High-corrosion-resistance silicon carbide ceramic connecting material, and connecting method for silicon carbide ceramic
A technology of silicon carbide ceramics and high corrosion resistance, which is applied in the field of connecting silicon carbide ceramic materials by using the connection material, which can solve the problems that the connection position is easy to be corroded, achieve high connection temperature, reduce the thickness of titanium film, and avoid corrosion-prone phases. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
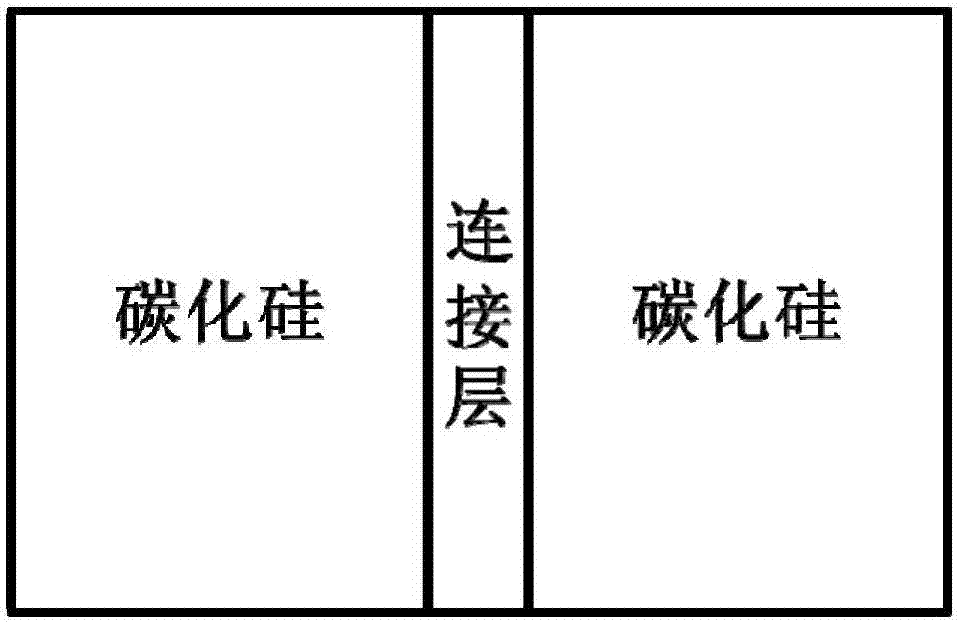
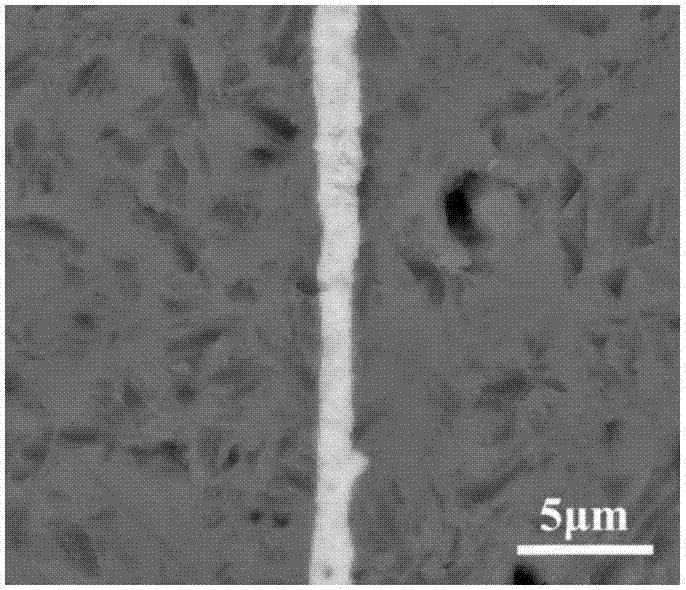
[0028] In this example, if figure 1 The silicon carbide ceramic materials to be joined are shown as being joined using the joining layer material. The material to be connected is two pieces of Ф20*20mm silicon carbide, the roughness of the connection surface is 0.1μm, and the material of the connection layer is a pure titanium film with a thickness of 1μm. The connection interface is heated by an external heat source to make the connection interface reach the connection temperature, so that the The SiC materials to be joined are joined together. The method of external heat source heating connection is electric field assisted thermocompression connection. Specific steps are as follows:
[0029] (1) Polish the silicon carbide surface to be connected with 0.1 micron diamond polishing liquid to remove larger defects and impurities on the surface;
[0030] (2) Coating a 1 μm Ti film on the surface of a piece of silicon carbide to be connected by PVD method, and then docking anot...
Embodiment 2
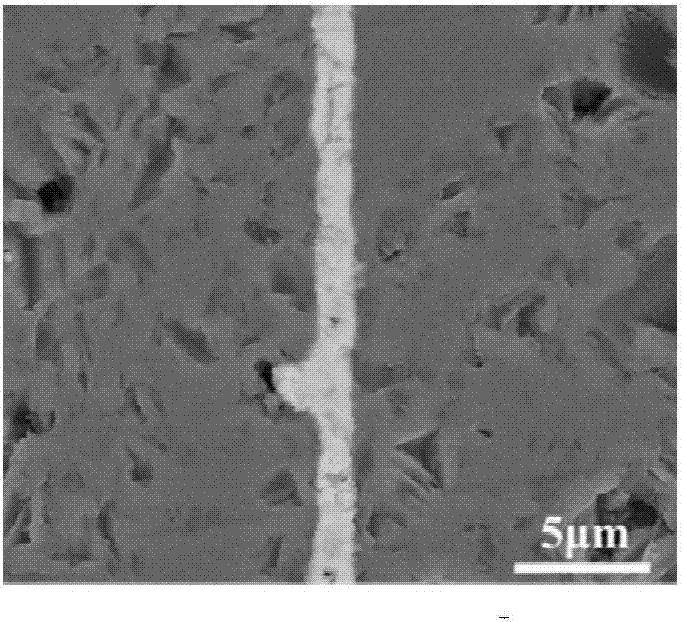
[0034] In this example, if figure 1 The silicon carbide ceramic materials to be joined are shown as being joined using the joining layer material. The material to be connected is exactly the same as that in Example 1. Same as in Example 1, the material of the connection layer is a pure titanium film with a thickness of 1 μm, except that the connection temperature in this embodiment is 1000° C. Same as Example 1, the connection interface is heated by an external heat source to bring the connection interface to the connection temperature, thereby connecting the SiC materials to be connected together, and the method of heating the connection by the external heat source is electric field assisted thermocompression connection. Specific steps are as follows:
[0035] (1) Polish the silicon carbide surface to be connected with 0.1 micron diamond polishing liquid to remove larger defects and impurities on the surface;
[0036] (2) Coating a 1 μm Ti film on the surface of a piece of...
Embodiment 3
[0040] In this example, if figure 1 The silicon carbide ceramic materials to be joined are shown as being joined using the joining layer material. The material to be connected is exactly the same as that in Example 1, except that the material of the connection layer in this experiment is a pure titanium film with a thickness of 500 nm. Same as in Example 1, the connection interface is heated by an external heat source to reach the connection temperature. The connection temperature is 1300° C., so that the SiC materials to be connected are connected together. The method of heating the connection by the external heat source is electric field assisted thermocompression connection. Specific steps are as follows:
[0041] (1) Polish the silicon carbide surface to be connected with 0.1 micron diamond polishing liquid to remove larger defects and impurities on the surface;
[0042] (2) Coating a 500nm Ti film on the surface of a piece of silicon carbide to be connected by PVD metho...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com