A kind of preparation method of magnetic control protein composite cell membrane sheet
A cell membrane, protein technology, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, prostheses, drug delivery, etc., can solve problems that have not been reported in literature, and achieve the effect of promoting bone regeneration in vivo, high saturation magnetization, and improving the effect of regeneration and repair in vivo.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
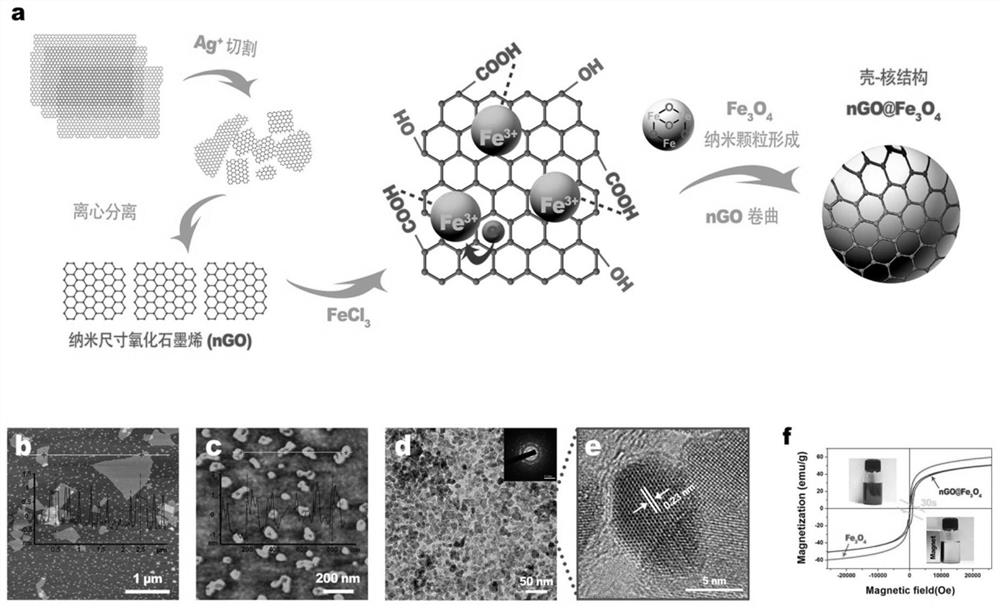
[0028] Example 1. nGO@Fe 3 o 4 Preparation and Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles
[0029] Step 1. Preparation of nano-sized graphene oxide (nGO)
[0030] according to figure 1 As shown in a, in order to prepare nGO@Fe3O 4 For magnetic nanoparticles, nanometer-sized graphene oxide is firstly prepared. 20mL of AgNO 3 The solution was added to an equal volume of 0.5mg / mL graphene oxide solution, stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes, and then left to stand for 48 hours (AFM characterization results are as follows: figure 1 As shown in b, graphene oxide particles vary in size). Centrifuge at 2000 rpm for 10 minutes, collect the supernatant and mix it with 10 mL of nitric acid solution (2 mM), concentrate in a rotary vacuum evaporator for 5 hours to dissolve the silver particles. The concentrated solution was centrifuged at 6000rpm for 10 minutes to remove the precipitate containing large pieces of graphene oxide. The supernatant was further centrifuged at 100...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2. Phagocytosis of nGO@Fe by stem cells 3 o 4 Magnetic nanoparticles for cell labeling
[0036] Step 1. Cells and nGO@Fe 3 o 4 Magnetic nanoparticle co-culture
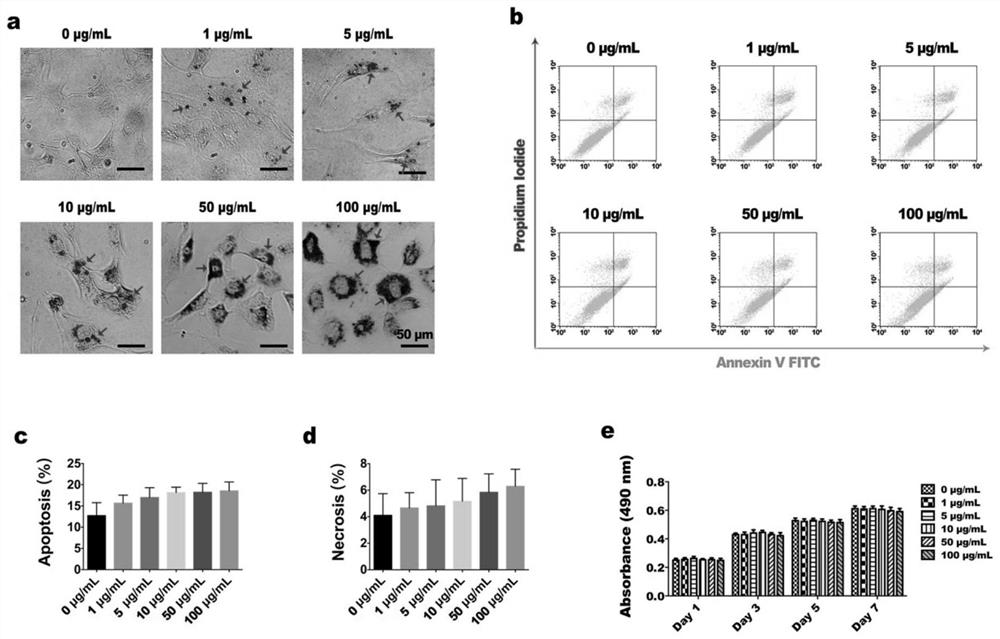
[0037] Use serum-free DMEM culture medium to prepare a 200 μg / mL magnetic nanoparticle solution for later use. Dental pulp stem cells were extracted from clinically impacted teeth. When the dental pulp stem cells were cultured to about 50% confluence, the serum-free DMEM medium was replaced, and magnetic nanoparticles with final concentrations of 0, 1, 5, 10, 50, and 100 μg / mL were added to co-culture for 2 hours, and observed by Prussian blue staining Phagocytosis of granules by cells. Such as image 3 As shown in a, with the increase of particle concentration, cells phagocytized more particles, which were mainly distributed around the nucleus.
[0038] Step 2. Detection of cell apoptosis and cell proliferation activity
[0039] When the dental pulp stem cells were cultured to about 80% conflu...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3. nGO@Fe 3 o 4 Magnetic control effect of magnetic nanoparticles labeling stem cells
[0041] Step 1. Cells and nGO@Fe 3 o 4 Magnetic nanoparticle co-culture
[0042] The procedure for cell labeling was the same as in Example 2: when the dental pulp stem cells were cultured to about 80% confluency, the serum-free DMEM medium was replaced, and magnetic nanoparticles with a final concentration of 100 μg / mL were added for co-cultivation for 2 hours. Such as Figure 4 As shown in a, the cells labeled with magnetic particles were added to the culture medium, and adsorbed and immobilized under the control of a magnet for 4 hours to form a cell membrane.
[0043] In addition to dental pulp stem cells, we also used other cells that can also be labeled with magnetic particles, such as the NIH3T3 cell line ( Figure 5 a). At the same time, NIH3T3 cells labeled with magnetic particles can also be magnetically adsorbed to form cell membranes of specific shapes ( F...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com