Electrolytic solution for lithium-sulfur battery
A lithium-sulfur battery and electrolyte technology, applied in secondary batteries, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as complex preparation processes, increase battery costs, etc., and achieve the effects of good repeatability, improved utilization, and improved Coulombic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Dissolve N,N-carbonyldiimidazole (with a water content of 20ppm) with a purity of 99.5% in ethylene glycol dimethyl ether to make a 10% N,N-carbonyldiimidazole solution, and then press the lithium-sulfur battery Addition of 0.5% of the mass of the positive electrode active material Add the N,N-carbonyldiimidazole solution into the standard electrolyte solution of the lithium-sulfur battery to prepare the electrolyte solution.
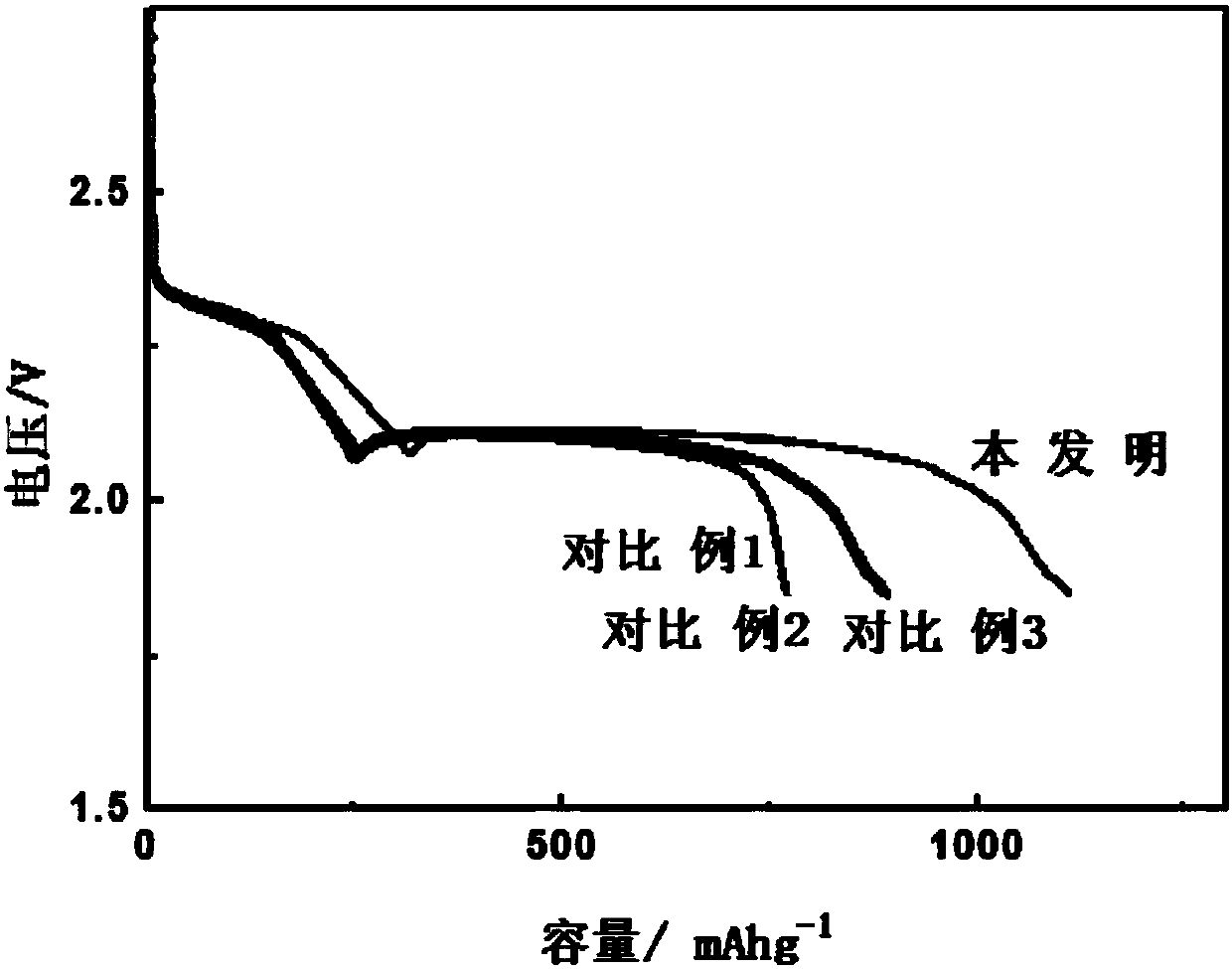
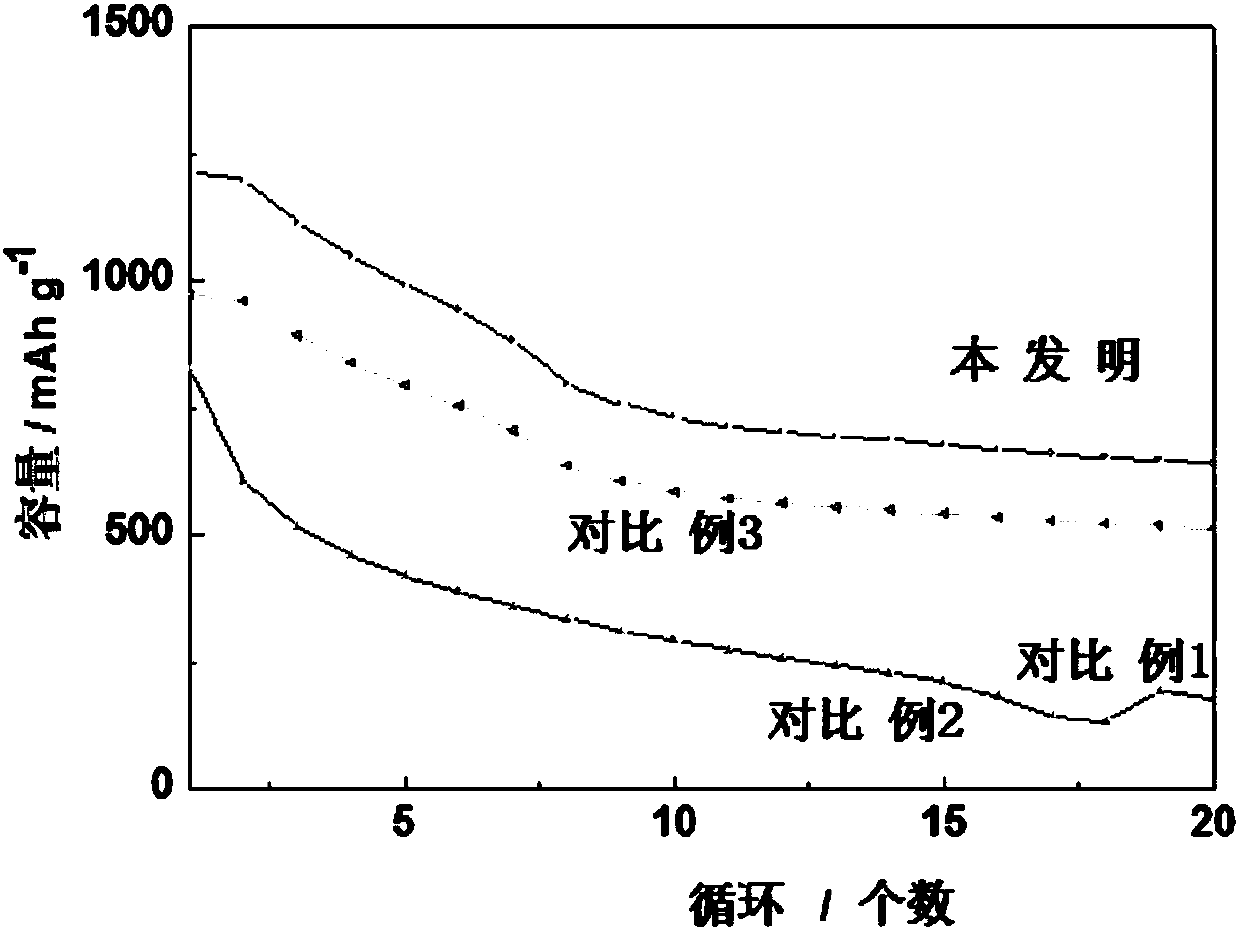
[0035] Adopt the same process as Comparative Example 1 to prepare the positive electrode and assemble the battery. Others are the same as Comparative Example 1. Test its battery performance. For performance, see figure 1 , figure 2 .
[0036] Test conditions: voltage window: 1.85-2.8V, discharge rate: 0.1C. The benchmark electrolyte for lithium-sulfur batteries is: 1M lithium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide solution (LiTFSI) as the electrolyte solution, and the solvents are 1,3-dioxolane (DOL) and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether ( DME) mixtu...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The thiocarbonyldiimidazole (water content is 200ppm) with a purity of 99.8% is dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide to make a 5% thiocarbonyldiimidazole solution, and then 3% of the lithium-sulfur battery positive active material mass The amount of addition of thiocarbonyl diimidazole solution is added to the standard electrolyte of lithium-sulfur batteries to form an electrolyte.
[0041] The same process as in Comparative Example 1 was used to prepare the positive electrode and assemble the battery, and test its battery performance.
[0042] The difference from Comparative Example 1 is that the reference electrolyte of the lithium-sulfur battery is: 1M lithium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide solution (LiTFSI) is the electrolyte solution, and the solvent is dimethyl sulfoxide.
Embodiment 3
[0044] The diphenylimidazole (water content is 50ppm) that the purity is 99% is dissolved in tetraglyme, and the concentration that makes is 5% diphenylimidazole solution, then press lithium-sulfur battery cathode active material quality 0.1% Inject the diphenylimidazole solution into the lithium-sulfur battery reference electrolyte to form an electrolyte.
[0045] The same process as in Comparative Example 1 was used to prepare the positive electrode and assemble the battery, and test its battery performance.
[0046] The difference from Comparative Example 1 is that the lithium-lithium-sulfur battery reference electrolyte is: 1M lithium hexafluorophosphate solution (LiPF 6 ) is an electrolyte solution, and the solvent is a mixture of dimethyl carbonate and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether (DME) (volume ratio v / v=1:1).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com