Bionic double-shaft hair sensor device
A sensor device, silicon micro-sensor technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, gyroscopes/steering sensing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of multi-physical signal sensitivity, single physical quantity, and single function, so as to improve detection sensitivity and accuracy , Strong anti-interference ability, and the effect of suppressing swing motion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
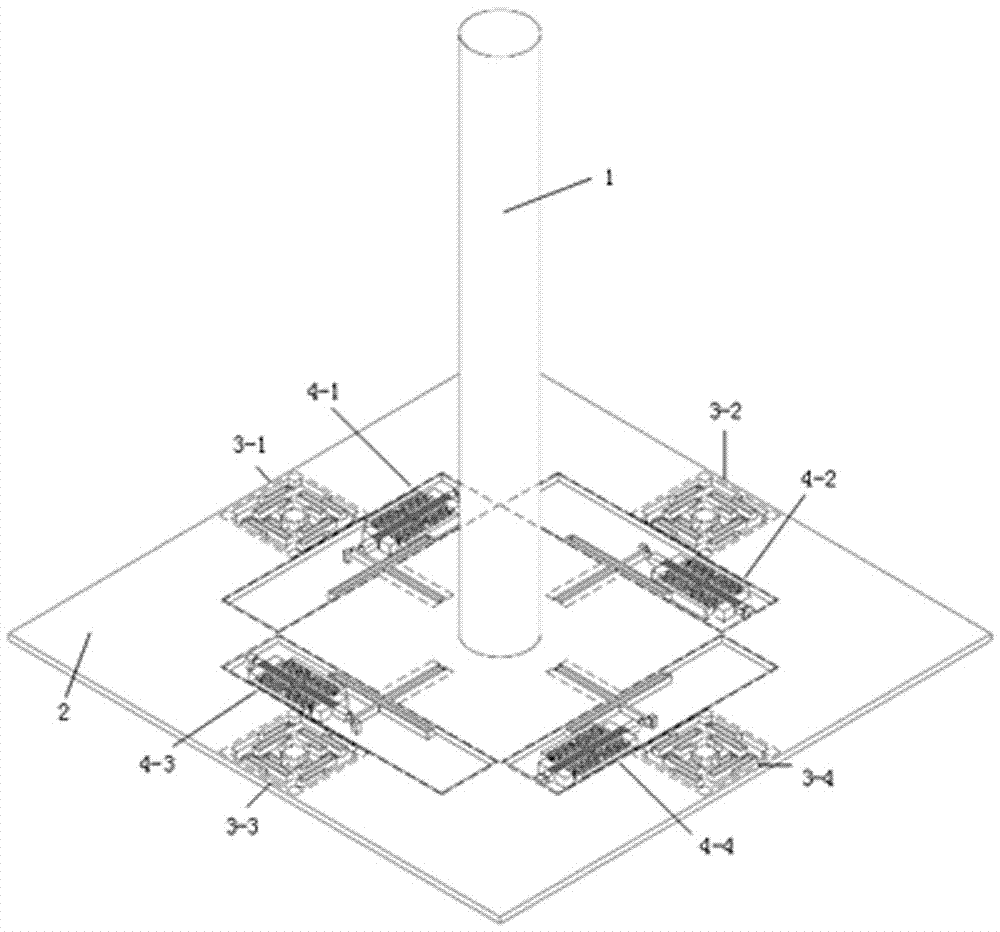
[0034] Such as Figure 1 ~ Figure 2 As shown, the present invention provides a bionic biaxial hair sensor device, comprising a three-layer structure consisting of an upper layer of metal aluminum alloy hair 1, a middle layer of silicon micro sensors, and a lower layer of a glass substrate with signal leads. The metal aluminum alloy The hair is glued to the center position of the upper surface of the silicon micro sensor, the silicon micro sensor is composed of a base mass 2, four swing suppression elastic structures and four resonator substructures, the four resonator substructures are respectively located on the base In the hollow area on the four sides of the mass 2, the four swing suppression elastic structures are respectively located in the hollow areas on the sides of the four resonator substructures, and the four swing suppression elastic structures and the four resonator substructures all pass through the anchor points. Bonded to a glass substrate on which signal leads a...
Embodiment 2
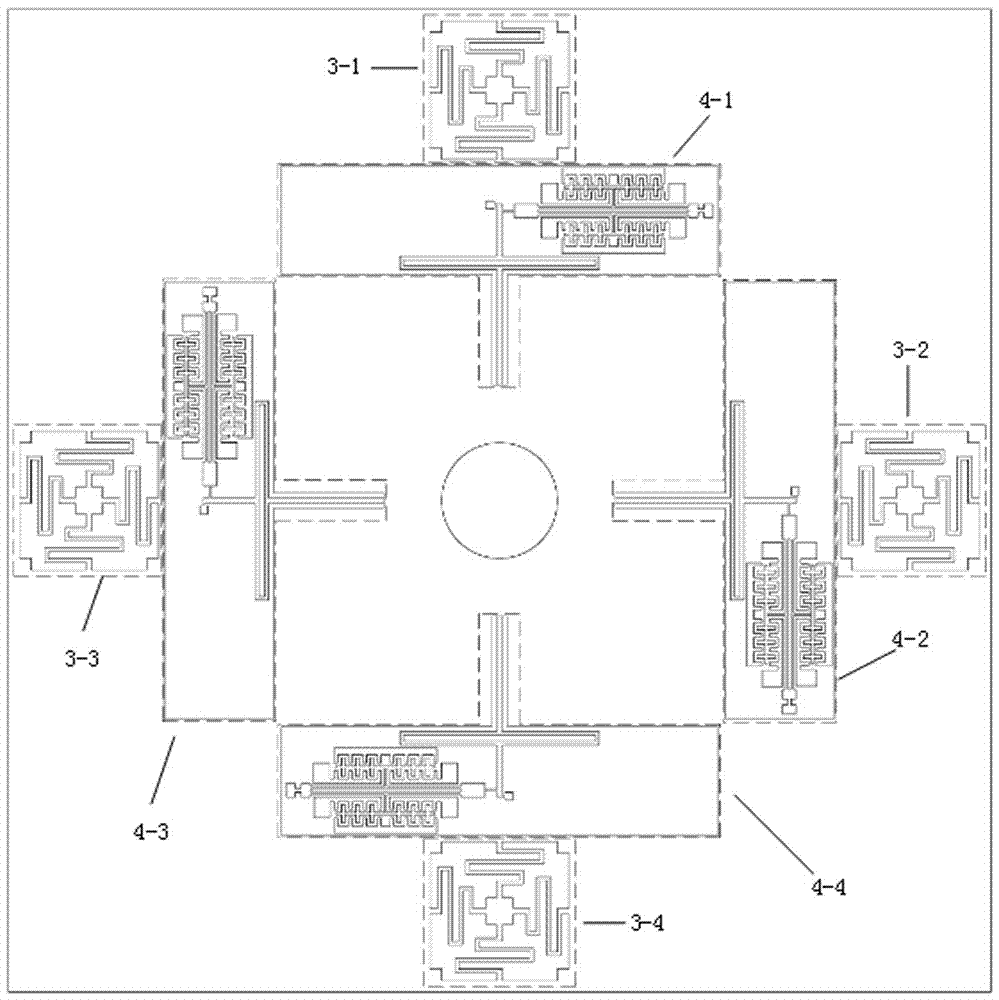
[0036] The first swing restraining elastic structure 3-1, the second swing restraining elastic structure 3-2, the third swing restraining elastic structure 3-3, and the fourth swing restraining elastic structure 3-4 have exactly the same structure and the adjacent interval is 90 Degree, specifically taking the first swing restraining elastic structure 3-1 as an example, such as Figure 4 As shown, the first swing suppression elastic structure 3-1 is composed of a first square wave elastic beam 3-1a, a second square wave elastic beam 3-1b, a third wave elastic beam 3-1c, and a fourth square wave elastic beam 3-1d. One end of the first square wave elastic beam 3-1a is connected to the base mass 2 and the other end is connected to the anchor point 5-1. The first square wave elastic beam 3-1a is located at the anchor The upper side of point 5-1; one end of the second square wave elastic beam 3-1b is connected to the base mass 2, and the other end is connected to the anchor point 5-1...
Embodiment 3
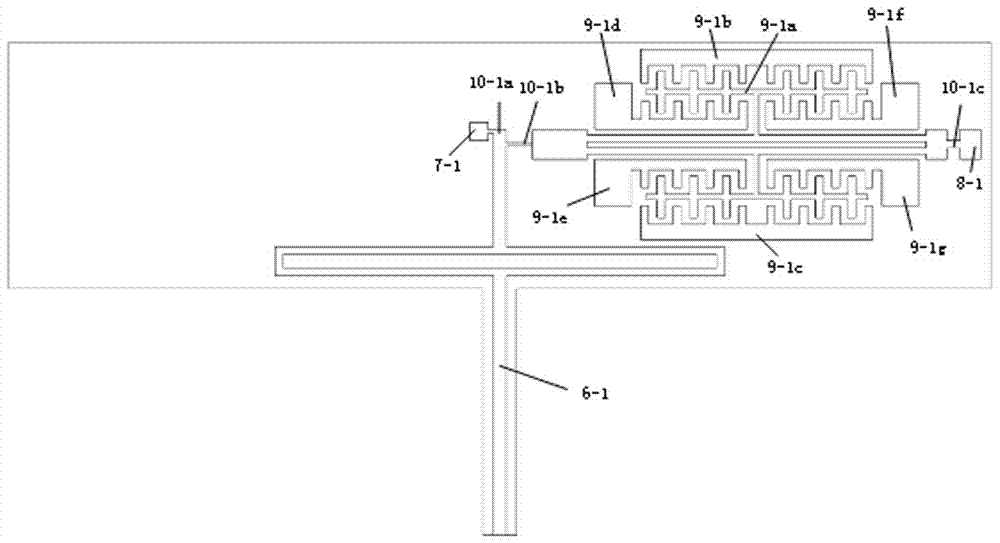
[0038] The first resonator sub-structure 4-1, the second resonator sub-structure 4-2, the third resonator sub-structure 4-3 and the fourth resonator sub-structure 4-4 have exactly the same structure and the adjacent interval is 90 Degree, such as image 3 As shown, specifically taking the first resonator sub-structure 4-1 as an example, the first resonator sub-structure 4-1 consists of a first lever elastic beam 6-1, a first double-ended fixed tuning fork and its driving detection comb. The structure 9-1 is composed of a first double-ended fixed tuning fork and its drive detection comb structure 9-1 consisting of a first double-ended fixed tuning fork 9-1a containing comb teeth, a first drive comb 9-1b, and a The two driving comb teeth 9-1c and the first detecting comb teeth 9-1d, the second detecting comb teeth 9-1e, the third detecting comb teeth 9-1f, and the fourth detecting comb teeth 9-1g are composed, the first lever The input end of the elastic beam 6-1 is connected to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com