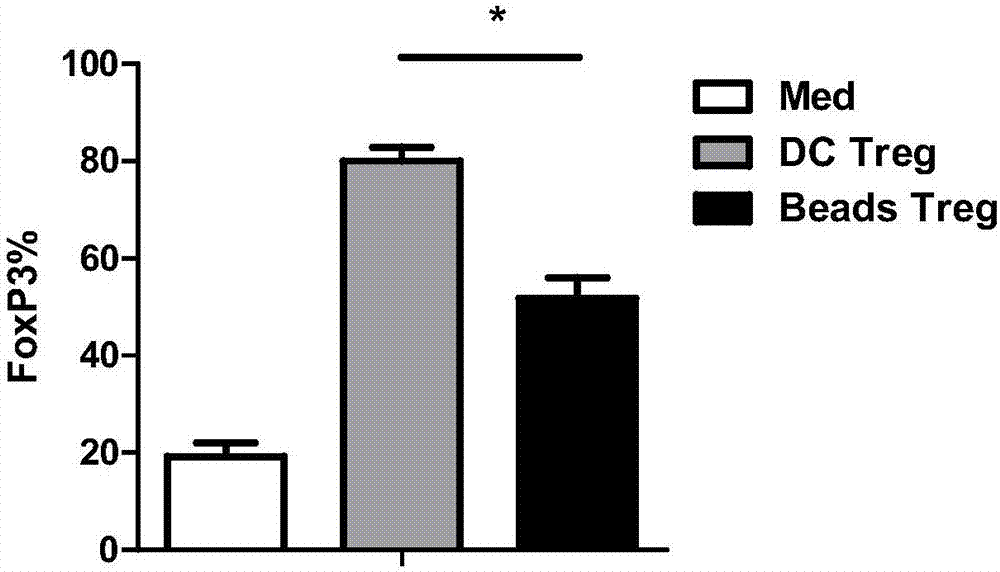
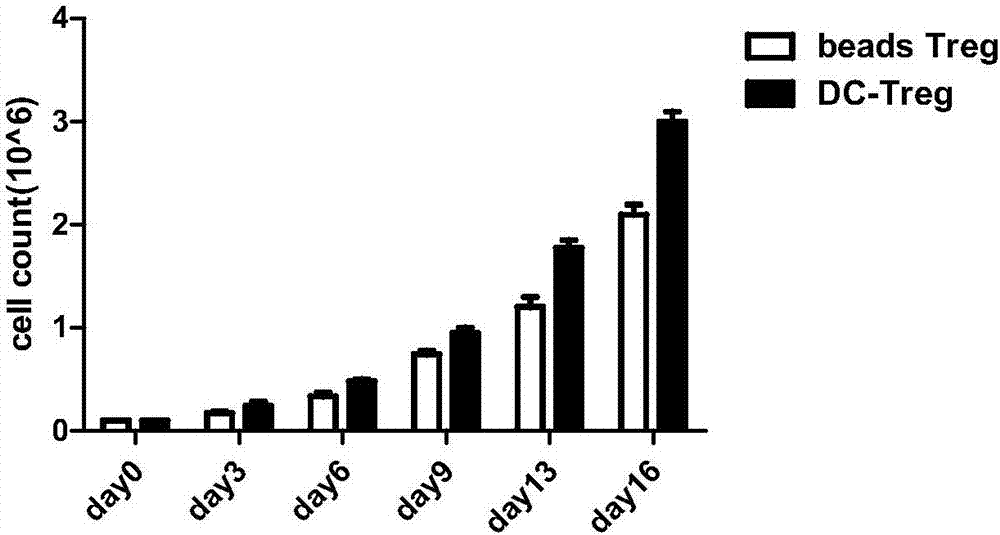
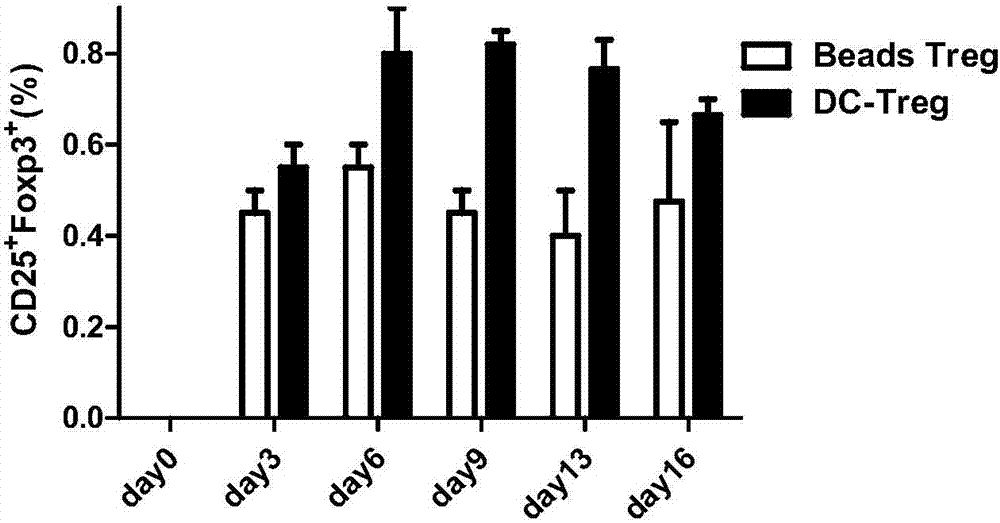
Method for in-vitro inducing antigen-specific T cells
A specific, cellular technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of prolonging the survival of allografts, failing to achieve tolerance, and reducing cellular Foxp3, and achieve the effect of large clinical application value and sufficient quantity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Materials: CD4+CD45RA+T cell isolation kit (purchased from Miltenyi Biotec, USA), anti-human CD14 cell isolation kit (purchased from Miltenyi Biotec, USA), systemic immunodeficiency (SCID) mice (purchased from Jackson, USA) laboratory).
[0049] Instruments: magnetic bead separator (Auto MACS from Miltenyi, Germany), flow cytometer (BD company, model: Vantage SE).
[0050] Reagents: rhIL-2 (final concentration of 100 IU / ml after addition), rhIL-15 (10 ng / ml), Rapamycin (final concentration of 10 nM after addition) were purchased from Wyeth Pharmaceuticals. The medium is supplemented with 100U / ml penicillin, 100ug / ml streptomycin, 2mM L-glutanoic acid, 10mM 4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid, 0.1mM non-essential amino acid, 1mM pyruvate in complete RPMI-1640 medium Sodium (purchased from BioSource International Company above) and 50uM dihydroxyethanol (purchased from SigmaAldrich Company) were prepared.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com