Design of polypeptides specifically binding to immune protein of pseudomonas aeruginosa type VI secretion system, and validation of antibacterial activity of polypeptides
A secretion system and immune protein technology, which is applied in the field of design of polypeptides specifically binding to the immune protein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type VI secretion system and the verification of antibacterial activity, which can solve the problems of treatment failure and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1. Discovery of functional short peptides
[0064] 1. Use petDUET-1 vector as starting plasmid to construct recombinant plasmid. In the recombinant plasmid, the first open reading frame expressed with His N-terminal 6 TplEi mature peptide, the second open reading frame expresses TplE protein.
[0065] 2. Introduce the recombinant plasmid constructed in step 1 into Escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3) to obtain recombinant bacteria.
[0066] 3. Cultivate the recombinant bacteria obtained in step 2, and carry out IPTG induction during the culture process, and then proceed to the following steps in sequence: cell crushing and supernatant, nickel column purification, ion exchange chromatography, Superose 6 molecular sieve chromatography to obtain TplE-TplEi composite Things.
[0067] 4. Take the TplE-TplEi complex obtained in step 3, add subtilisin for in-situ enzymatic digestion and crystallization, and then obtain the crystal and perform structural analysis.
[0068] 5. Accordi...
Embodiment 2
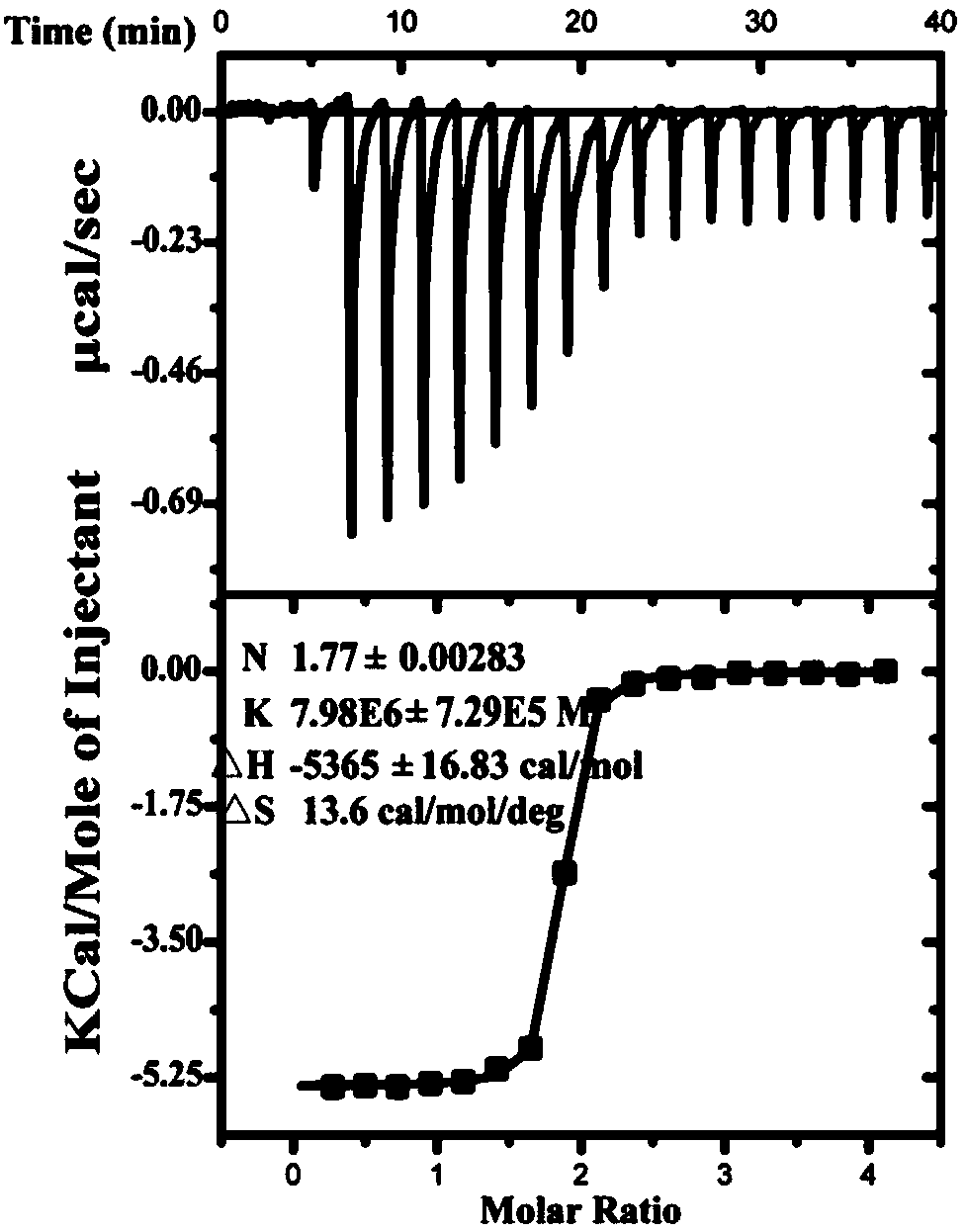
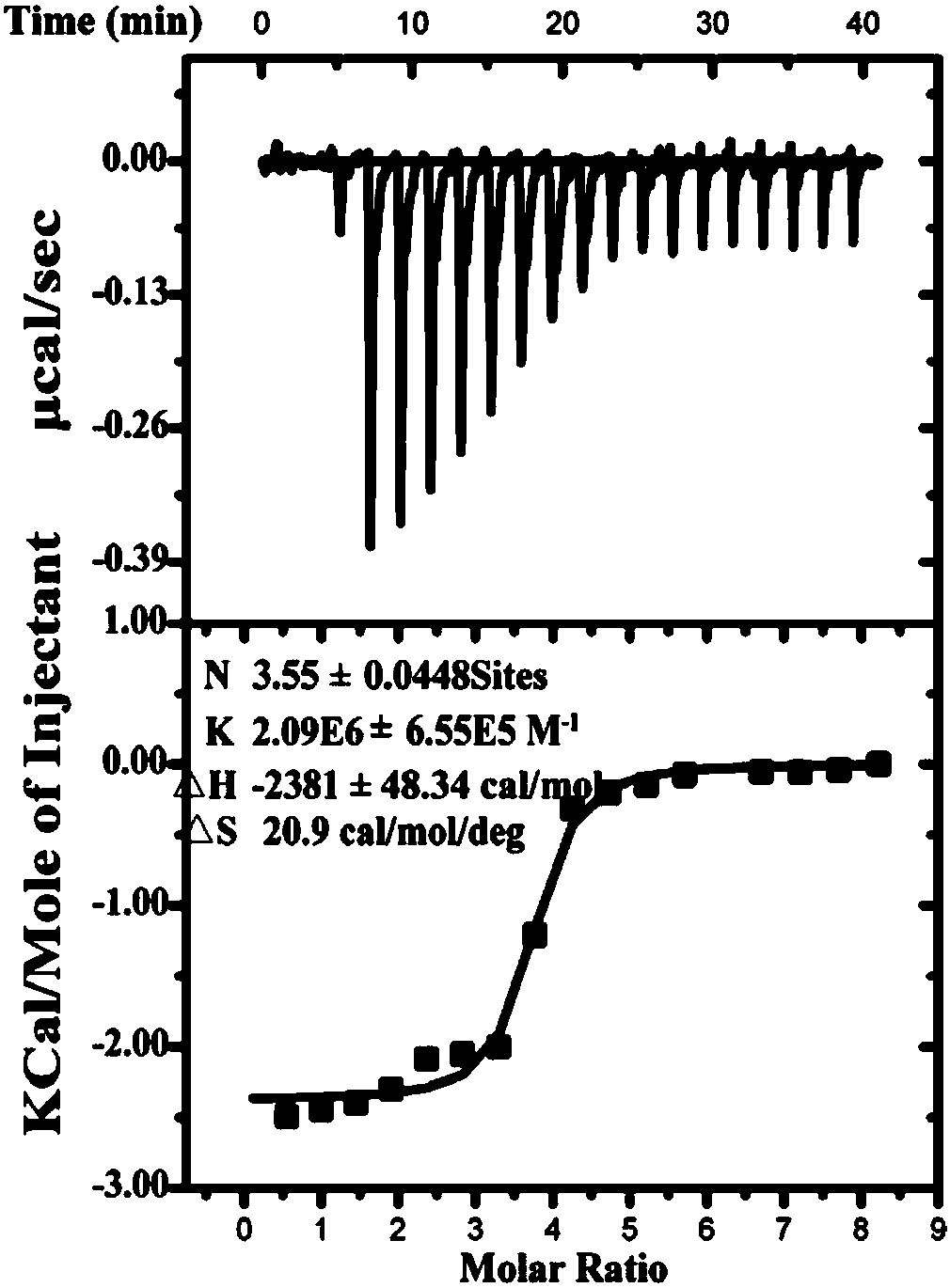
[0071] Example 2. Affinity of functional short peptides to TplEi protein
[0072] The functional short peptide and TplEi protein were combined in vitro to determine the affinity of the functional short peptide. The high affinity of functional short peptides is the first step for the development of new anti-infective drugs.
[0073] 1. Preparation of functional short peptides
[0074] Artificial synthesis of A peptide.
[0075] Artificial synthesis of B peptide.
[0076] 2. Preparation of TplEi protein
[0077] 1. Insert the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in nucleotides 64-1131 of sequence 5 in the sequence table between the NdeI and XhoI restriction sites of pET-28a(+) vector to obtain a recombinant plasmid. After sequencing, the recombinant plasmid has the open reading frame shown in sequence 5 of the sequence list, and the expression N-terminal has His 6 TplEi mature peptide labeled.
[0078] 2. Introduce the recombinant plasmid obtained in step 1 into Escherichia coli Rosetta (DE...
Embodiment 3
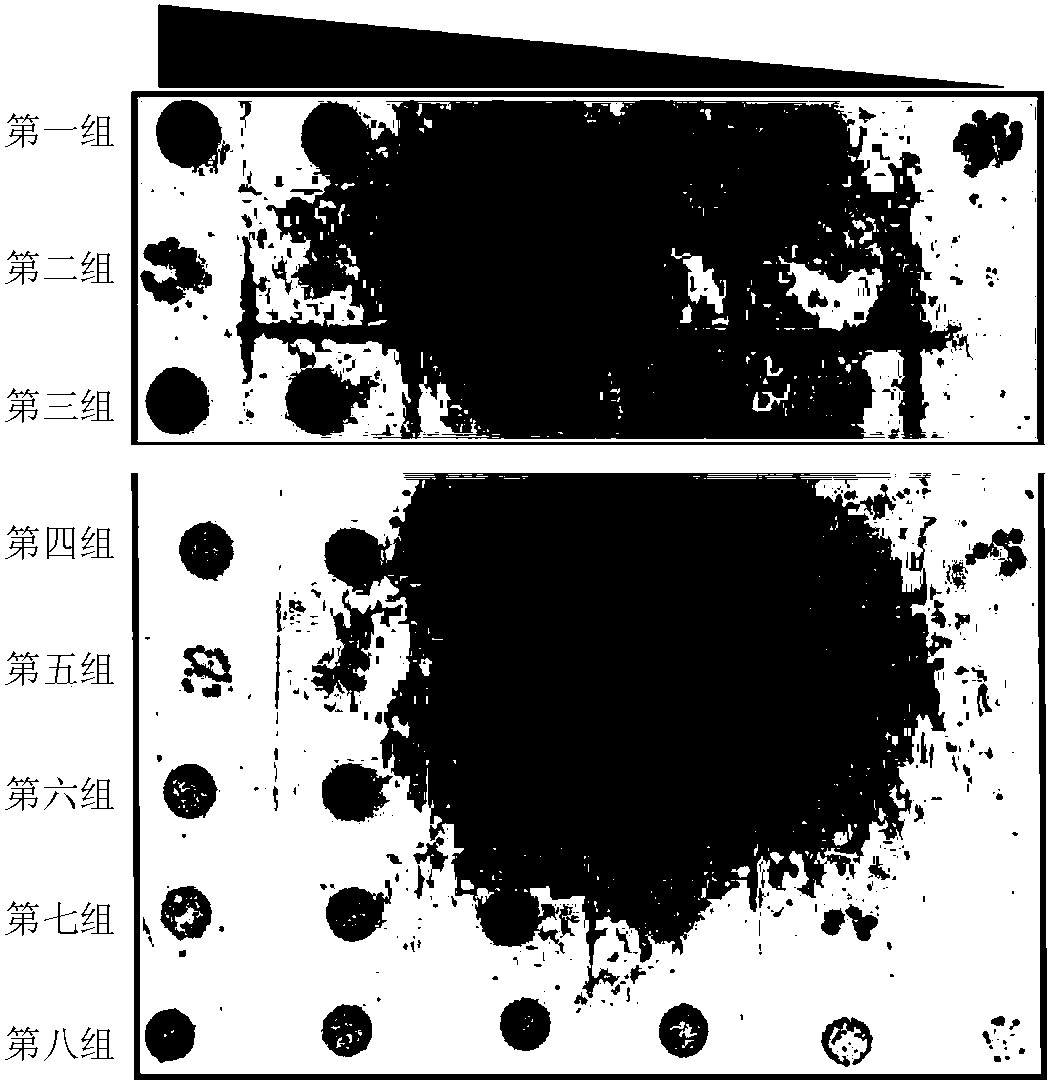
[0107] Example 3. Functional short peptides trigger bacterial self-death by activating TplE protein
[0108] 1. Construction of recombinant plasmid
[0109] 1. Insert the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in sequence 6 of the sequence table between the NcoI and XhoI restriction sites of pET-26b(+) vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET26b-TplE. After sequencing verification, the recombinant plasmid pET26b-TplE has an open reading frame shown in sequence 6 of the sequence listing. The DNA molecule shown in sequence 6 of the sequence listing encodes the protein shown in sequence 7 of the sequence listing. In sequence 7 of the sequence table, the amino acid residues 1-23 constitute the signal peptide (promoting the secretion of the protein into the periplasmic space), and the amino acid residues 24-592 constitute the TplE protein.
[0110] 2. Insert the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in sequence 8 of the sequence list between the NcoI and XhoI restriction sites of the pET-2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com