Preparation method of imidazoline inhibitor for drilling fluid
A technology of imidazoline and inhibitors, which is applied in the field of preparation of imidazoline inhibitors for drilling fluids, can solve the problems of limited adsorption capacity and loss of inhibition, and achieves little impact on rheology, good inhibition, and good temperature resistance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
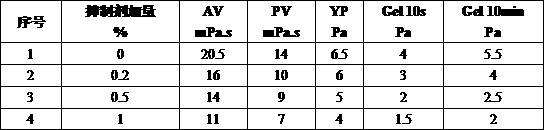
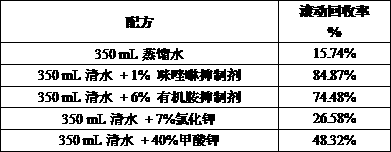
[0026] (1) Feed oleic acid A and hydroxyethylethylenediamine B in a molar ratio of 2:1, and raise the temperature to 220°C at a heating rate of 5~15°C / min under a residual pressure of 11kPa and stirring , At this temperature, keep it for 2h, and then steam the excess amine under the residual pressure of 3kPa to synthesize the intermediate.
[0027] (2) At 60°C, add water to the synthetic intermediate in step (1) in a molar ratio of 1.5:1 to oleic acid A, and react for 5 hours under the action of catalyst sodium hydroxide C (catalyst sodium hydroxide The molar ratio of C to oleic acid A is 1:15), raise the temperature of the product to 120°C, keep this temperature, and steam off excess water.
[0028] (3) Add methyl acrylate D in the amount of oleic acid A and other substances into the hydrolyzate produced in step (2) dropwise at 50°C, and keep the temperature for 5 hours to obtain the intermediate.
[0029] (4) At 50°C, add phosphorus pentoxide E with a molar ratio of 1:2 to ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) Feed lauric acid A and hydroxymethylethylenediamine B in a molar ratio of 1.5:1, and raise the temperature to 235°C at a heating rate of 5~15°C / min under a residual pressure of 10kPa and stirring , At this temperature, keep it for 2h, and then steam the excess amine under the residual pressure of 2kPa to synthesize the intermediate.
[0033] (2) At 60°C, add water to the synthetic intermediate in step (1) in a molar ratio of 1.5:1 to lauric acid A, and react for 5 hours under the action of catalyst sodium hydroxide C (catalyst sodium hydroxide The molar ratio of C to lauric acid A is 1:20), raise the temperature of the product to 140°C, keep this temperature, and steam off excess water.
[0034] (3) Add ethyl acrylate D in the amount of lauric acid A and other substances into the hydrolyzate produced in step (2) dropwise at 50°C, keep the temperature and react for 4 hours to obtain an intermediate.
[0035] (4) At 50°C, add phosphorus pentoxide E with a molar ratio...
Embodiment 3
[0038] (1) Feed linoleic acid A and hydroxyethylethylenediamine B in a molar ratio of 1:1, raise the temperature to below 220°C at a heating rate of 5~15°C / min under a residual pressure of 9kPa and stirring At this temperature, keep it for 1.5h, and then distill off the excess amine under the residual pressure of 2.5kPa to synthesize the intermediate.
[0039] (2) At 60°C, add water to the synthetic intermediate in step (1) in a molar ratio of 1.1:1 to linoleic acid A, and react for 5 hours under the action of catalyst sodium hydroxide C (catalyst hydrogen oxidation The molar ratio of sodium C to linoleic acid A is 1:30), raise the temperature of the product to 140°C, keep this temperature, and distill off excess water.
[0040] (3) Add propyl acrylate D in the amount of linoleic acid A and other substances to the hydrolyzate generated in step (2) dropwise at 50°C, keep the temperature and react for 4 hours to obtain an intermediate.
[0041] (4) At 50°C, add phosphorus pento...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com