Method for manufacturing graphene, transparent electrode and active layer comprising the same, and display, electronic device, optoelectronic device, battery, solar cell, and dye-sensitized solar cell including the electrode and the active layer
A transparent electrode, graphene technology, applied in the production of graphene, transparent electrodes and active layers comprising graphene, and displays, electronic devices, optoelectronic devices, batteries, solar cells and In the field of dye-sensitized solar cells, it can solve the problems of uneven threshold voltage and leakage current, and achieve the effect of excellent physical and electrical properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
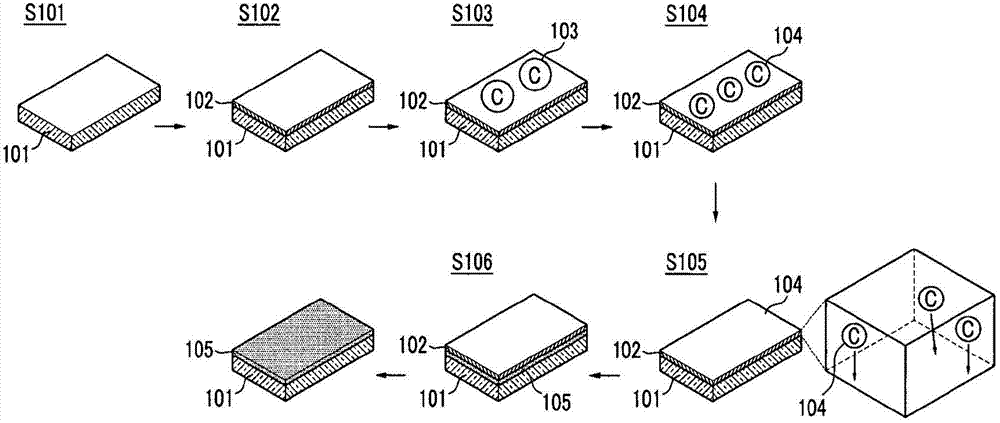
[0177] Example 1: Graphene grows directly on SiO 2 / Si substrate
[0178] A liquid carbon source material according to one embodiment of the present invention is used to directly grow on SiO 2 / Si substrate. SiO 2 is a 300nm thick layer and is deposited on a Si substrate by conventional thermal growth methods.
[0179] Clean SiO 2 / Si substrate surface. Then, a 100 nm thick Ni film was deposited on SiO using an electron beam evaporator 2 / Si substrate. During nickel deposition the SiO 2 / Si substrate maintained at 400°C.
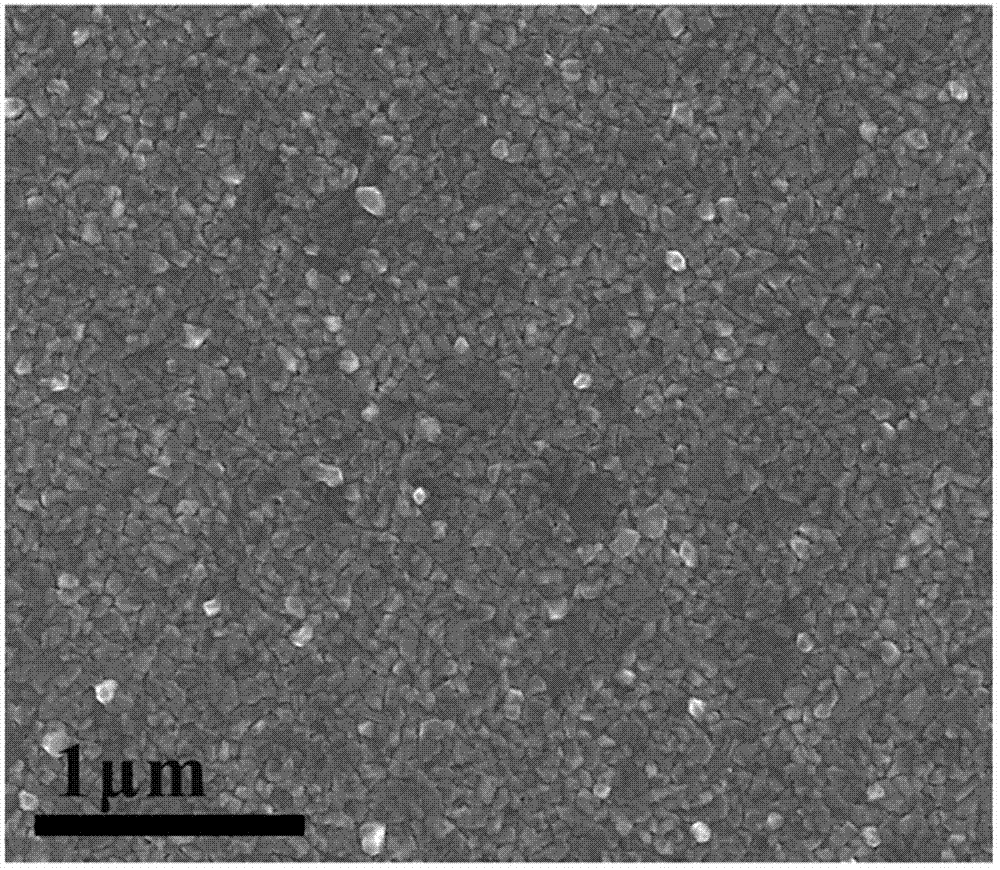
[0180] image 3 SEM images of the deposited nickel films are provided.
[0181] SEM images show that the nickel thin film is polycrystalline. It has grains with an average size of about 100 nm.
[0182] The nickel thin film is heat treated to improve orientation and increase average grain size. Heat treatment is carried out in a high vacuum chamber. The chamber was subjected to a hydrogen atmosphere using high purity (99.9999%) hydrogen. ...
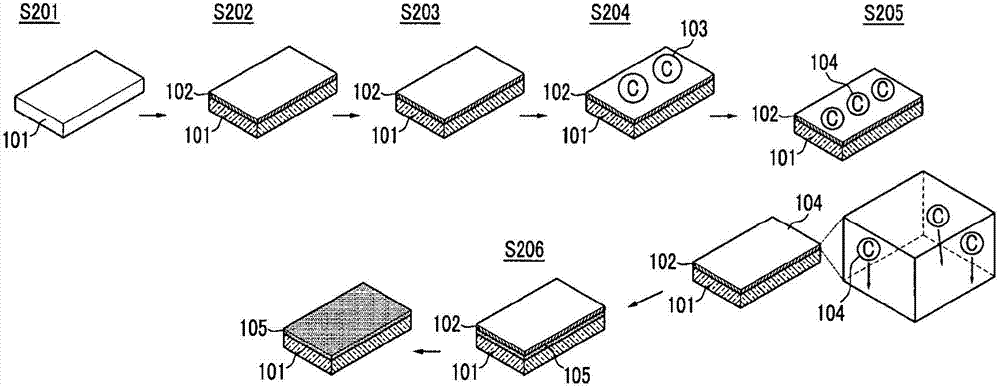
Embodiment 2
[0190] Graphene was formed according to the same method as in Example 1, except that the heating temperature after placing the carbon source material on the nickel thin film was 160°C.
[0191] Figure 6 SEM images of graphene according to Example 2 are provided.
[0192] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the graphene according to Example 2 has large grains with an average size ranging from several micrometers to tens of micrometers. The SEM images show clear brightness contrasts that depend on thickness. The brightest image indicates single-layer graphene C, the brightest image indicates bilayer graphene B, and the darkest image indicates multilayer graphene A.
[0193] In addition, if Figure 6 As shown, the graphene according to Example 2 is formed at low temperature and thus has no wrinkles due to the difference in thermal expansion coefficient between the graphene and the underlying substrate. In general, wrinkles may degrade the physical properties of graphene.
Embodiment 3
[0195] Graphene was formed according to the same method as in Example 1, except that the heating temperature and time after placing the carbon source material on the nickel thin film were 60° C. and 10 minutes, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com