Cell Lines For Screening Odorant And Aroma Receptors
An odorant, cell-based technology for use in the field of assays for the identification of odorants and/or aroma compounds or such modulators, capable of solving the problems of inefficient, cumbersome molecular biology methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
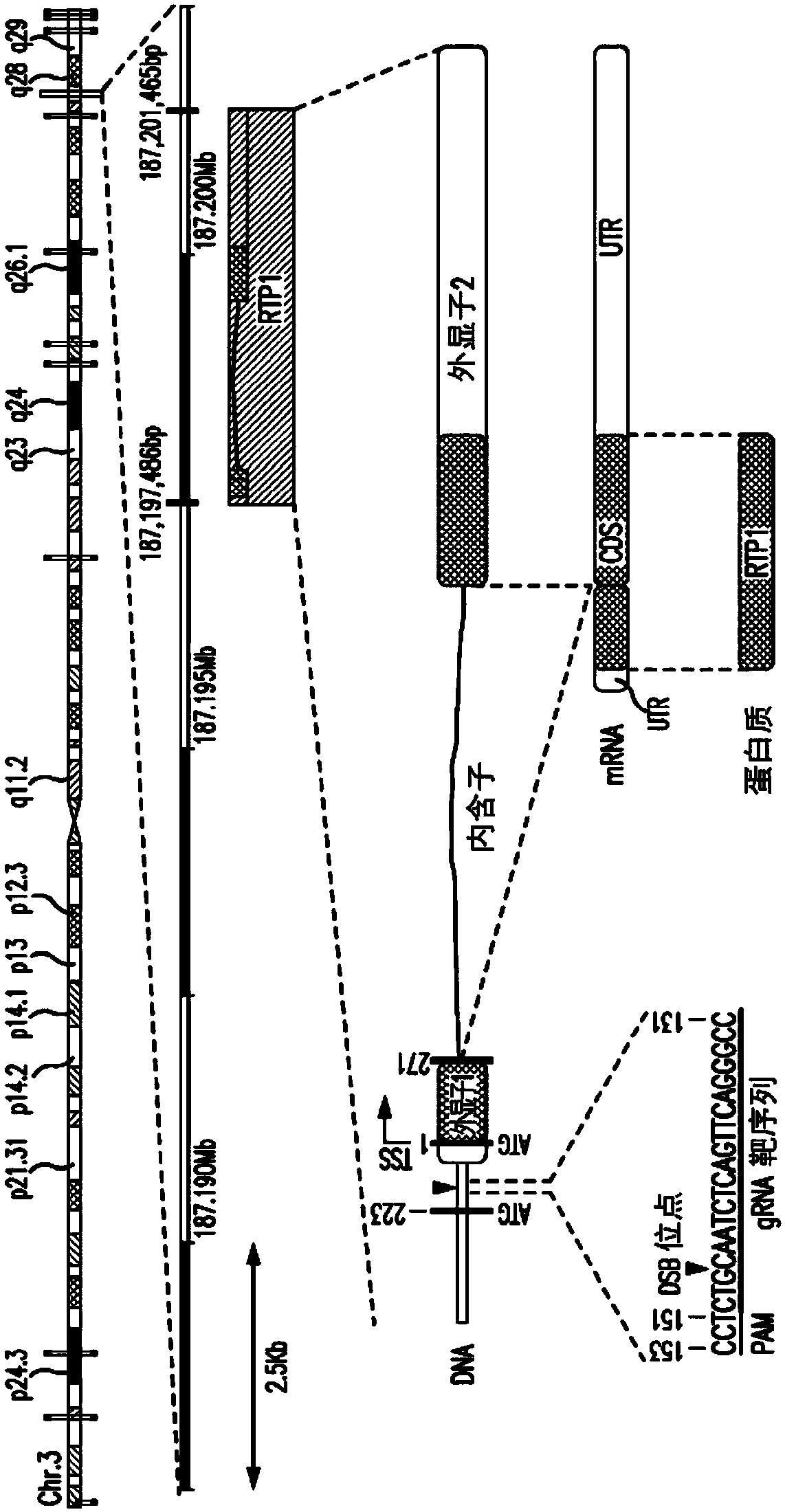
[0139] Genome editing strategies induce constitutive activation of the endogenous RTP1 gene in HEK293T cells.
[0140] A strategy to develop enhanced expression of functional odorant receptors in a heterologous expression system is described. Using a newly available genome editing technology called CRISPR / Cas9, the silenced (inactive) endogenous RTP1 gene in normal HEK293T cells was specifically targeted by introducing a constitutive promoter (CMV) upstream of its coding sequence Activated constitutively. figure 1 ) The RTP1 gene is located on chromosome 3, showing the DNA sequence around its start site. The Cas9 endonuclease is guided by a 20 base pair (bp) guide RNA (gRNA) homologous to the target. Upon delivery to cells (GeneArt CRISPR Nuclease (CD4 Enriched) Vector Kit, cat#A21175), the guide RNA molecule and Cas9 protein form an active complex that induces the desired double-strand DNA break (DSB) upstream of the coding sequence . Boxes indicate the RTP1 gene on chrom...
Embodiment 2
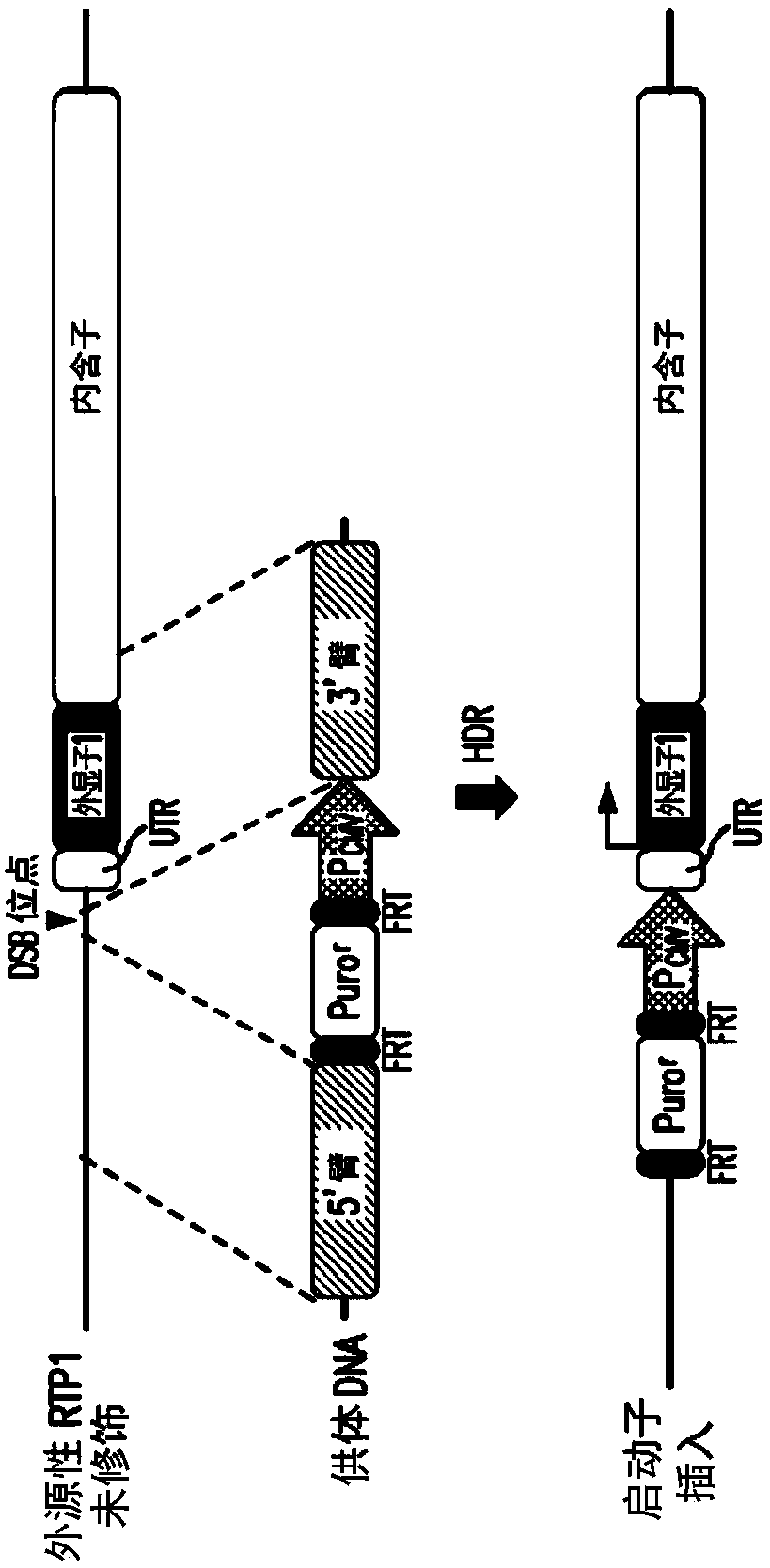
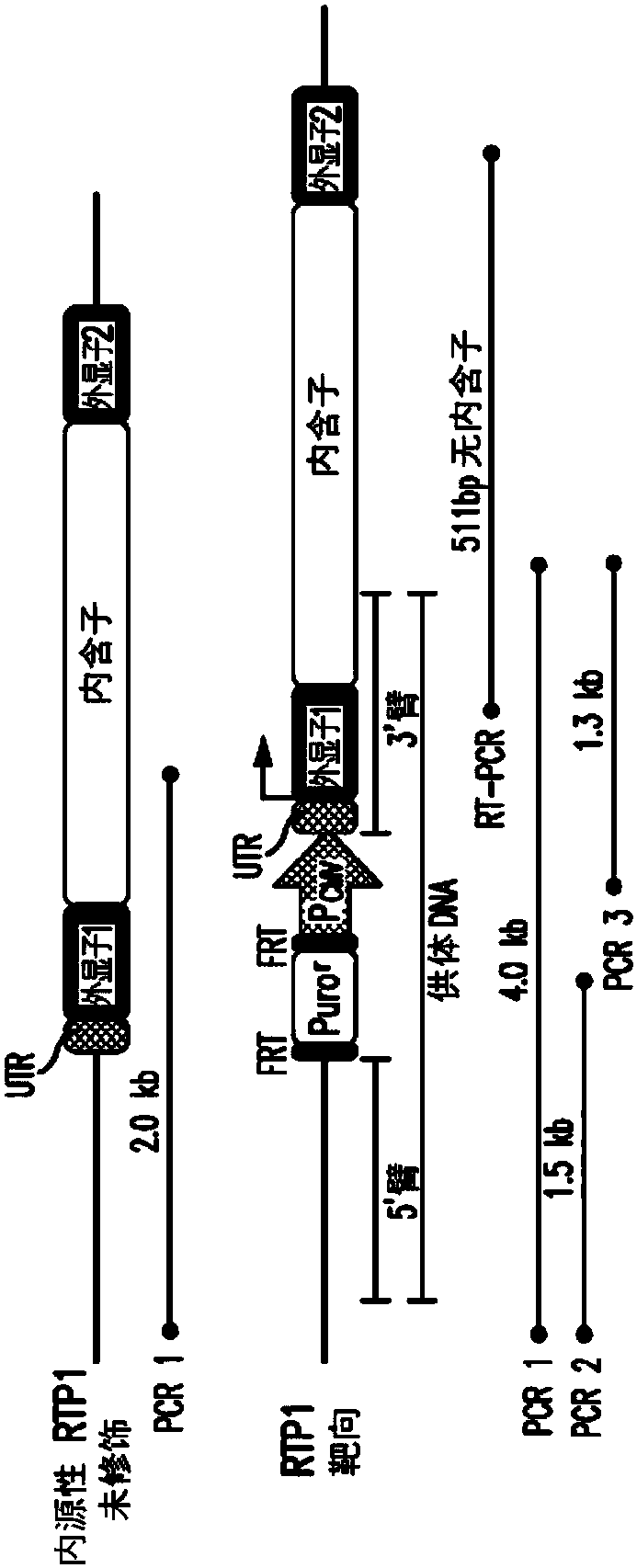
[0142] Selection of modified cell lines endogenously expressing the RTP1 gene.
[0143] Several control steps help characterize the modification of the cell line and its integrity. image 3 ) shows a schematic representation of wild-type and recombinant alleles. Gray lines indicate relative amplicon positions (not to scale) of PCR and RT-PCR experimental results for DNA genotyping and RNA expression controls, respectively. Figure 4 ) Genomic DNA from puromycin-resistant cell lines was extracted and PCR was performed to differentiate non-recombinant wild-type (WT) from modified cell lines (Mod.). PCR1 amplified the 2.0 kb band only in wild-type HEK293T cells, but not in the modified cell line. The modified line should produce a 4.0 kb band with PCR 1, but this is not possible due to the length and complexity of the genome structure. Genotyping of the modified cell line failed to yield a 2.0 kb band, indicating homozygous integration of the CMV promoter. Correct integration...
Embodiment 3
[0145] Characterization of RTP1 protein expression.
[0146] RTP1 protein expression in selected modified cell lines was determined by Western blot analysis using RTP1-specific antibodies. The long (RTP1L) and short (RTP1S) protein forms can be derived from the endogenous RTP1 gene. The genome modification strategy described here involves introducing the CMV promoter upstream of the RTP1L start codon to avoid any modification of the endogenous coding sequence; RTP1L is thus expected to be expressed. However, the results showed that the modified cell lines were heavily biased towards the expression of RTP1S, suggesting that the endogenous RTP1 gene preferentially expresses a short version without further genome editing. The latter is the preferred form as it is known to better promote cell surface expression of odorant receptors. Figure 6 ) shows a Western blot of RTP1 protein. Arrows indicate the expected protein sizes for RTP1S - 25 kDa, RTP1L - 28 kDa and the control pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com