Primer and method for detecting tomato gray leaf spot germs
A gray leaf spot pathogen, tomato technology, applied in the field of primers for the detection of tomato gray leaf spot pathogen, can solve the problems of narrow detection range of tomato gray leaf spot pathogen, detection sensitivity, specificity, and large impact on detection results, etc. Achieve high sensitivity, wide detection range and good detection specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
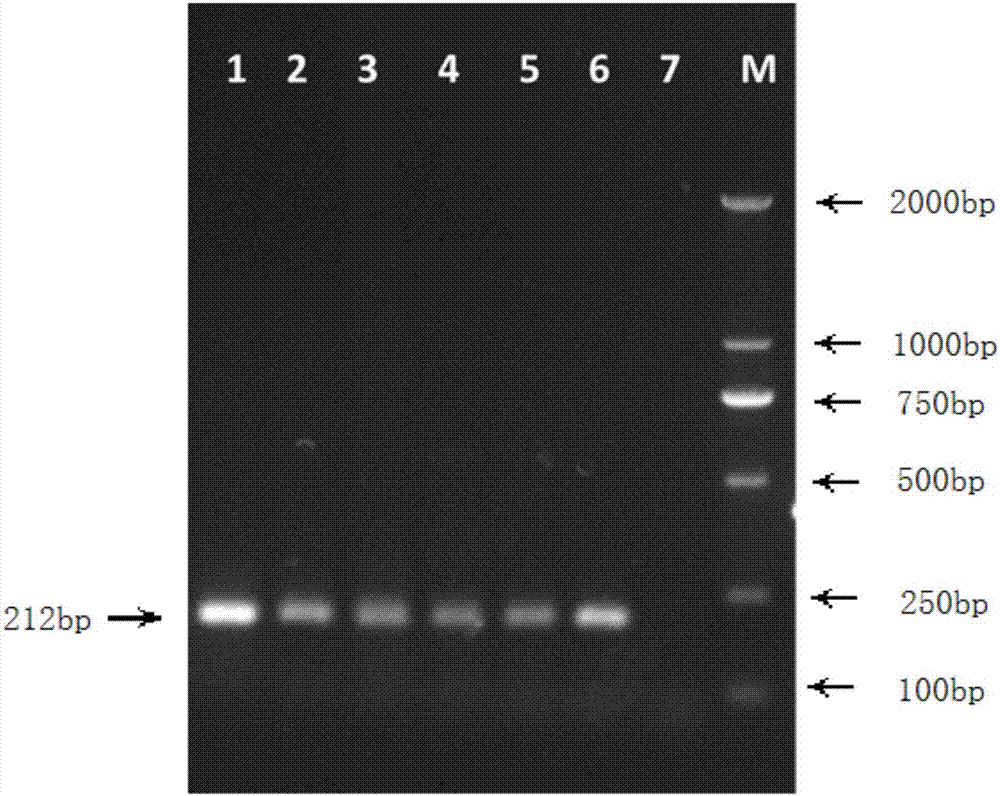
[0040] In this example, according to the S. lycopersici genome sequence numbered KY290555 in GenBank, a kind of primers for detecting tomato gray leaf spot was designed with NCBI primer online software Primer-BLAST, including upstream primers and downstream primers. The specific sequences are as follows:
[0041] Upstream primer: HYB5-1: 5'-CTTACTTCGGTGAGGGCTCC-3';
[0042] Downstream primer: HYB3-1: 5'-GTATCGCATTTCGCTGCGTT-3'.
[0043] The company that specifically produces the primers is Huada Gene Biotechnology Company.
[0044] The S. lycopersici cultivated in this example was provided and preserved by Northeast Forestry University.
[0045] The genomic DNA of the tomato cinerea leaf spot on the S. lycopersici medium was extracted with the improved CTAB method, and the steps were as follows:
[0046] (1) Scrape the mycelium of S.lycopersici on the culture medium, add liquid nitrogen and grind it thoroughly in a mortar, weigh 0.2g of ground material and add it to 700μL 65...
Embodiment 2
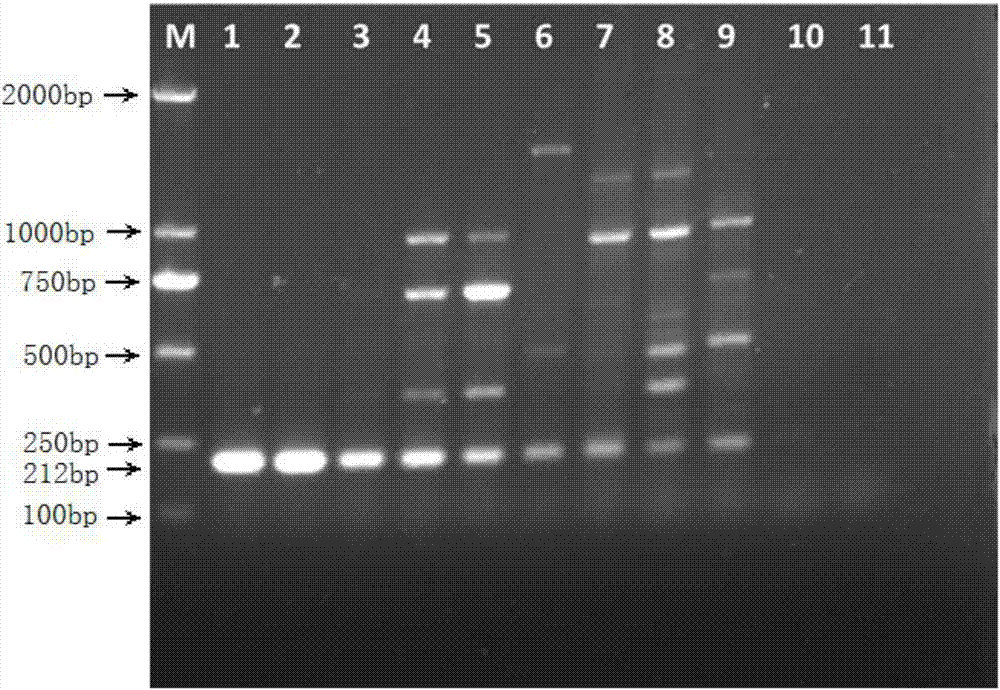
[0056] The primers designed in this embodiment are the same as in Example 1, and the genomic DNA of the tomato leaf spot bacteria on the tomato leaves infected with S.lycopersici bacteria is extracted by the improved CTAB method, and the steps are as follows:
[0057] (1) Add liquid nitrogen to the tomato leaves infected with S. lycopersici and grind them thoroughly in a mortar. Weigh 0.2 g of ground material and add it to 700 μL of CTAB solution preheated at 65°C. Shake well after a period of time to make the solid and liquid fully contact;
[0058] (2), the sample after the water bath in step (1) was cooled to room temperature, and 700 μL of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol mixture was added. The volume ratio of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol in the mixture was 24:1. set for 10min;
[0059] (3) Centrifuge the sample at 4°C at 13,000rmp for 10min after step (2), take 550 μL of the supernatant and add the same volume of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol mixture, shake well and let...
Embodiment 3
[0067] The primers designed in this embodiment are the same as in Example 1, and the genomic DNA of the tomato ash leaf spot bacteria in the S. lycopersici bacteria suspension is extracted with the improved CTAB method, and the steps are as follows:
[0068] (1) Centrifuge the S. lycopersici bacterial suspension at 3000rmp for 3min, add the precipitate to liquid nitrogen and blow repeatedly with the tip of a pipette in the centrifuge tube, weigh 0.2g of the precipitate and add it to 700μL of CTAB solution preheated at 65°C, quickly After mixing, place in a water bath at 65°C for 1 hour and shake fully at regular intervals to fully contact the solid and liquid;
[0069] (2), the sample after the water bath in step (1) was cooled to room temperature, and 700 μL of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol mixture was added. The volume ratio of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol in the mixture was 24:1. set for 10min;
[0070] (3) Centrifuge the sample at 4°C at 13,000rmp for 10min after step ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com