High frequency power amplifier circuit
A power amplifier circuit and high-frequency amplifier technology, applied in power amplifiers, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as low output power and input signal distortion, and achieve the effect of increasing output power and reducing distortion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
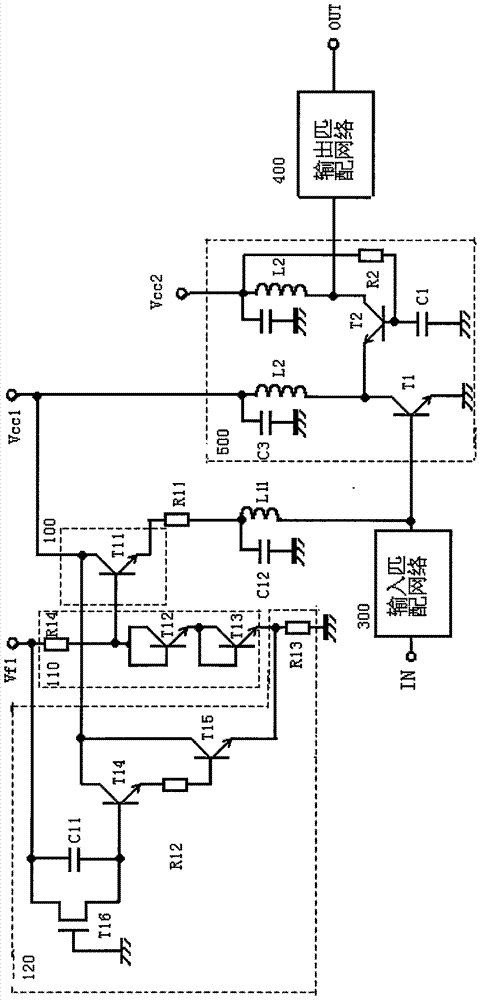
[0019] figure 1 It is the circuit diagram of the high-frequency power amplifier provided by the first embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, the high-frequency power amplifier provided by the first embodiment of the present invention includes a high-frequency signal input terminal IN, an input matching network 300, a high-frequency amplifier 500, an output matching network 400, a high-frequency signal output terminal OUT, and a first bias circuit 100 and a second bias circuit, wherein the high frequency amplifier 500 includes: a first transistor T1, a second transistor T2, a first high frequency choke coil L1, a second high frequency choke coil L2 and a capacitor C1, the first A bias circuit 100 is connected to the base of the first transistor T1 for providing a bias current to the base of the first transistor T1 according to the control voltage Vcon1; the emitter of the first transistor T1 is grounded, and the collector is connected to the first high ...
no. 2 example
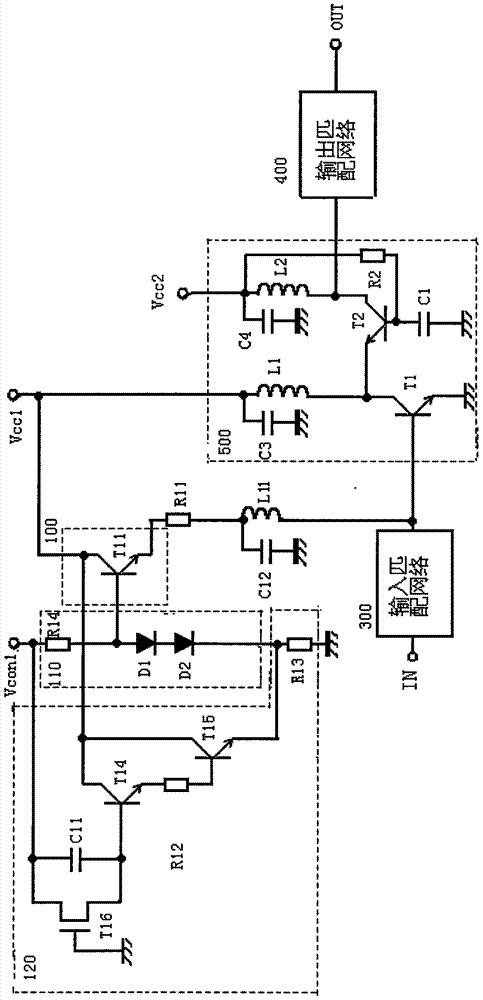
[0025] Combine below figure 2 Describe the high-frequency power amplifier circuit provided by the second embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 2 As shown, the difference between the high-frequency power amplifying circuit provided by the second embodiment of the present invention and the high-frequency power amplifying circuit provided by the first embodiment is only that the first power supply circuit used to provide the reference voltage for the first bias circuit The configurations are different. In the second embodiment, the first power supply circuit 110 includes a resistor R14, a diode D1 and a diode D2. The first end of the resistor R14 is connected to the control voltage Vcon1, the second end is connected to the anode of the diode D1, and the cathode of the diode D1 is connected to the ground through the surge circuit. The control signal Vcon1 is used to control the start and stop of the bias circuit 100. In the first power supply circuit 110, the res...
no. 3 example
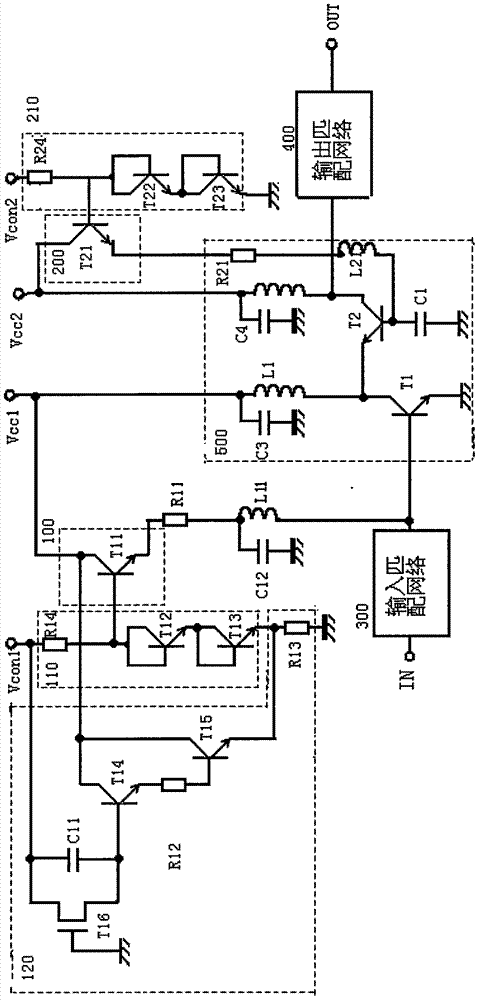
[0027] Combine below image 3 Describe the high-frequency power amplifying circuit provided by the third embodiment of the present invention, such as image 3 As shown, the high-frequency power amplifying circuit provided by the third embodiment of the present invention is different from the high-frequency power amplifying circuit provided by the first embodiment only in that the second bias circuit is different. In the second embodiment, the transistor T2 The bias circuit for providing the bias voltage includes a transistor T21, the collector of the transistor T21 is connected to the second power supply Vcc2, and the emitter is connected to the base of the transistor T2 through the resistor R21 and the high frequency choke coil L21 in turn. The second reference voltage is provided by the second power supply circuit 210, which is used to control the bias of the transistor T2. The second power supply circuit 210 includes a resistor R24, a transistor T22, and a transistor T23. The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com