A three-terminal magnetic random access memory and its reading and writing method
A technology of random access memory, reading and writing method, applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage and other directions, can solve the problems of reducing the signal resolution ability of the storage unit, low signal resolution ability, etc., to improve the signal resolution ability, great application prospects Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
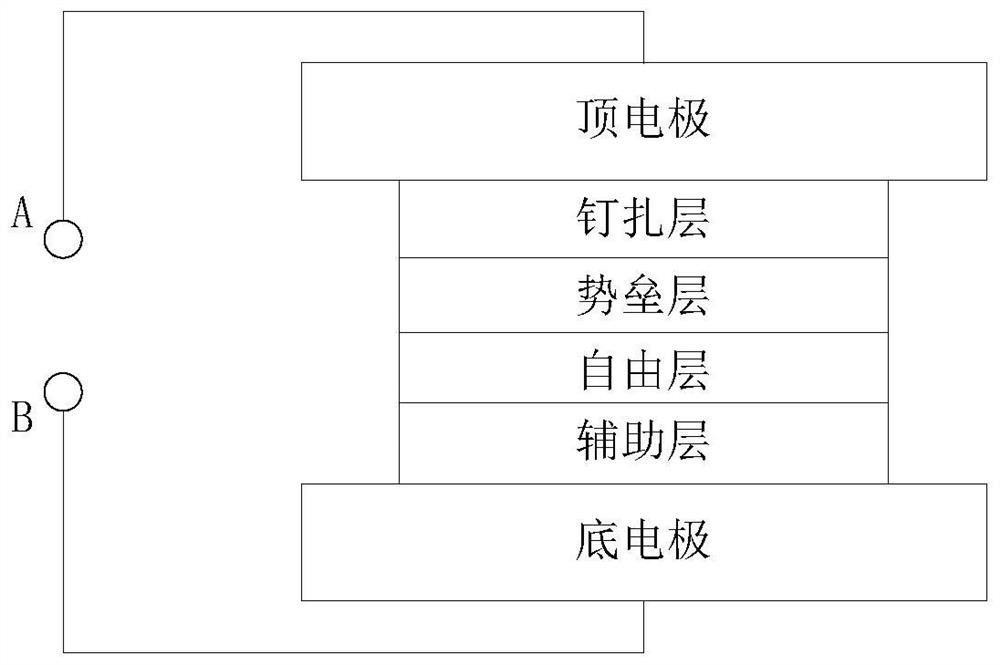
[0023] Such as Figure 2a As shown, the bottom electrode, auxiliary layer, free layer, barrier layer, pinning layer and top electrode are sequentially deposited on the silicon wafer (substrate) that has been prepared for the front-end process. On the free layer, a third terminal C is drawn out from the side that is in contact with the auxiliary layer. The magnetization direction of the pinned layer is fixed perpendicular to the film plane, and the magnetization direction of the free layer is variable.
[0024] By applying an electric field at the A and B terminals to change the magnetization direction of the free layer, the writing and erasing functions of the memory cell are realized. The resistance value of the memory cell is read by applying an electric field at the A and C terminals.
Embodiment 2
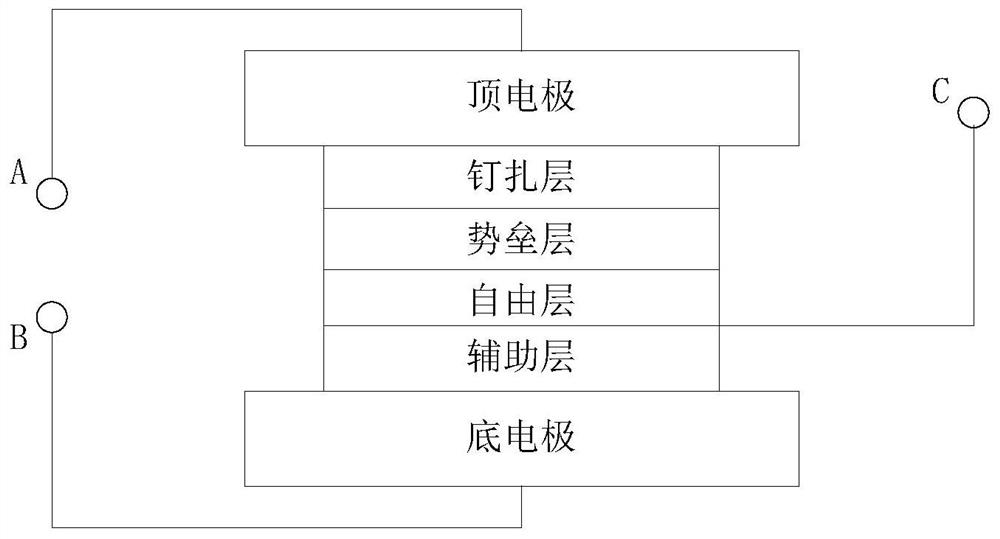
[0026] The order of the individual layers of the STT-MRAM stack can be reversed, as Figure 2b As shown, on the free layer, a third terminal C is led out from the side in contact with the auxiliary layer, and its properties have not changed. By applying an electric field at the A and B terminals to change the magnetization direction of the free layer, the writing and erasing functions of the memory cell are realized. The resistance value of the memory cell is read by applying an electric field at the B and C terminals.
Embodiment 3
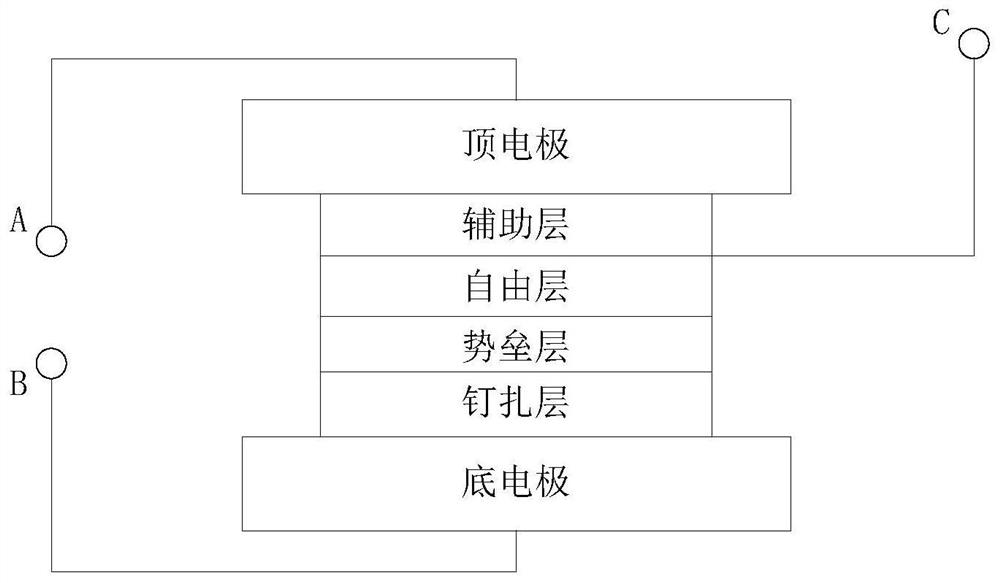
[0028] Such as Figure 3a As shown, the difference from Embodiments 1 and 2 is that the magnetization direction of the pinned layer is fixed by the coupling between the antiferromagnetic coupling layer and the pinned layer. The bottom electrode, the auxiliary layer, the free layer, the barrier layer, the pinning layer, the antiferromagnetic coupling layer, the fixed layer and the top electrode are sequentially deposited on the silicon wafer that has been prepared for the front-end process. The magnetization direction of the pinned layer is fixed perpendicular to the film plane, and the magnetization direction of the free layer is variable. Likewise, on the free layer, a third terminal C is led out from the side that is in contact with the auxiliary layer. By applying an electric field at the A and B terminals to change the magnetization direction of the free layer, the writing and erasing functions of the memory cell are realized. The resistance value of the memory cell is r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com