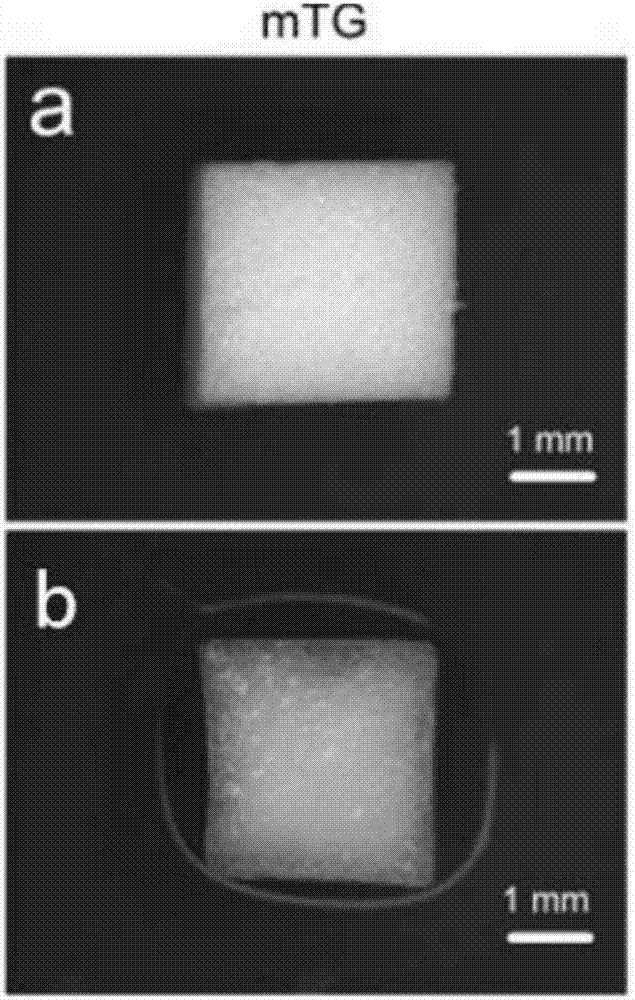
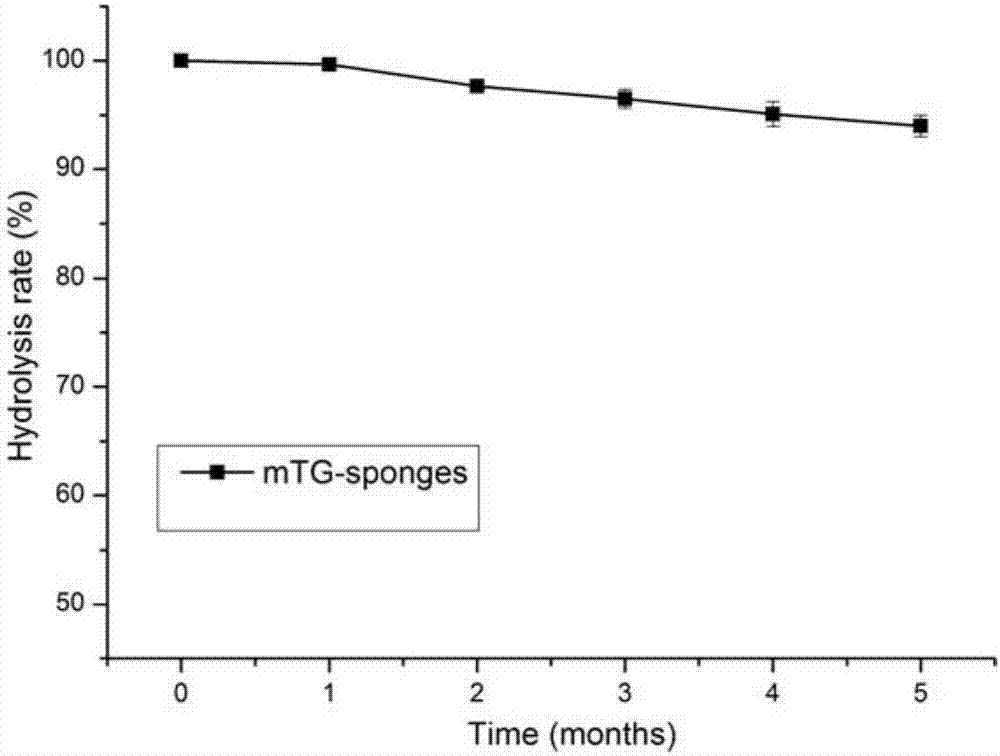
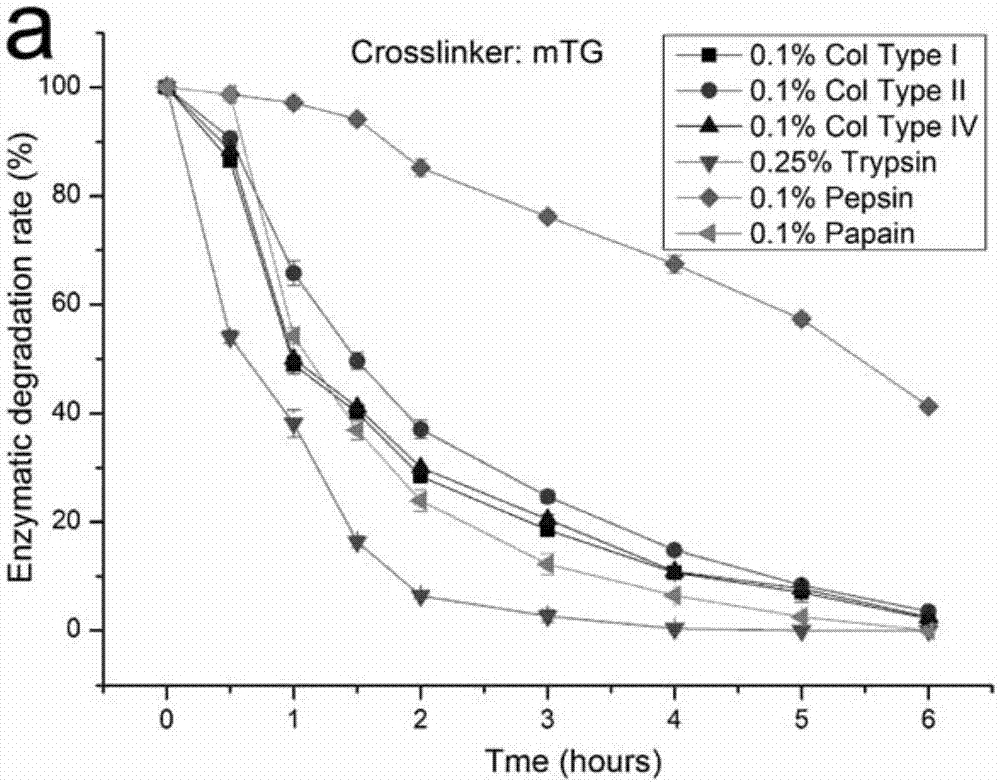
Preparation method of gelatin sponge scaffold
A technology of gelatin sponge and gelatin, which is applied in the fields of pharmaceutical formulation, application, and medical science, and can solve the problems of host damage, low degree of cross-linking, and poor stability, and achieve excellent comprehensive performance, good porosity, and good biocompatibility Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1 The preparation method of sponge support of the present invention
[0031] 1. Preparation method
[0032] (1) Hydrogel preparation: Gelatin (Type A, 300 Bloom; Sigma, USA) was quantitatively weighed and dissolved in deionized water at 50°C to obtain a 4% (w / v) solution, which was sterilized by filtration with a 0.22 μm needle filter. mTG (Bomei Bio, China, enzyme activity > 100 U / g) was dissolved in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) to obtain a 10% (w / v) solution, and sterilized by filtration. Prepare a mixed solution according to the ratio of adding 40 μm of TG solution per ml of gelatin solution, and place it in a constant temperature incubator at 37° C. until gelatinized.
[0033] (2) Preparation of the sponge scaffold: the hydrogel was freeze-dried, specifically at -10°C to -20°C for 8 hours, and then dried at 15 to 25°C for 48 hours to obtain the sponge scaffold.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 The preparation method of sponge support of the present invention
[0035] 1. Preparation method
[0036] (1) Hydrogel preparation: Gelatin (Type A, 300 Bloom; Sigma, USA) was quantitatively weighed and dissolved in deionized water at 50°C to obtain a 2% (w / v) solution, which was sterilized by filtration with a 0.22 μm needle filter. mTG (Bomei Bio, China, enzyme activity > 100 U / g) was dissolved in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) to obtain a 5% (w / v) solution, and sterilized by filtration. Prepare a mixed solution according to the ratio of adding 40 μm of TG solution per ml of gelatin solution, and place it in a constant temperature incubator at 37° C. until gelatinized.
[0037] (2) Preparation of the sponge scaffold: the hydrogel was freeze-dried, specifically at -10°C to -20°C for 8 hours, and then dried at 15 to 25°C for 48 hours to obtain the sponge scaffold.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3 The preparation method of sponge support of the present invention
[0039] 1. Preparation method
[0040] (1) Hydrogel preparation: Gelatin (type A, 300 Bloom; Sigma, USA) was quantitatively weighed and dissolved in deionized water at 50°C to obtain a 10% (w / v) solution, which was sterilized by filtration with a 0.22 μm needle filter. mTG (Bomei Bio, China, enzyme activity > 100 U / g) was dissolved in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) to obtain a 15% (w / v) solution, and sterilized by filtration. Prepare a mixed solution according to the ratio of adding 66.7 μl of mTG solution per ml of gelatin solution, and place it in a constant temperature incubator at 37° C. until gelatinized.
[0041] (2) Preparation of the sponge scaffold: the hydrogel was freeze-dried, specifically at -10°C to -20°C for 8 hours, and then dried at 15 to 25°C for 48 hours to obtain the sponge scaffold.
[0042] The beneficial effect of the present invention is illustrated below in the mo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com