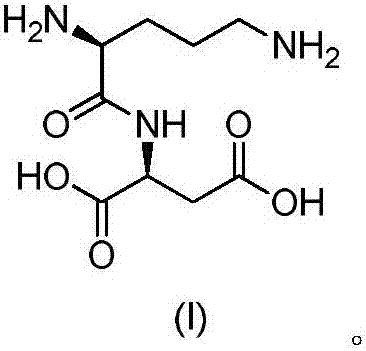
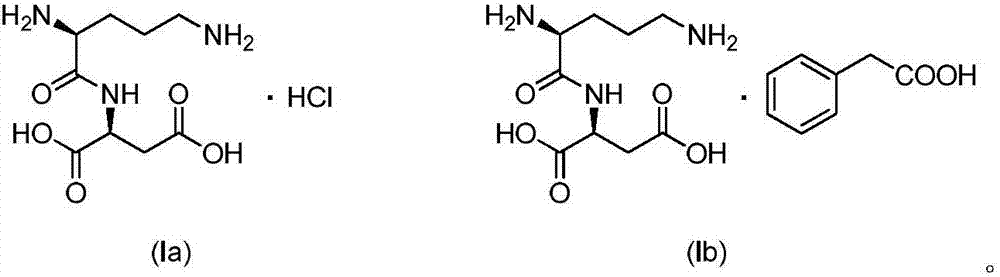
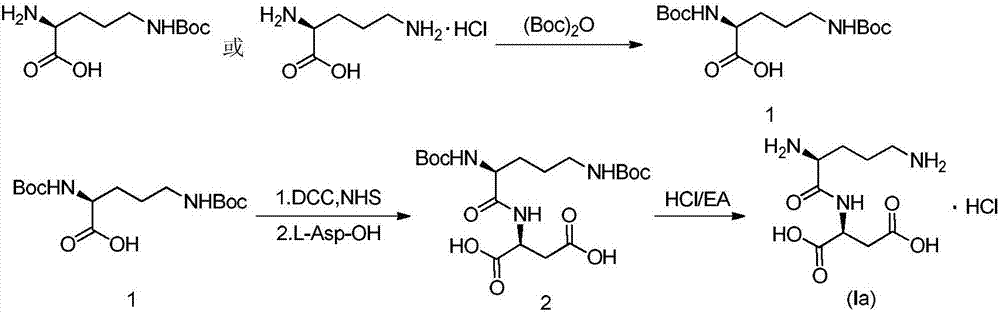
Active salt of dipeptide compound of ornithine and aspartic acid as well as application thereof
A peptide compound, aspartic acid technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of undisclosed ornithine and aspartic acid dipeptide compound active salts, undisclosed uses, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] The preparation of embodiment 1 intermediate 1
[0040] Add 0.258g (6.45mmol, 3eq) of sodium hydroxide, 10ml of purified water and 0.5g (2.15mmol, 1eq) of N-δ-Boc-L-ornithine into a 100ml reaction flask, and add Boc anhydride at 0-10°C 0.563g (2.58mmol, 1.2eq) / 10ml THF solution, after the dropwise addition, stirred at room temperature. After the reaction was monitored by TLC until the reaction was complete, the temperature was lowered to below 10°C, dilute hydrochloric acid was added dropwise to pH 4-5, the aqueous phase was extracted with ethyl acetate (15ml×2), the ethyl acetate layers were combined, washed once with purified water, organic The phase was dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain 0.81 g of intermediate 1 as a foamy solid crude product, and the yield was basically quantitative.
Embodiment 2
[0041] The preparation of embodiment 2 intermediate 1
[0042] Add 11.8g (296.5mmol, 5eq) of sodium hydroxide and 200ml of purified water into a 500ml three-necked flask, cool down to 0°C, add 10g (59.3mmol, 1eq) of L-ornithine hydrochloride, stir to dissolve, 0 A solution of Boc-anhydride (38.8g, 177.9mmol, 3eq) in tetrahydrofuran (200ml) was added dropwise at about ℃, and reacted at room temperature after the addition was complete. After TLC monitoring to the completion of the reaction, concentrate tetrahydrofuran under reduced pressure at 45°C, adjust the aqueous phase to about pH 4-5 with 1N hydrochloric acid, extract with ethyl acetate (100ml×2), combine the ethyl acetate layers, wash twice with purified water, and organic The phase was dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure at 45°C to obtain 20 g of white foamy solid, Intermediate 1, with a quantitative yield.
Embodiment 3
[0043] The preparation of embodiment 3 intermediate 2
[0044] In a 500ml round bottom flask, add intermediate 1 compound 18.0g (54.2mmol, 1eq), add 180ml tetrahydrofuran and stir to dissolve, then add N-hydroxysuccinimide 6.86g (59.6mmol, 1.1eq), stir to The temperature was lowered to about 0°C, and a solution of DCC (12.3g, 59.6mmol, 1.1eq) in tetrahydrofuran (100ml) was slowly added dropwise, and stirred at room temperature after the dropwise addition, solids slowly precipitated at room temperature, monitored by TLC until the reaction was complete , filtered with suction, and the filtrate was kept for use.
[0045] Take another 1000ml three-necked flask, add 7.9g (59.35mmol, 1.1eq) of L-aspartic acid, 200ml of purified water, 18.2g (21.66mmol, 4eq) of sodium bicarbonate and stir until the solid dissolves, then add dropwise at room temperature The remaining filtrate obtained in the previous step (i.e. the prepared activated ester solution), after the dropwise addition, was ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com