Preparation method of high-energy 3.5-valent pure hydrochloric acid system vanadium electrolyte
An electrolyte and hydrochloric acid technology, applied in circuits, fuel cells, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient stability and low vanadium ion concentration, and achieve a solution that reduces storage space and transportation costs, has high vanadium ion concentration, and is easy to operate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
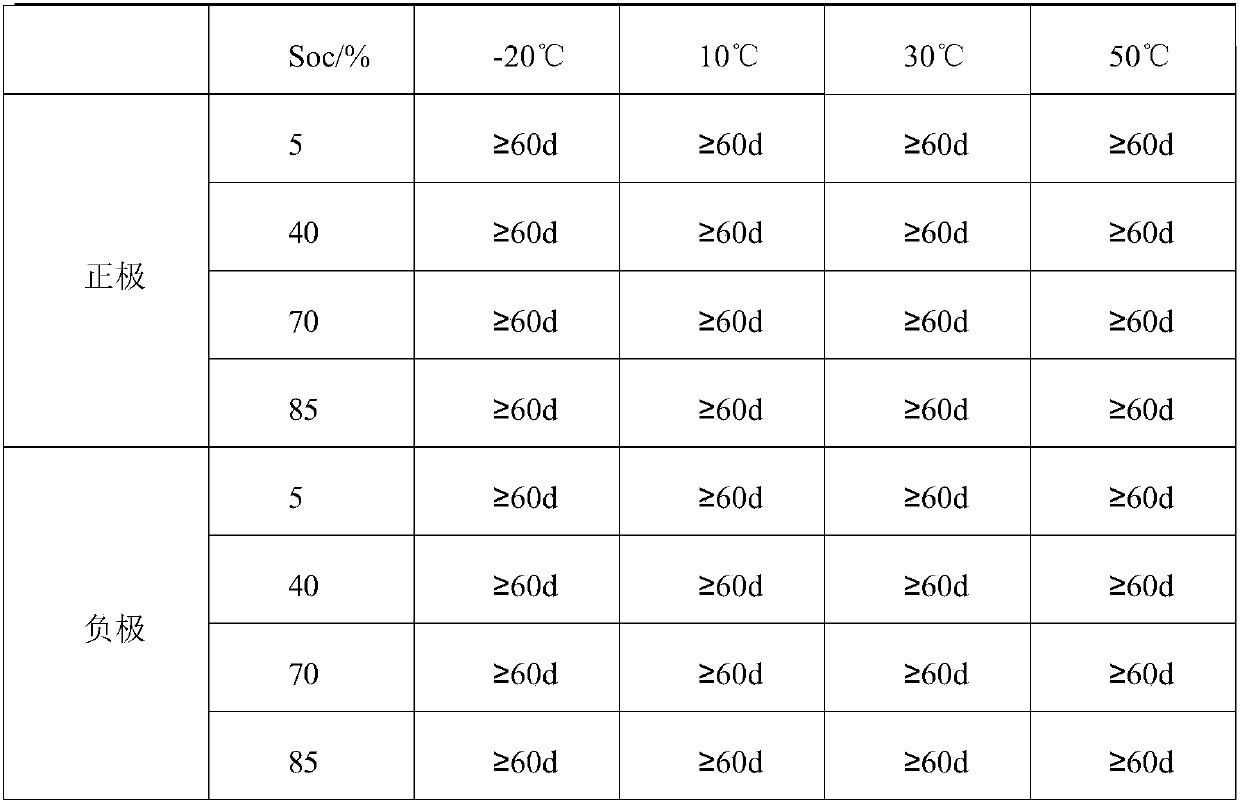
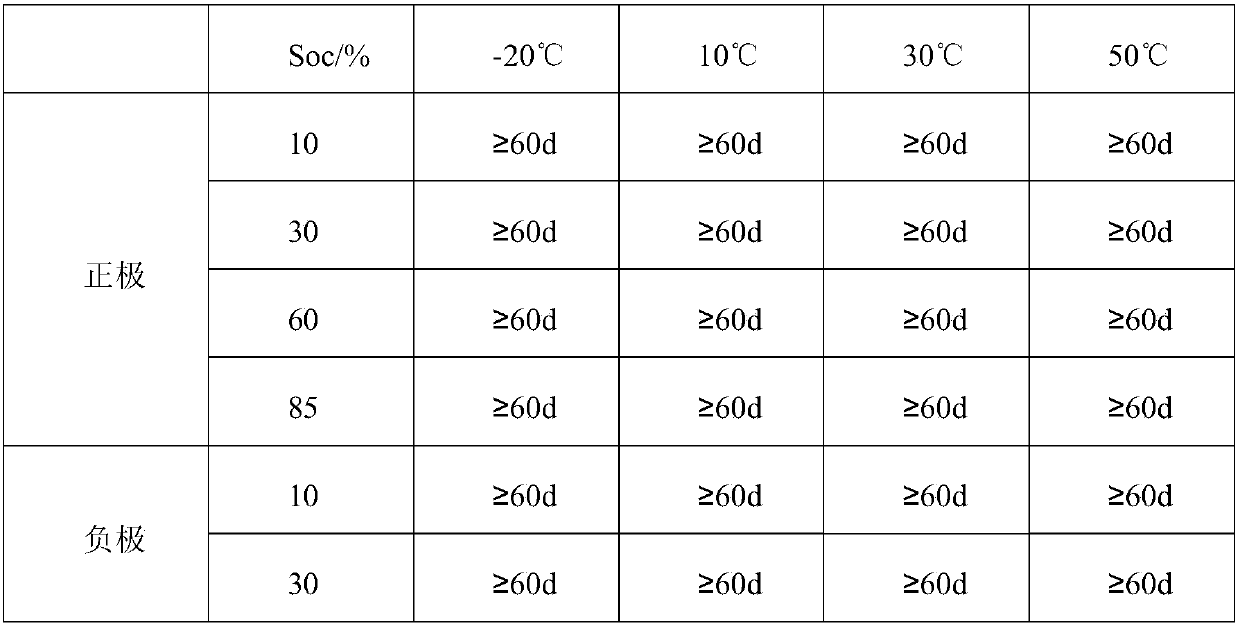
[0040] Weigh 74.94g V 2 O 3 And 82.94g VO 2 Mix (mixing ratio is 1: 1.106, mixed valence is 3.5 valence) into the reactor and add 50.00g of water (the ratio of vanadium mixture c to water: 1:0.76), start heating and stirring, then add 36% Hydrochloric acid 625.00g (3.96 times the mass of the vanadium mixture c), raise the temperature of the solution to 118℃, keep the temperature for 3.5h, stop heating, add 100.00g of water (0.63 times the mass of the vanadium mixture c), continue to stir and dissolve When the temperature drops to 45℃ and the reaction is stopped, the unactivated electrolyte can be obtained; vanadium ion concentration is 2.80mol / L, chloride ion concentration is 8.50mol / L, hydrogen ion concentration is 1.50mol / L; The charge and discharge test after activation shows that the current efficiency is 97.60%, the voltage efficiency is 87.00%, the energy efficiency is 84.91%, and the energy density is 39.68Wh / L. The stability of the positive and negative electrode electr...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Weigh 158.00g V 4 O 7 (Add only vanadium mixture d) Add 60.00g of water to the reactor (the ratio of vanadium mixture c to water: 1:0.38), start heating and stirring, and then add 36% hydrochloric acid 770.00g (4.87 of the mass of vanadium mixture) The temperature of the solution was raised to 90°C, the temperature was kept for 6.0 hours, the heating was stopped, 483.00g of water (3.06 times the mass of the vanadium mixture c) was added, the stirring was continued, and the reaction was stopped when the temperature dropped to 30°C. The unactivated electrolyte can be obtained; the vanadium ion concentration is 1.50 mol / L, the chloride ion concentration is 8.24 mol / L, and the hydrogen ion concentration is 2.74 mol / L; the electrolyte is activated and charged and discharged, and the current efficiency is 96.40 %, the voltage efficiency is 87.10%, the energy efficiency is 83.96%, and the energy density is 33.74Wh / L. The stability of the positive and negative electrolytes after...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Weigh 5.36g VO and 515.20g 3.54-valence and 29.7% vanadium-containing chlorine-containing mixture and mix (mixing ratio is 1:96.12, mixed valence is 3.5 valence) into the reactor and add 50.00g water (vanadium mixture c and water The ratio is: 1:0.096), start heating and stirring, then add 302.1g of 36% hydrochloric acid (0.58 times the mass of the vanadium mixture c) to raise the temperature of the solution to 80°C, keep the temperature for 2h, stop heating, make up Add 403.00g of water (0.77 times the mass of vanadium mixture c) and continue to stir and dissolve. When the temperature drops to 30℃ and stop the reaction, the unactivated electrolyte can be obtained; the vanadium ion concentration is 2.60mol / L, and the chloride ion concentration is 8.64 mol / L, hydrogen ion concentration is 2.14mol / L; the electrolyte is activated and charged and discharged. The current efficiency is 95.73%, the voltage efficiency is 87.12%, the energy efficiency is 83.35%, and the energy den...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com