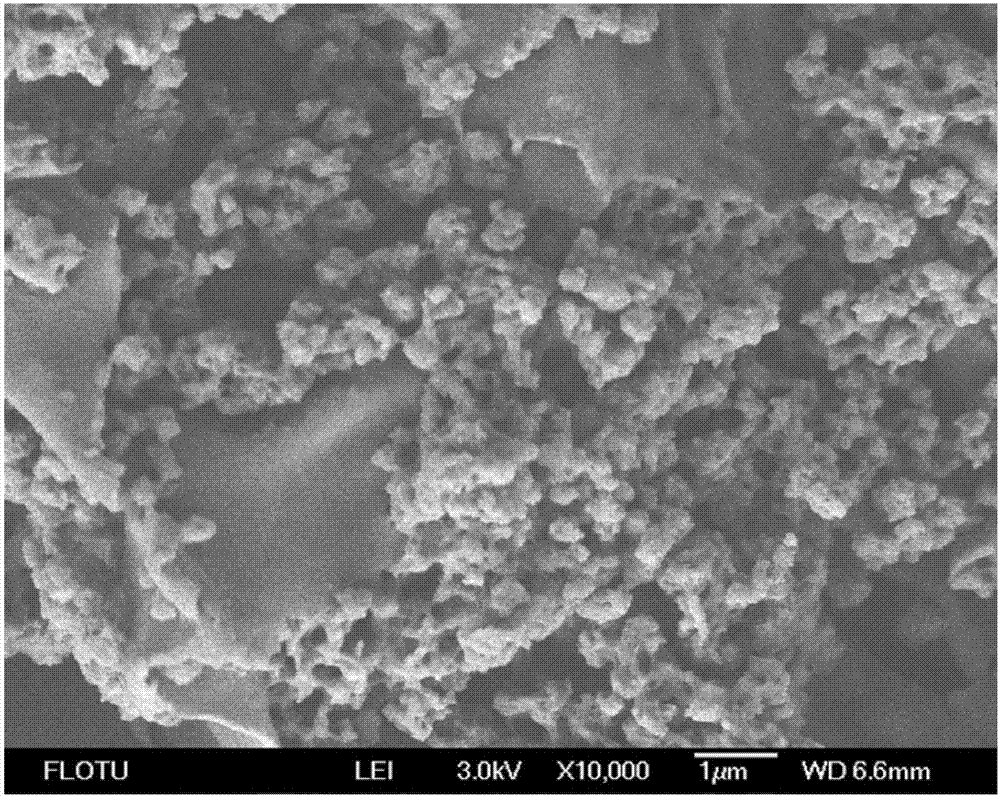
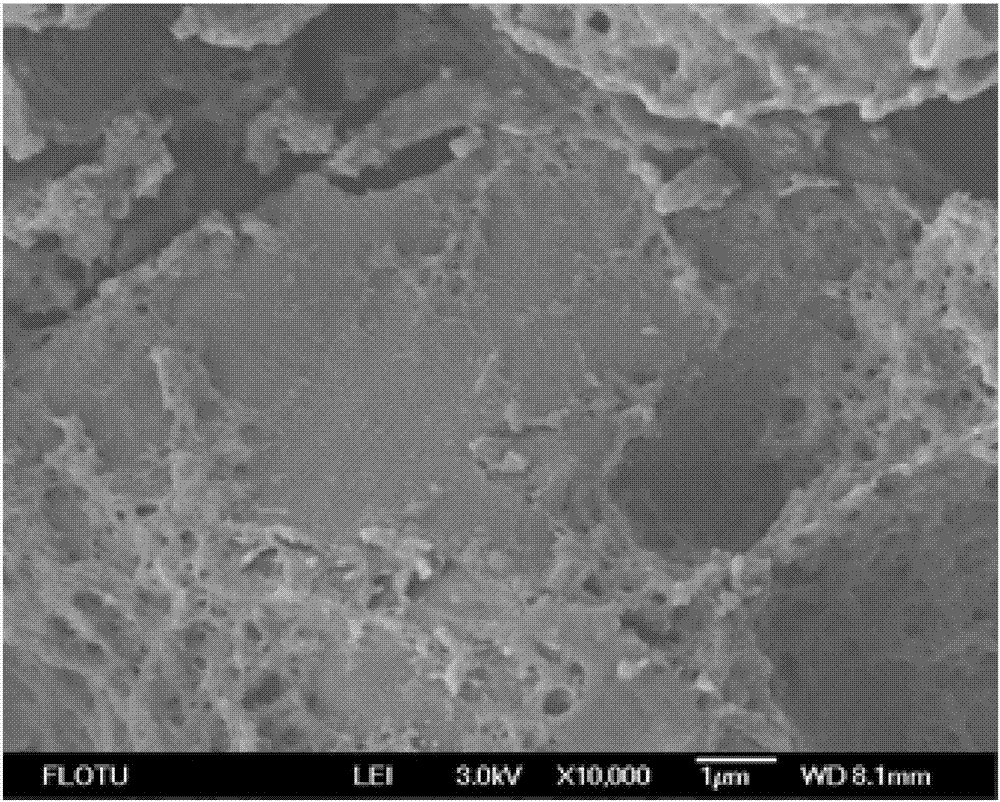
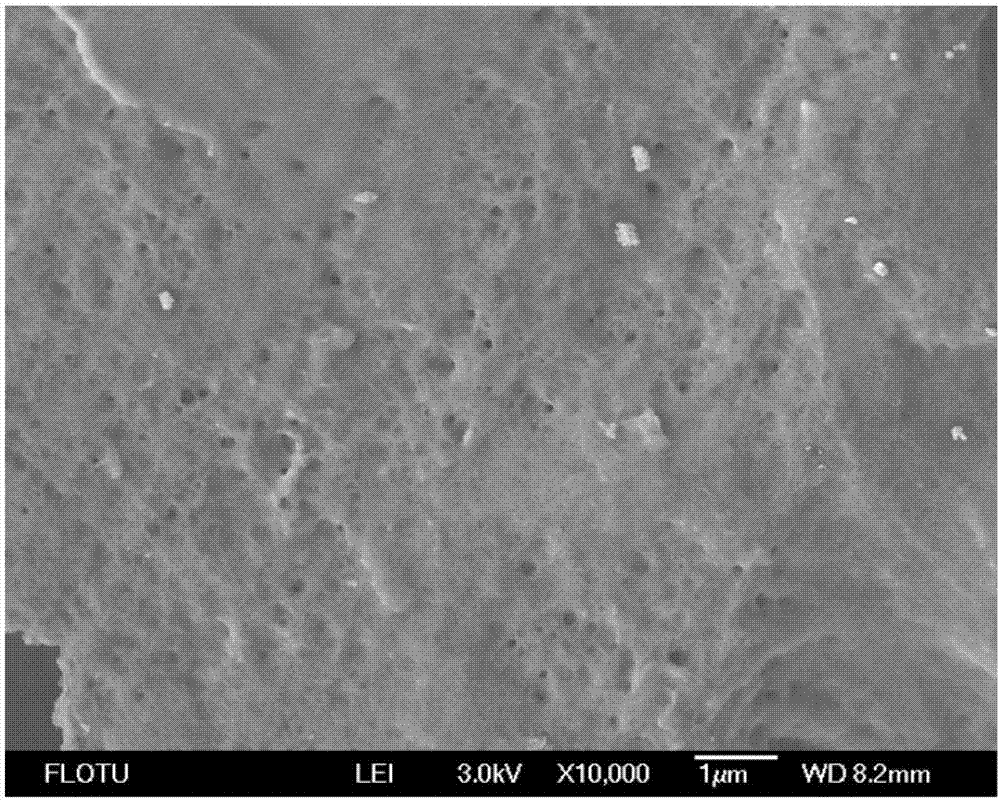
Method for improving pretreatment effect of acid catalysis ionic liquid with organic solvent-aqueous solution
A technology of ionic liquid and organic solvent, which is applied in the field of pretreatment and separation of fiber raw materials, can solve the problems of hindering the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification, increasing energy loss, high energy consumption, etc., and achieve the effect of improving economic feasibility, efficiency and effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Weigh 28.5g of ionic liquid [Bmim]Cl into a three-neck flask, preheat to 80°C to dissolve it. Add 1.5 g of Arundis stalk powder and heat to 120° C. for 3 h under mechanical stirring at 170 rpm. Subsequently, 0.3 g of solid acid Amberlyst 35DRY was added and incubated for 1.0 h. After the reaction, three times the volume of reverse phase solvent 50% ethanol-water solution was added, heated at 50° C. and stirred for 30 minutes. Centrifugation yielded an IL-rich solution and a solid residue. The solid residue was repeatedly washed with 50% ethanol-water solution for 6-7 times until the washing liquid was colorless. The washed solid residue was dried under vacuum at 45 °C for 24 h. Finally, sieve the solid residue to obtain the regeneration raw material of Phyllostachys arundis. Under the condition of 15FPU cellulase / g substrate, after 72 hours of enzymatic hydrolysis, the yield of monosaccharide is 98.7% (relative to the raw material glucose). Under the same enzymatic...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Weigh 28.5g of ionic liquid [Bmim]Cl into a three-neck flask, preheat to 80°C to dissolve it. Add 1.5 g of Arundis stalk powder and heat to 120° C. for 3 h under mechanical stirring at 170 rpm. Subsequently, 0.3 g of solid acid Amberlyst 35DRY was added and incubated for 1.0 h. After the reaction, three times the volume of reverse phase solvent 70% ethanol-water solution was added, heated at 50° C. and stirred for 30 minutes. Centrifugation yielded an IL-rich solution and a solid residue. The solid residue was repeatedly washed with 70% ethanol-water solution for 6-7 times until the washing liquid was colorless. The washed solid residue was dried under vacuum at 45 °C for 24 h. Finally, sieve the solid residue to obtain the regeneration raw material of Phyllostachys arundis. Under the condition of 15FPU cellulase / g substrate, after 72 hours of enzymatic hydrolysis, the monosaccharide yield was 97.3% (relative to the raw material glucose). Under the same enzymatic h...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Weigh 28.5g of ionic liquid [Bmim]Cl into a three-neck flask, preheat to 80°C to dissolve it. Add 1.5 g of Arundis stalk powder and heat to 120° C. for 3 h under mechanical stirring at 170 rpm. Subsequently, 0.3 g of solid acid Amberlyst 35DRY was added and incubated for 1.0 h. After the reaction, three volumes of reverse phase solvent 60% ethanol-water solution were added, heated at 50° C. and stirred for 30 minutes. Centrifugation yielded an IL-rich solution and a solid residue. The solid residue was repeatedly washed with 60% ethanol-water solution for 6-7 times until the washing liquid was colorless. The washed solid residue was dried under vacuum at 45 °C for 24 h. Finally, sieve the solid residue to obtain the regeneration raw material of Phyllostachys arundis. Under the condition of 15FPU cellulase / g substrate, after 72 hours of enzymatic hydrolysis, the yield of monosaccharide is 99.6% (relative to the raw material glucose). Under the same enzymatic hydroly...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com