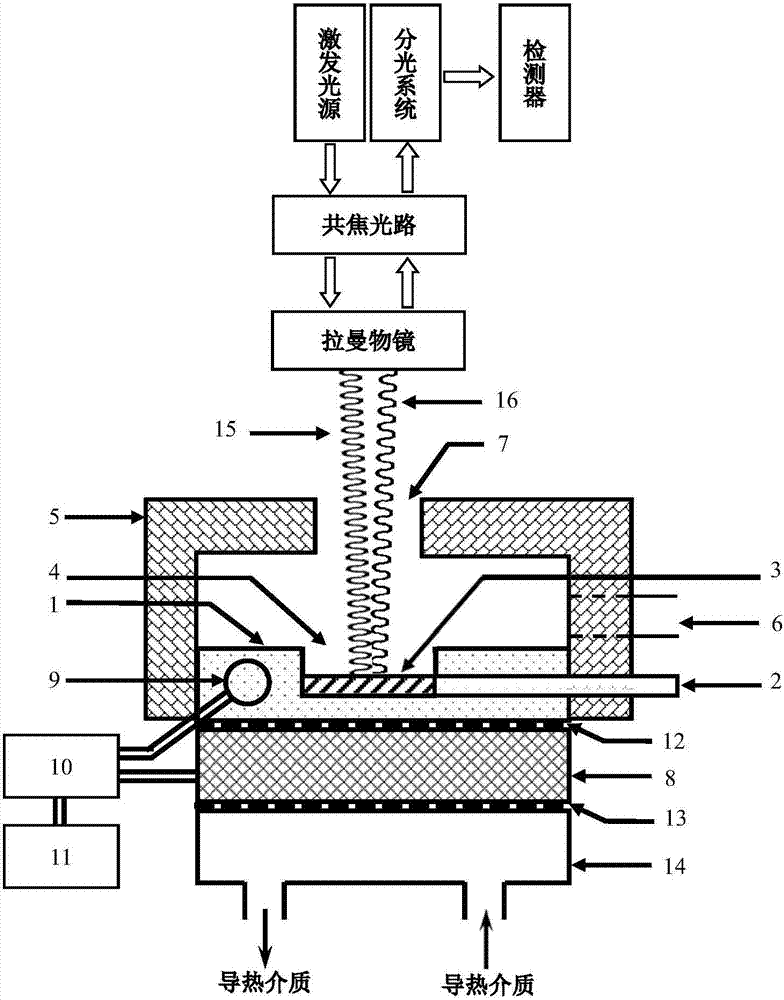
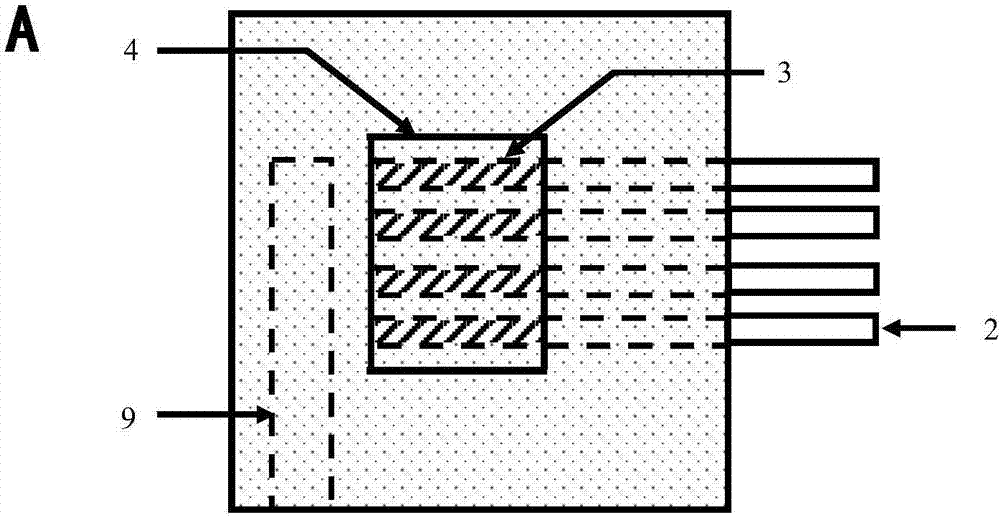
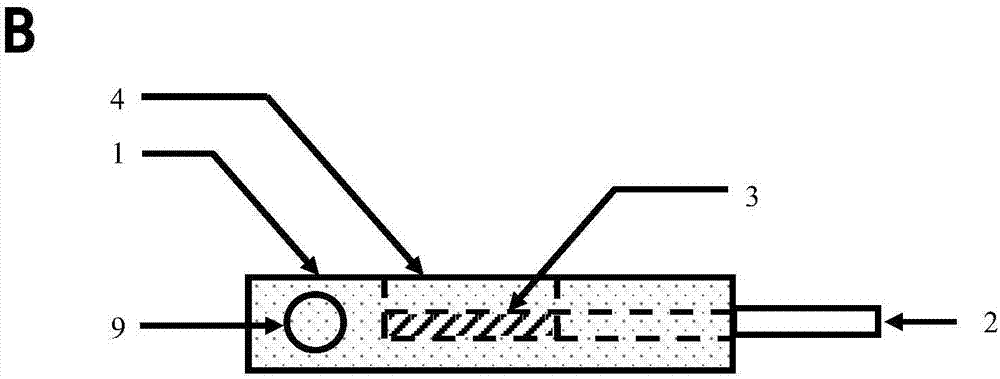
[0050] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of a variable temperature Raman measurement experiment using a high-efficiency non-destructive detection device for organic matter based on variable temperature Raman technology. In the figure, the device includes a sample stage 1 with a groove structure, a window 4 is arranged directly above the groove of the sample stage 1, and one or more parallel sample tubes are arranged on the side of the sample stage 1 2, the socket communicates with the groove; the oil sample 3 contained in the sample tube 2 is inserted into the groove through the socket. The excitation light 15 emitted by the excitation light source passes through the confocal optical path through the Raman objective lens, and then passes through the upper window 7 of the waterproof vapor cover 5 and the upper window 4 of the groove of the sample stage 1, and irradiates the oil sample in the sample tube 2 3. The excited sample signal 16 reaches the detector and is recorded af...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Using Horiba JY XploRA micro confocal Raman spectrometer, in the temperature range from +15°C to -25°C, with an interval of 5°C, the genuine first-grade refined soybean oil, 1# and 2# refined waste oil, 3# and 4 #Standard samples and blind samples of blended oil samples are used to collect Raman spectral fingerprint data at different temperatures. The excitation wavelength is 532nm, the filter is set to 100%, the aperture and slit are 500μm and 200μm respectively, the grating is 1800T, the objective lens is 50×, and the detection range is 2850-2975cm -1 , the CCD detector temperature is -70°C, the exposure time is 1s, and each spectrum is accumulated 20 times; the protective gas is high-purity N 2 Gas, flow rate 60ml / min. All samples were tested under the same test conditions, and the spectral data were not subjected to any fluorescence background subtraction processing, and the two-dimensional synchronous correlation spectral data were calculated.
[0058] image 3 ...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Use the method identical with embodiment 2 to carry out the acquisition of Raman spectrum information to oil sample, and calculate two-dimensional synchronous correlation spectrum data; Systematic cluster analysis method and blind sample identification.
[0070] Figure 10 A and B show the results of systematic clustering analysis of the above-mentioned two-dimensional synchronous correlation Raman spectra by using the furthest neighbor element method, standardizing by Z score, and adopting the fourth-order Minkowski distance and Chebyshev distance respectively. As shown in the figure, the blind samples of authentic soybean oil, 1# refined waste oil, 2# refined waste oil, and two adulterated oils were all accurately identified.
[0071] Figure 11 A and B show the use of the furthest neighbor element method, the standardization method with a standard deviation of 1, and the fourth-order Minkowski distance and Chebyshev distance to systematically cluster the above two-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com