Method for Catalyzing Lactide Polymerization Using Asymmetric Aluminum Complex Containing Acetylacetone Derivatives
A technology of acetylacetone and aluminum complexes, which is applied to compounds containing elements of Group 3/13 of the periodic table, chemical instruments and methods, organic chemistry, etc. The effect of narrow distribution, high stereoselectivity and high product yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
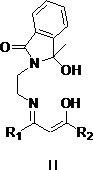
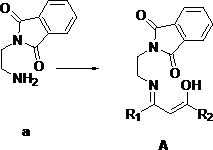
[0044] The structural formula of the synthesized ligand is the above formula (A), where R 1 is methyl; R 2 For methyl, the reaction process is: Add 0.30 g of ethylenediamine (a) with unilateral protection and equimolar amount of acetylacetone into 12 mL of methanol, heat and reflux for 12 hours, cool, filter and wash with cold methanol after the reaction , filtered, collected, dried and weighed to obtain 0.35 g of solid, with a yield of 81.4%.
[0045] The NMR information of the obtained product is as follows, as can be seen from the NMR information, R 1 is methyl; R 2 The ligand for the methyl group was successfully synthesized.
[0046] 1 H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ 10.85 (s, 1H, O H ), 8.03 (d, J = 6.4Hz, 2H,Ar– H ), 7.56 (d, J = 6.4Hz, 2H, Ar– H ), 5.23 (s, 1H, C H ), 4.25 (m, 2H, NC H 2 ),3.42 (m, 2H, =NC H 2 ), 2.08 (s, 6H, C H 3 ). HRESI-MS: m / z ccld. C 15 h 16 N 2 o 3 [M-H] - ;271.1085, found: 271.1090.
Embodiment 2
[0048] The structural formula of the synthesized ligand is the above formula (A), where R 1 is methyl; R 2 It is trifluoromethyl, and the reaction process is as follows: Add 0.20 g of ethylenediamine (a) with unilateral protection and equimolar amount of trifluoroacetylacetone into 10 mL of methanol, heat and reflux for 12 hours, cool and filter after the reaction is completed and use Washed with cold methanol, filtered, collected, dried and weighed to obtain 0.30 g of solid, yield 88.2%.
[0049] The NMR information of the obtained product is as follows, as can be seen from the NMR information, R 1 is methyl; R 2 The ligand for trifluoromethyl was synthesized successfully.
[0050] 1 H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ 11.25 (s, 1H, O H ), 8.05 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H,Ar– H ), 7.58 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H, Ar– H ), 5.62 (s, 1H, C H ), 4.26 (m, 2H, NC H 2 ),3.45 (m, 2H, =NC H 2 ), 2.09 (s, 3H, C H 3 ). HRESI-MS: m / z cacld.C 15 h 12 f 3 N 2 o 3 F[M-H] - ; 325.0802, fo...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The structural formula of the synthesized ligand is the above formula (A), where R 1 is trifluoromethyl; R 2 is phenyl, the reaction process is: Add 0.25 g of ethylenediamine (a) with unilateral protection and equimolar amount of benzoyltrifluoroacetone into 20 mL of methanol, heat and reflux for 12 hours, cool and filter after the reaction and use Washed with cold methanol, filtered, collected, dried and weighed to obtain 0.45 g of solid, yield 88.2%.
[0053] The NMR information of the obtained product is as follows, as can be seen from the NMR information, R 1 is trifluoromethyl; R 2 The ligand for phenyl was synthesized successfully.
[0054] 1 H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ 12.05 (s, 1H, O H ), 8.07 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H,Ar– H ), 7.60 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H, Ar– H ), 7.56-7.47(m, 3H, Ar– H), 7.19 (d, J =6.0 Hz, 2H, Ar– H ), 6.47 (s, 1H, C H ), 4.34 (m, 2H, NC H 2 ), 3.92 (m, 2H, =NC H 2 ). HRESI-MS: m / z cacld.C 20 h 15 f 3 N 2 o 3 [M-H] - ; 387...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com