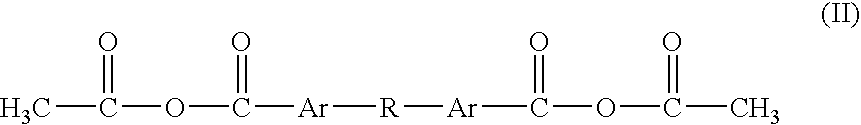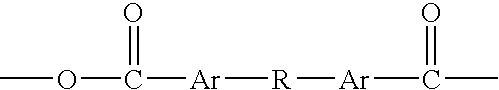Polyanhydrides with therapeutically useful degradation products
a technology of polyanhydrides and degradation products, applied in the field of biocompatible aromatic polyanhydrides, to achieve the effect of enhancing solubility and processability, and degradation properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Preparation of 1,6-Bis(o-Carboxyphenoxy)Hexane Dicarboxylic Acid
[0040]To a mixture of salicylic acid (77.12 g, 0.5580 mole) and distilled water (84 mL) sodium hydroxide (44.71 g, 1.120 mole) was added. The reaction was brought to reflux temperature before 1,6-dibromohexane (45.21 g, 0.2790 mole) was added drop-wise. Reflux was continued for 23 hours after which additional sodium hydroxide (11.17 g, 0.2790 mole) was added. The mixture was refluxed for 16 more hours, cooled, filtered, and washed with methanol. The yield was 48.8%.
example ii
Preparation of 1,6-Bis(o-Carboxyphenoxy)Hexane Monomer (o-CPH)
[0041]The dicarboxylic acid of Example I was acetylated in an excess of acidic anhydride at reflux temperature. The resulting monomer was precipitated from methylene chloride into an excess of diethyl ether. The yield was 66.8%.
example iii
Preparation of Poly(1,6-Bis(o-Carboxyphenoxy)Hexane) (Poly(o-CPH))
[0042]The monomer of Example II was polymerized in a melt condensation performed at 180° C. for 3 hours under vacuum in a reaction vessel with a side arm. The polymerization vessel was flushed with nitrogen at frequent intervals. The polymer was isolated by precipitation into diethyl ether from methylene chloride. The yield was quantitative.
[0043]All compounds were characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, GPC, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermal gravimetric analysis, contact angle measurements, UV spectroscopy, mass spectroscopy, elemental analysis and high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC).
[0044]The o-CPH monomer was polymerized by melt polycondensation for 60 minutes at temperatures ranging from 100° to 300° C. Analysis of the resulting polymers by GPC indicated that the highest molecular weight, coupled with the lowest polydispersity index occurred at 260° C.
[0045]The poly(o-CPH) w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com