Method for reducing bioavailability of soil with combined heavy metal pollution
A technology of compound pollution and soil biology, applied in the field of soil pollution control, can solve problems such as human health impact and air pollution, achieve the effects of improving the quality and safety of tobacco leaves, increasing the content of soil nutrient elements, and simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Tobacco is one of the important economic crops in my country. The planting area and output both rank first in the world, with an annual planting area of about 1.4 million ha 2 , The output of tobacco leaves is as high as 1.5-1.7 million tons, and about 1.5-1.7 million tons of tobacco rods will be produced accordingly. Tobacco stems are neither suitable for fuel, nor are they suitable for direct return to the field as fertilizer. A large number of tobacco stems are discarded or burned, which will not only cause a large number of germs to grow in the tobacco fields, but also seriously pollute the atmospheric environment. Therefore, strengthening the comprehensive utilization of resources such as tobacco stems and other agricultural wastes can not only effectively deal with the above-mentioned wastes and turn wastes into treasures, but also increase the economic income of tobacco farmers, thereby realizing the sustainable development of the tobacco industry.
[0027]Aimi...
Embodiment 2
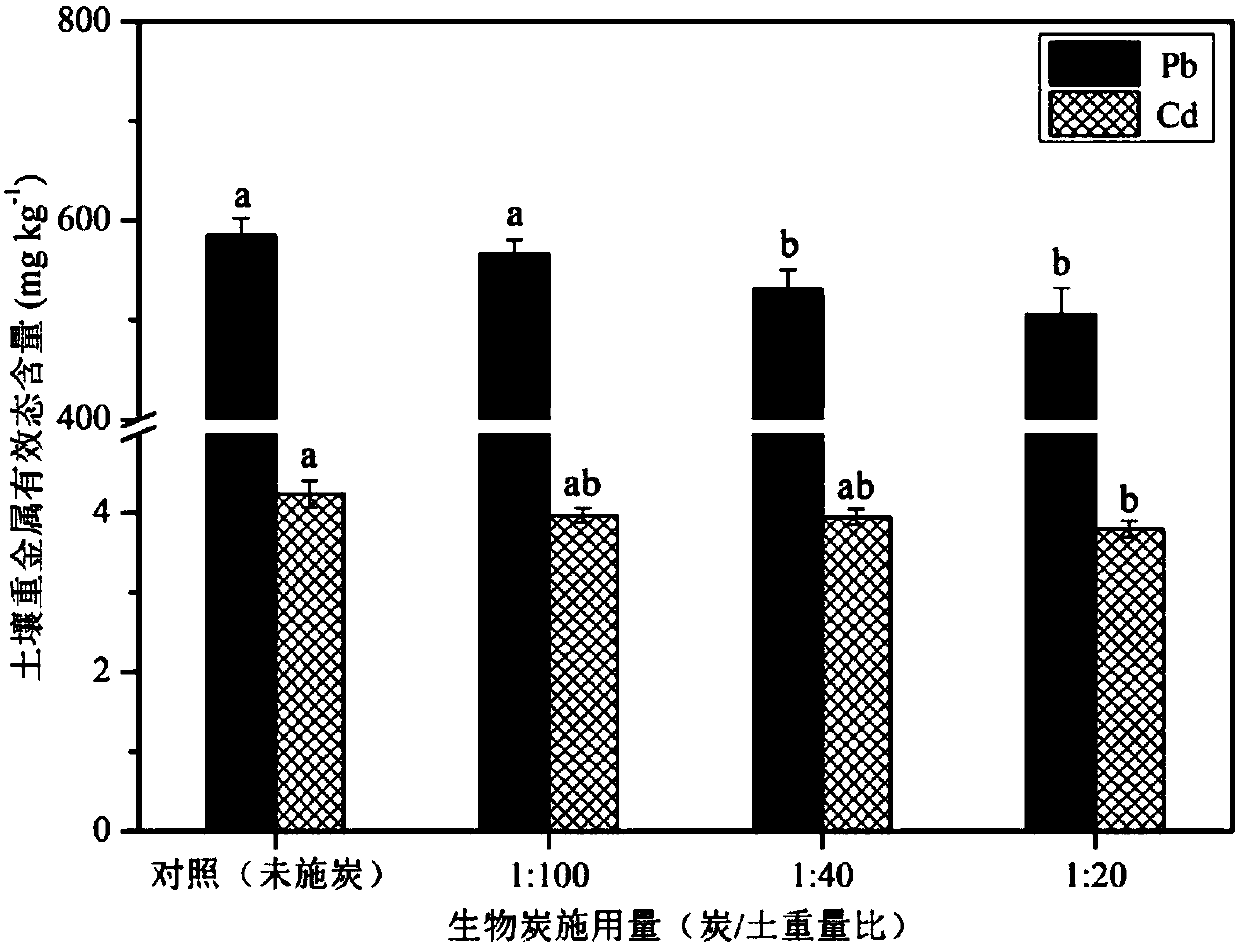
[0049] Embodiment 2: biochar is applied to the reducing effect of lime soil heavy metal (Cd and Pb) effective state content:
[0050] In lime soil, the available content of soil heavy metals is generally expressed by the concentration of soil heavy metals leached by DTPA. With the increase of biochar application rate, the available content of heavy metals Cd and Pb in lime soil gradually decreased. When the weight ratios of biochar and composite polluted (Cd and Pb) soils were 1:100, 1:40 and 1:20, the reduction rates of available Cd in lime soil were 6.37%, 6.84% and 10.38%, respectively. ; The reduction rates of effective Pb in lime soil were 3.28%, 9.20% and 13.55%. Compared with the control (no carbon application), when the biochar application rate reached 1:20 (char / soil weight ratio), the available Cd content in soil decreased significantly (Pfigure 1 shown).
Embodiment 3
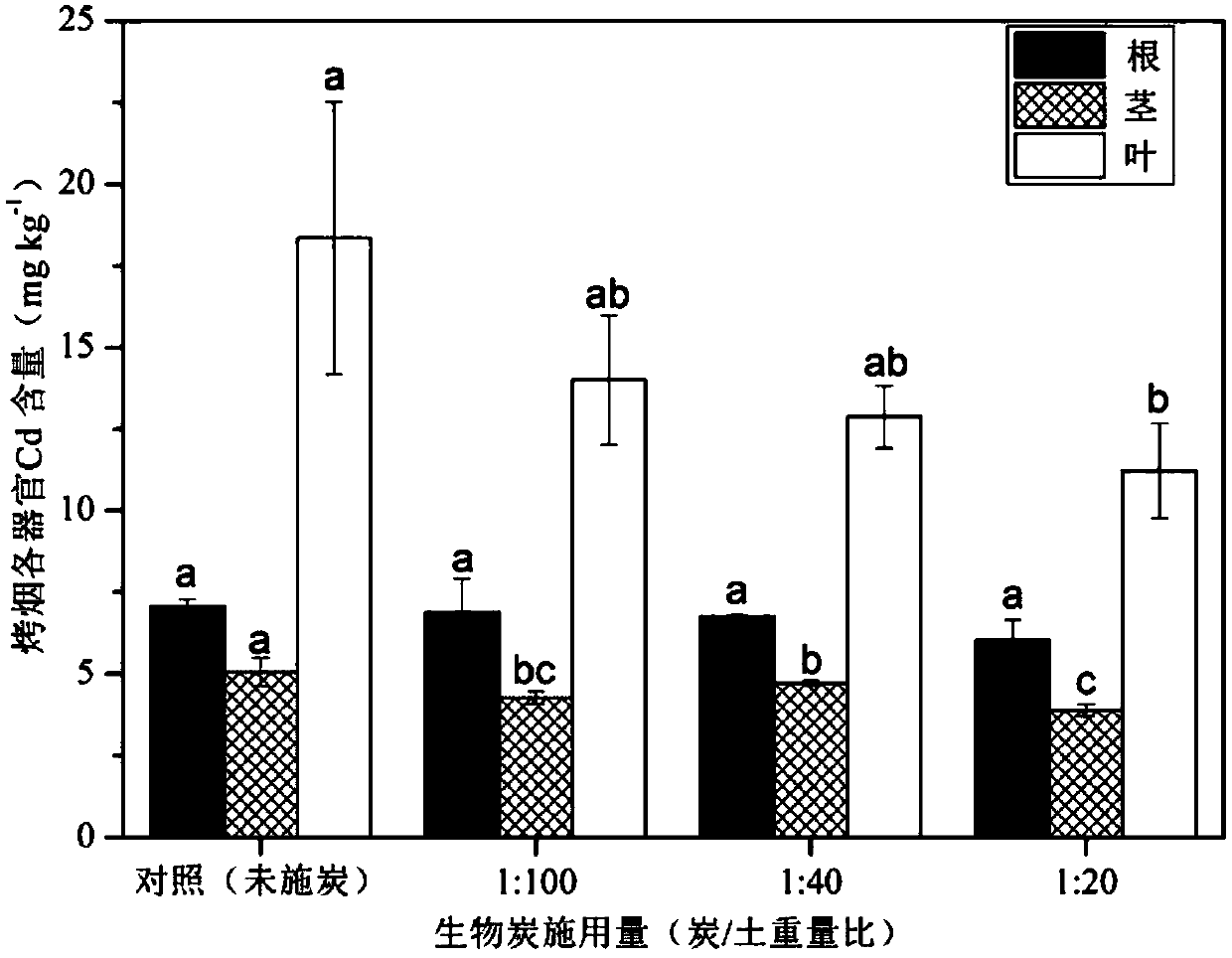
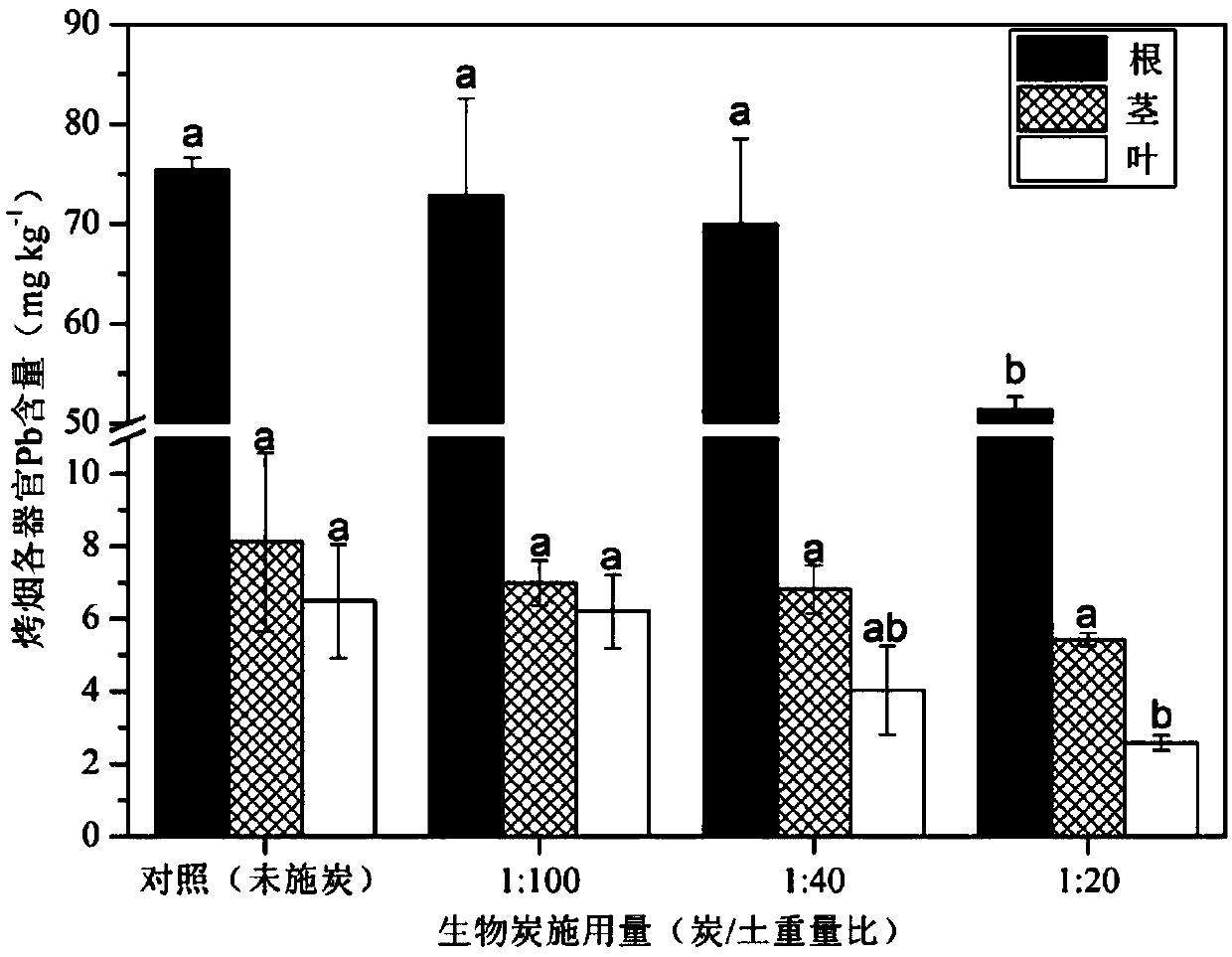
[0051] Embodiment 3, the reduction effect of biochar application on the residual amount of Cd in each organ of flue-cured tobacco:
[0052] With the increase of biochar application rate, the residual Cd in each organ of flue-cured tobacco (K326) decreased gradually. When the weight ratios of biochar and composite pollution (Cd and Pb) soil were 1:100, 1:40 and 1:20, the reduction rates of Cd residue in flue-cured tobacco roots were 2.48%, 4.04% and 14.59%, respectively; The reduction rates of residual Cd in flue-cured tobacco stems were: 15.51%, 6.52% and 23.12%; the reduction rates of residual Cd in flue-cured tobacco leaves were: 23.71%, 29.84% and 38.83%. Compared with the control (no charcoal application), when the biochar application rate reached 1:20 (charcoal / soil weight ratio), the Cd residue in flue-cured tobacco leaves was significantly reduced (P figure 2 shown).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com