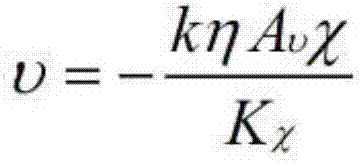Garden waste lignin component fermentative degradation method
A technology for garden waste and lignin, which is applied in the field of fermentation and degradation of lignin components of garden waste, can solve the problems of uneven heat, long fermentation period, low fermentation efficiency, etc., achieve accurate control of the temperature of the heap, and improve the degree of harmlessness , Improve the effect of decomposition effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
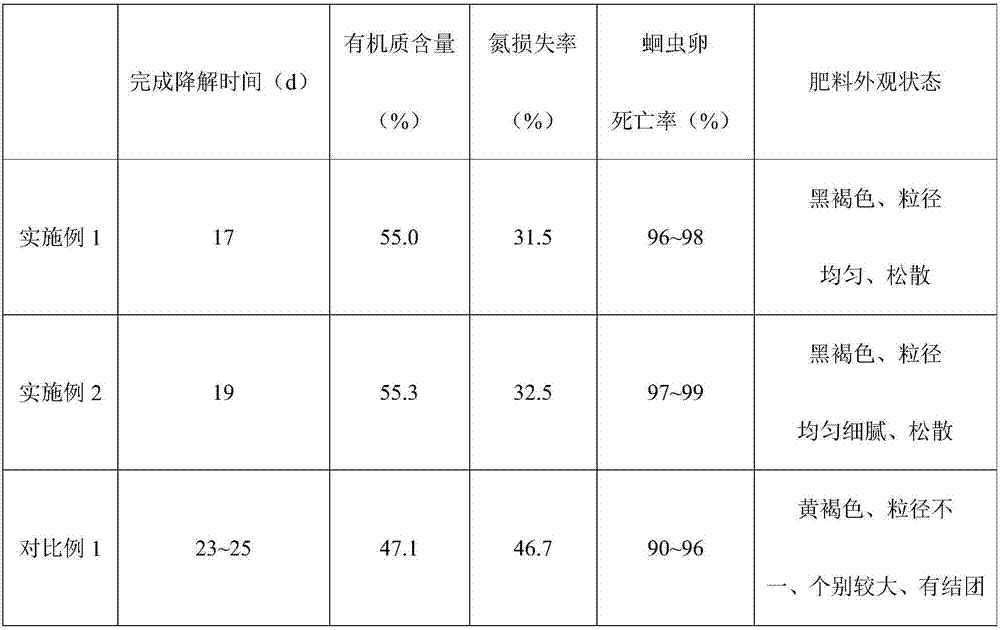
Embodiment 1
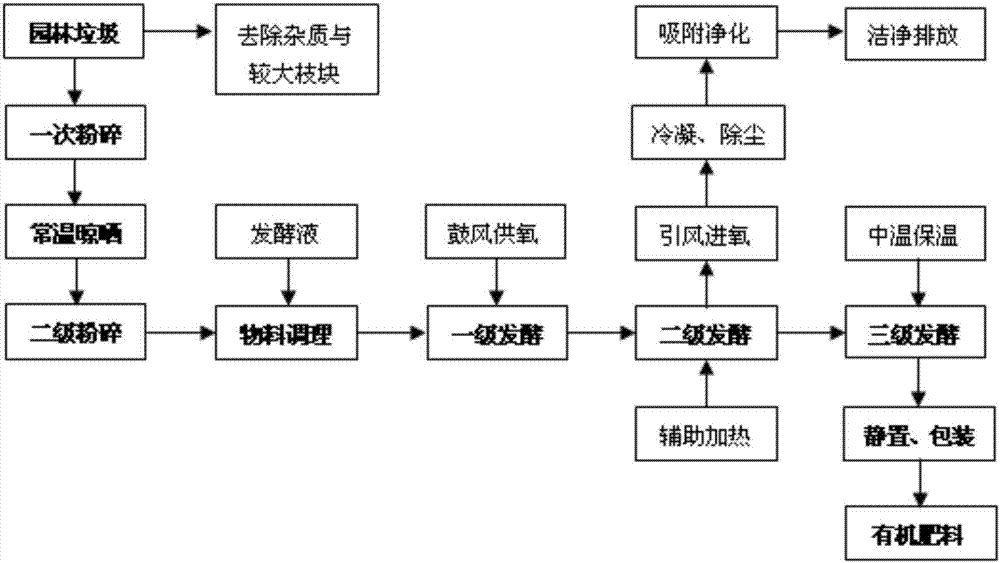
[0044] This embodiment adopts as figure 1 As shown in the process flow, the garden waste comes from the pruning of green trees in the urban area. The large branches have been picked out and used as fuel during pruning. Thick branches, leaving mainly leaves, including grass clippings and small branches with a diameter of less than 2cm, are used as materials for composting.
[0045] The material is sent to the coarse pulverizer and crushed into fragments with a particle size of 2 to 4 cm. Because garden waste sometimes has a high moisture content, especially after coarse crushing, the mucus in the leaves is released, which can easily cause material bonding. Therefore, put the coarsely crushed materials under the canopy to dry for about 24 hours to improve the looseness of the materials. , and then pulverize the material to a particle size of 0.4-0.7cm by a fine pulverizer.
[0046] When the fine pulverizer is discharged, the material is sent to the first-level fermentation tan...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Same as Example 1, the difference is:
[0053] Before the primary fermentation, adjust the moisture content of the material to 55% to 60%, the time of the primary fermentation is 5 days, the temperature of the secondary fermentation is 60°C to 65°C, the fermentation time is 8 days, and the temperature of the tertiary fermentation is 35 ℃ ~ 40 ℃, fermentation time is 6 days.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com