Antifungal methylobacterium compositions and methods of use
A Methylobacter, Methylobacter oryzae technology, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of not providing complete disease control, resistant varieties and limited options for seed treatment , expensive, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Example 1. PPFM suppression of Fusarium graminearum
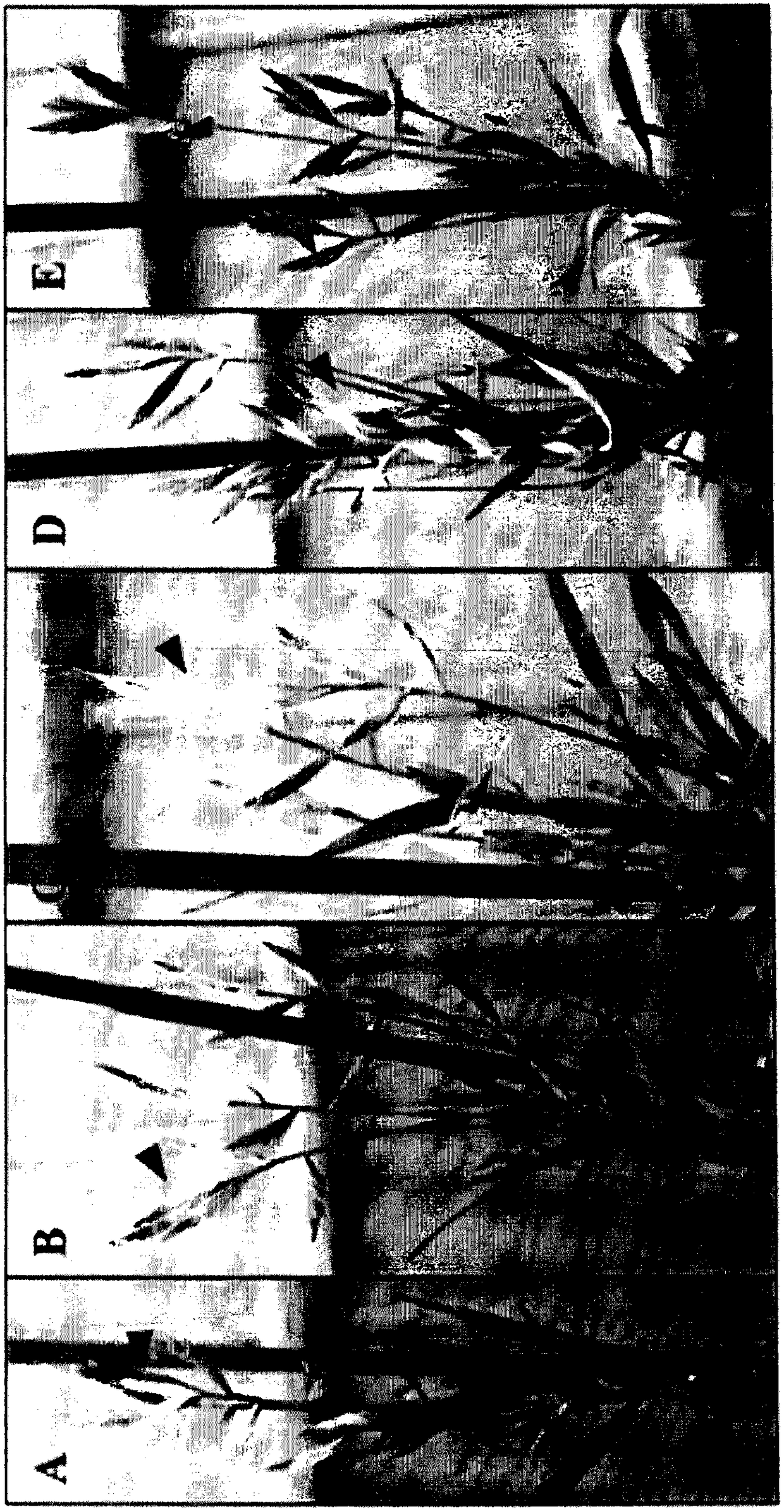
[0090] PPFM cultures for seed treatment were grown in AMS-GP medium modified with 0.2% w / v diatomaceous earth (International Patent Application PCT / US13 / 43722 filed 31 May 2013). Cells were harvested by centrifugation and resuspended in water to approximately 1.3x10 8 Final concentration of CFU / ml. Brachypodium distachyon seeds of the inbred line Bd21-3 were treated in plastic germination boxes by incubation overnight between two sheets of nursery paper saturated with 30 ml of PPFM suspension. During seed treatment, the germination boxes were placed in the dark at 4 °C. Seeds of the control group were similarly treated except that water was applied on the seedling paper.
[0091] The treated seeds were planted in soilless culture medium and allowed to grow in a controlled environment growth chamber (24°C, 50% relative humidity, 200 μmol / m 2 / s light intensity), and the day length is 20h to promote flowering. 42±...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Example 2. Identification of PPFM strains conferring FHB resistance in wheat in growth chamber and field tests
[0101] Head blight (FHB) susceptible wheat variety Bobwhite or another FHB susceptible variety was used for growth chamber studies. For each PPFM isolate to be tested, seeds will be planted without any PPFM treatment and allowed to grow in a growth chamber. Spray the ears of 15 plants with 10 6 or 10 8 cfu / ml of each PPFM strain suspension. Each ear was injected with 10 μl of F. graminearum PH-1 or another virulent F. graminearum isolate (10 5 spores / ml) or water control (mock) (in 0.01% Triton 60 or Tween 20 solution), two ears from each plant were spot-inoculated (Goswami and Kistler, 2005). After inoculation, the plants were placed in a growth chamber at 16°C for 8h (night) and 18°C for 16h (day). In order to ensure the severity of the disease itself, the ears were covered with plastic bags for 48 hours to increase the humidity. The first disease a...
Embodiment 3
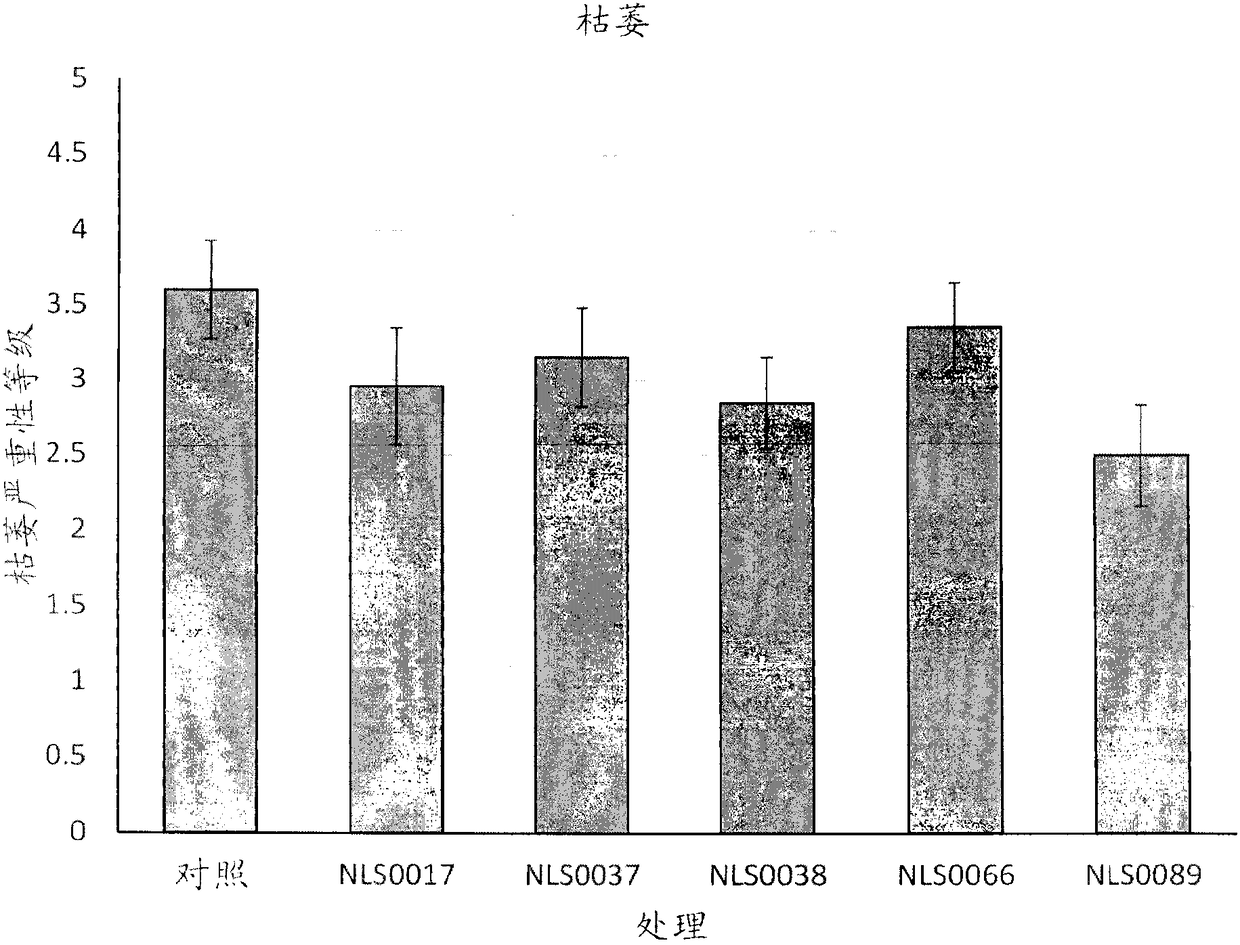
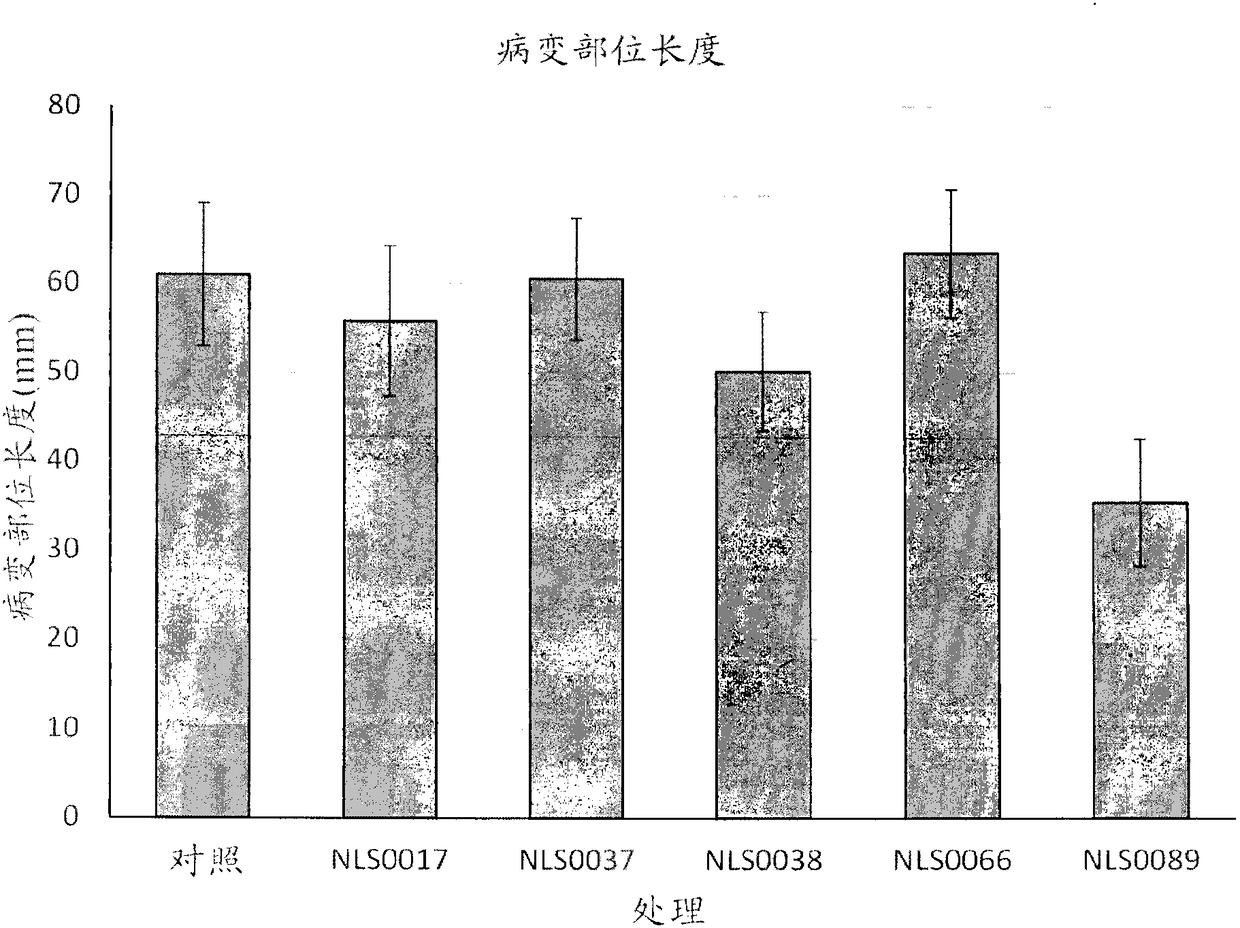
[0110] Example 3. Suppression of Scab in Greenhouse Grown Wheat
[0111] The frozen PPFM concentrate (1x10 8 CFU / mL) was thawed to room temperature. The PPFM concentrate was then vortexed for 10 seconds and 75 μL of each treatment was pipetted into a 15 mL conical tube (Triticum aestivum L., cv. 'Bobwhite) containing 100 spring wheat seeds. To simulate standard industrial seed treatment, 66.8 uL of an agricultural polymer solution prepared by combining 6.1 mL of polymer with 40 mL of deionized water (FloRite 1706 Plantability Polymer, BASF, North Carolina, USA) was added to each treatment tube. Cap the tube and vortex for approximately 90 seconds to coat the seeds well. Kimwipe on the bench for pre-treated seeds before use TM Air dry and keep at room temperature. Use all seeds within one week of treatment. Excess seeds were checked for PPFM concentration and viability by placing 10 seeds in sterile distilled water, vortexing for 10 seconds, and inoculating 100 uL of the r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com