Field identification method for evaluating aspergillus flavus infection resistance of corn
An identification method and technology of Aspergillus flavus, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problems of inability to directly act on grains, difficult to cause pathogenic relationships, etc., and achieve the effects of ensuring test reproducibility, avoiding area parameter errors, and reducing systematic errors.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
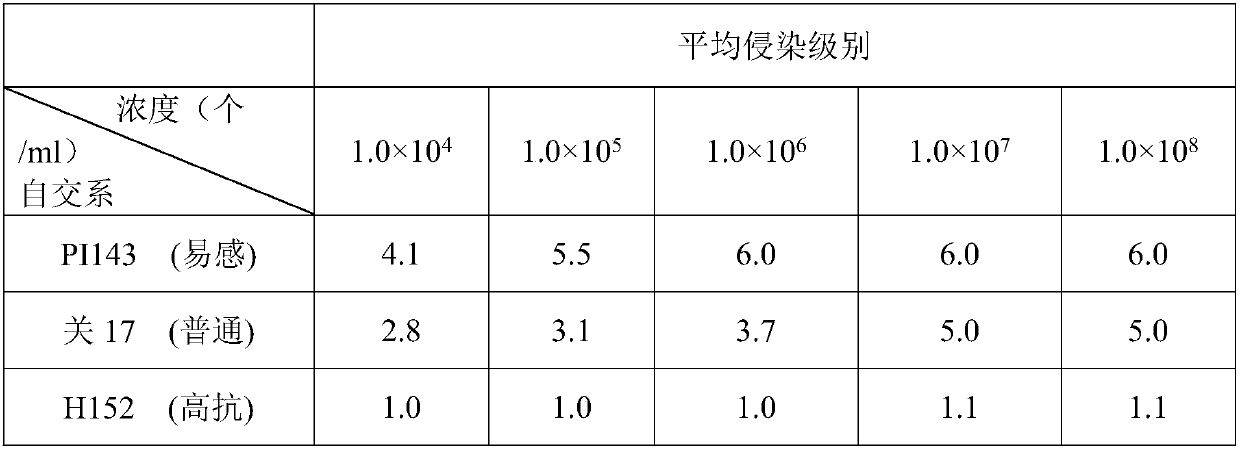
[0021] Spore suspension concentration parameter optimization in the Aspergillus flavus inoculation method of embodiment 1
[0022] This example aims to investigate the optimum spore suspension concentration for inoculating corn ears with Aspergillus flavus spores to cause disease. The test process is as follows: 1) Streak inoculation of Aspergillus flavus (3.4410) on the Cha's solid medium; 2) After culturing at 28°C for 7 days, the spores of Aspergillus flavus on the surface of the medium were eluted with distilled water, and filtered to prepare Aspergillus flavus spores suspension. Set five spore concentration gradients, the concentration is 1.0×10 4 pcs / ml, 1.0×10 5 pcs / ml, 1.0×10 6 pcs / ml, 1.0×10 7 pcs / ml, 1.0×10 8 pieces / ml. 3) Within 15 to 20 days after corn ear pollination, use a syringe to inoculate the spores of Aspergillus flavus, inoculate 0.5ml of spore suspension of different concentrations in the upper, middle and lower three parts of the corn ear with a th...
Embodiment 2
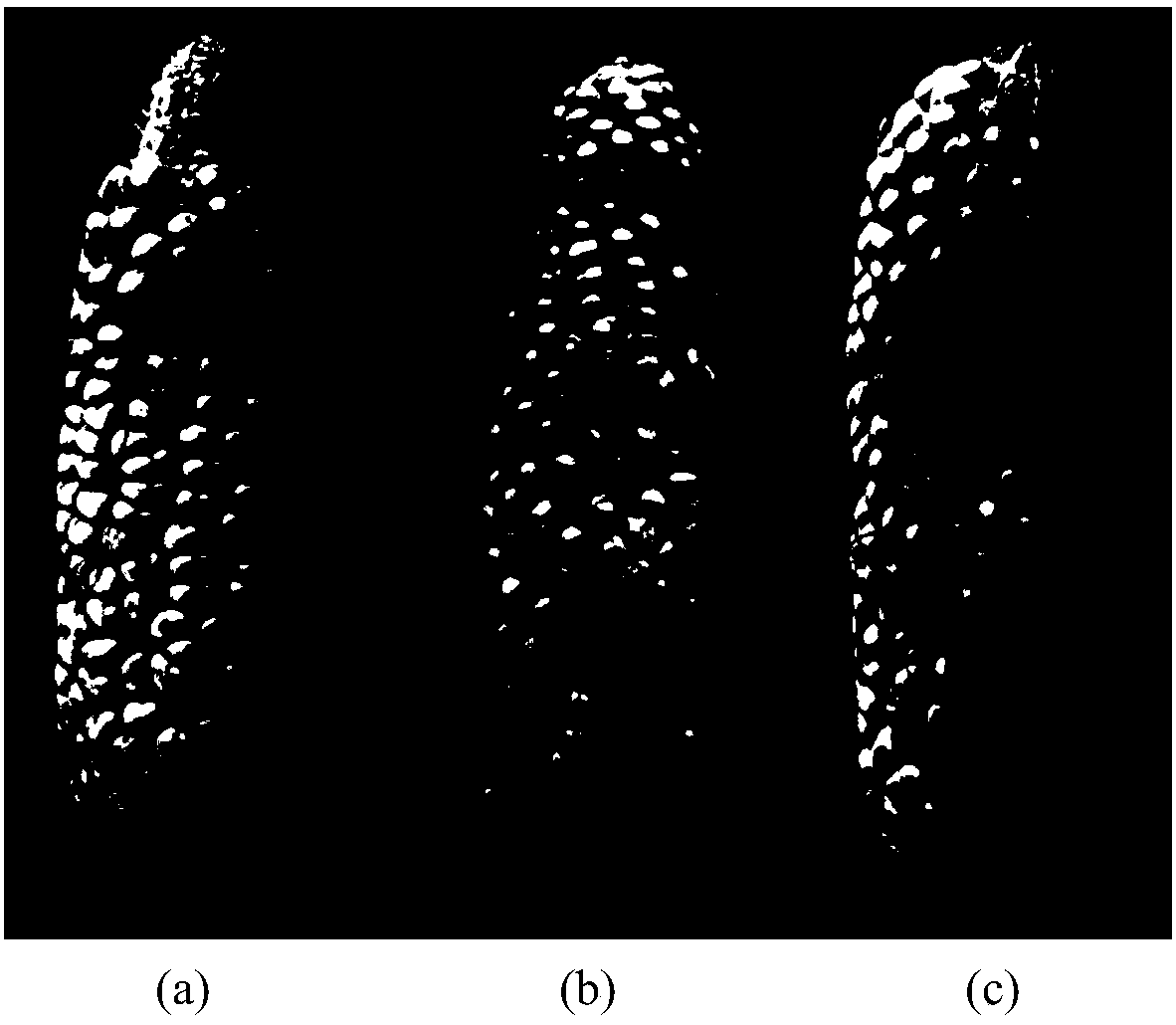
[0027] Example 2 Identification of Resistance Ability of Different Maize Inbred Lines to Aspergillus Aflatoxin Infection
[0028] The purpose of this example is to investigate the identification of the resistance of different maize inbred lines to Aspergillus flavus infection in field experiments. The test process is as follows:
[0029] 1) Streak inoculation of Aspergillus flavus (3.4410) on the Cha's solid medium;
[0030] 2) After culturing at 28°C for 7 days, the Aspergillus flavus spores were eluted with distilled water and filtered to prepare a suspension of Aspergillus flavus spores at a concentration of 1.0×10 6 a / ml;
[0031] 3) Within 15 to 20 days after corn ear pollination, use a syringe to inoculate the spores of Aspergillus flavus, inoculate 0.5ml of the spore suspension in the upper, middle, and lower three parts of the corn ear, and insert the needle into the bract leaf of the corn ear obliquely at 45 degrees. Pierce a single kernel.
[0032] 4) 12 corn inb...
Embodiment 3
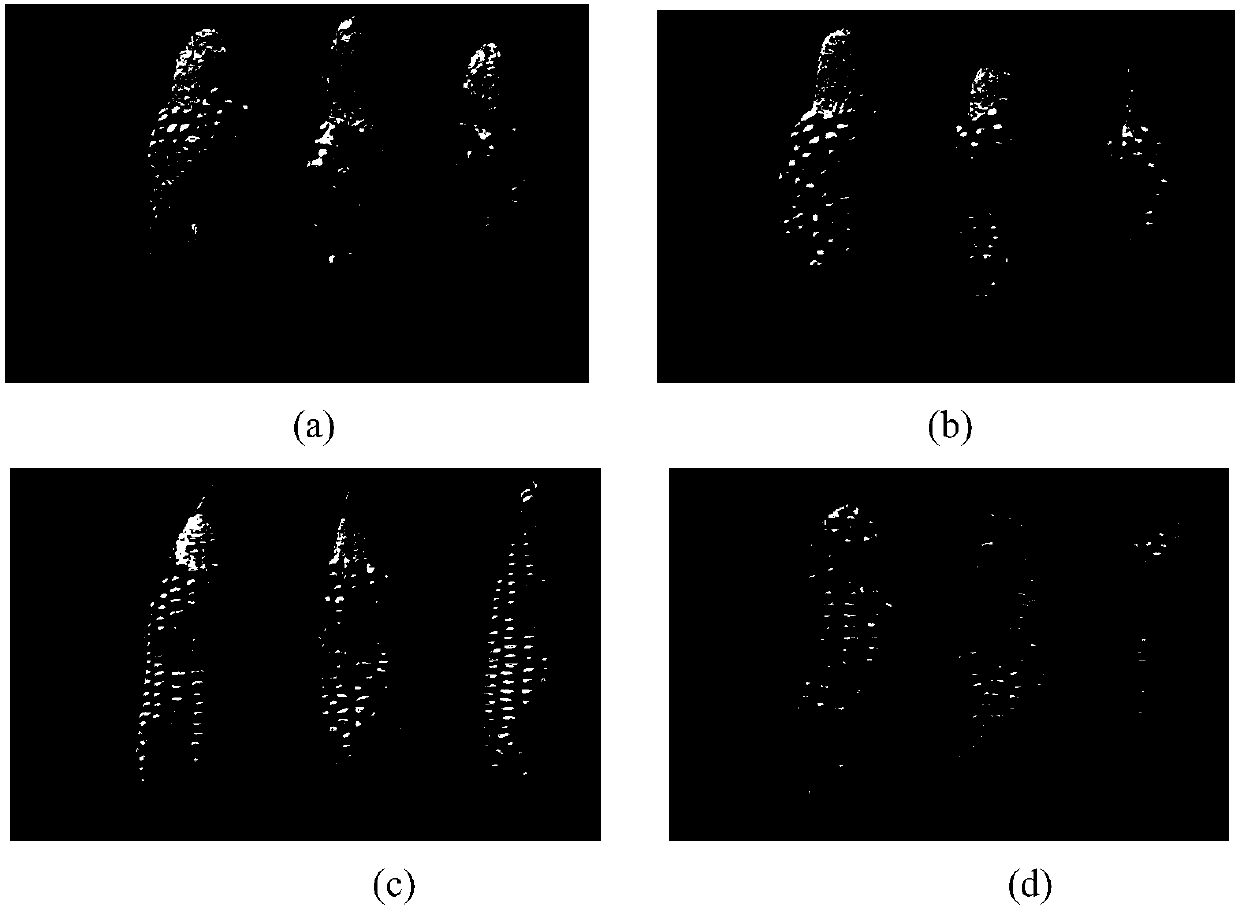
[0041] Example 3 Comparison of implementation differences between top injection inoculation method, row needle inoculation method and three-point spiral inoculation method
[0042] This example aims to compare the infection effects of three Aspergillus flavus inoculation methods on corn inbred lines, and optimize and obtain the best inoculation method.
[0043] Method 1, the top injection method is a non-injurious inoculation method. In this embodiment, in order to ensure that the inoculation amounts of the three methods are the same, on the 15th day after the ear pollination, 1.5ml of Aspergillus flavus spores with a concentration of 1.0×106 / ml The suspension is injected into the bracts from the middle of the top filaments to avoid damage to the top seeds.
[0044] Method 2, the row needle inoculation method is to use the needle to dip the suspension of Aspergillus flavus spores with a concentration of 1.0×106 / ml on the 15th day after the pollination of the ear, and insert th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com