Phase component fault range finding method based on mu PMU distribution line parameter identification
A technology for fault location and parameter identification. It is used in fault location, fault detection by conductor type, and information technology support systems. It can solve problems such as low communication requirements, high positioning accuracy, and small number of PMUs. The effect of anti-interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
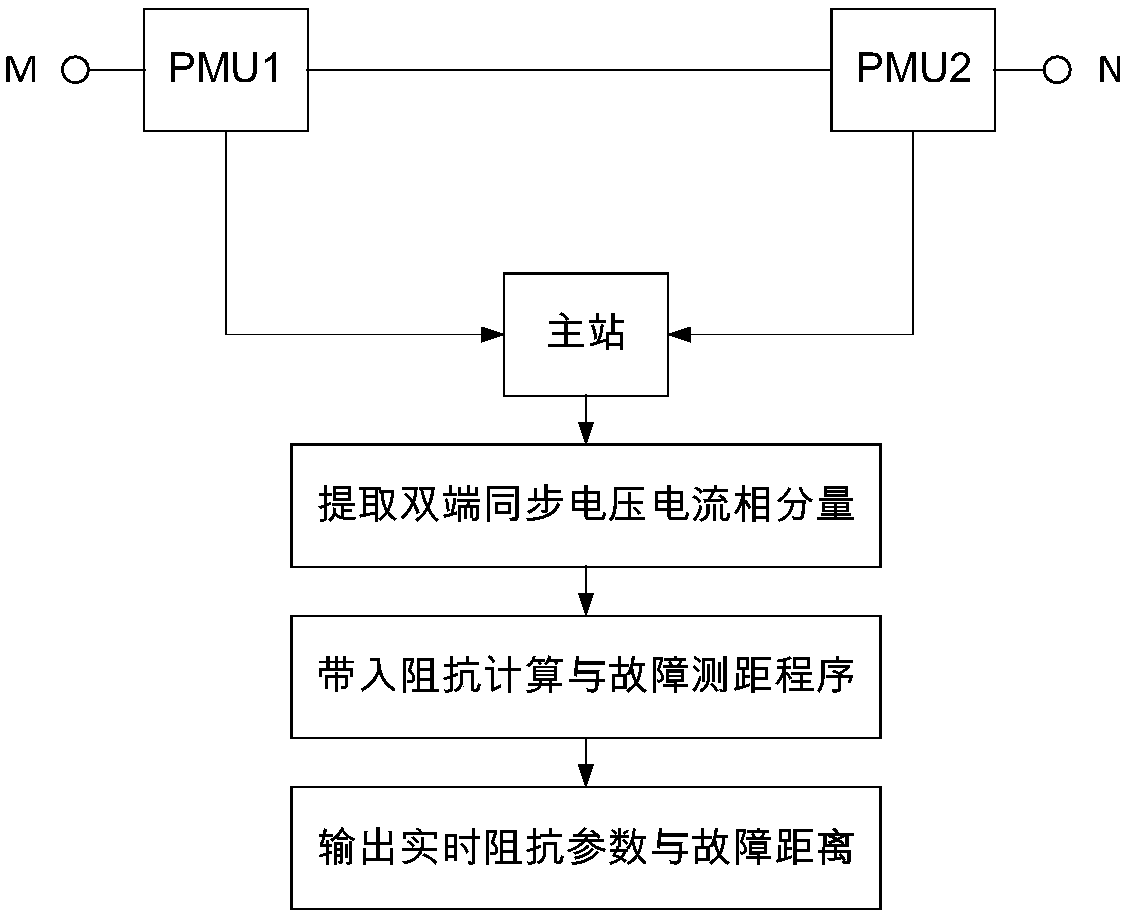
[0062] The embodiment of the present invention is based on the fault analysis method, extracts the voltage and current information collected by the double-ended μPMU of the line, fully considers the asymmetry of the line parameters, conducts real-time online identification of the self-impedance and mutual impedance parameters of the line, and uses The voltage and current phase components are used for fault location.
[0063] The method provided by the embodiment of the present invention specifically includes the following steps:
[0064] Step 1: Use μPMU to extract the phase components of the synchronous voltage and current at both ends of the line.
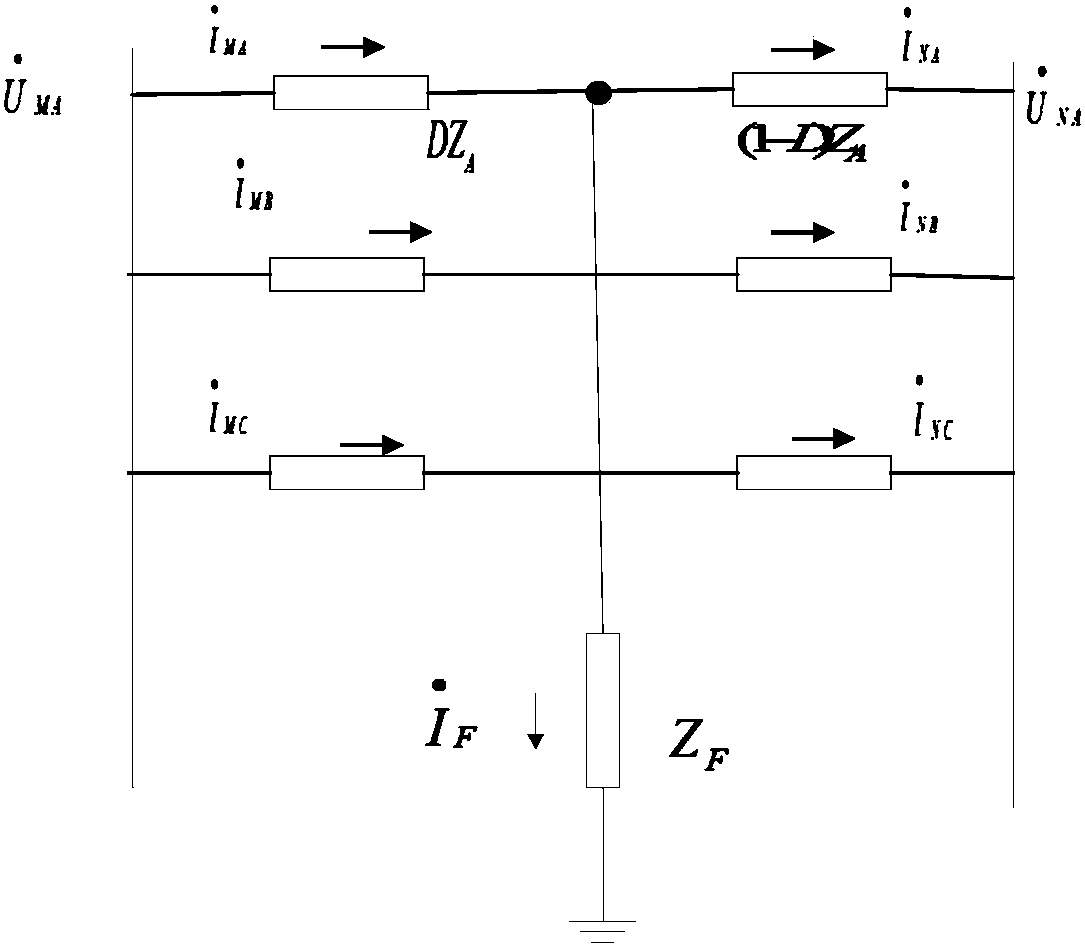
[0065] This embodiment provides a phase component fault location method based on the distribution line parameter identification of μPMU. The schematic diagram of the fault location of the double-ended network is as follows figure 1 shown. Common faults in AC distribution network include single-phase ground fault, two-phase grou...
Embodiment 2
[0100] This embodiment provides a phase component fault location method based on μPMU-based distribution line parameter identification. The method is simulated through a simulation platform. The specific simulation process and results are as follows:
[0101] In PSCAD / EMTDC, a single power supply radial distribution network system model with distributed fans is built, such as Figure 4 shown. The fault recorder is used to simulate the μPMU to sample the data, and the sampling period is 200 points / cycle; the simulation conditions are as follows: the AC bus side voltage is 10KV, the neutral point grounding method is ungrounded or grounded through the arc suppression coil, and the transition resistance is 5Ω. The total length of the line is 4Km, the time of fault occurrence is 0.2s, and the duration of the fault is 0.2s.
[0102] (1) Fault location results under different neutral point grounding methods:
[0103] Taking a single-phase ground fault with a distributed fan and a t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com