Micro-strip reflective array antenna
A reflect array antenna and microstrip technology, applied in antennas, slot antennas, antenna grounding devices, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient parallelism of the frequency characteristic curve, large cross-polarization component, and high cost, and achieve the parallelism of the unit frequency characteristic curve. Good, good phase shift curve linearity, easy to manufacture and process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0039] Example 1: A microstrip reflectarray antenna with an aperture distribution of 40mm×40mm.
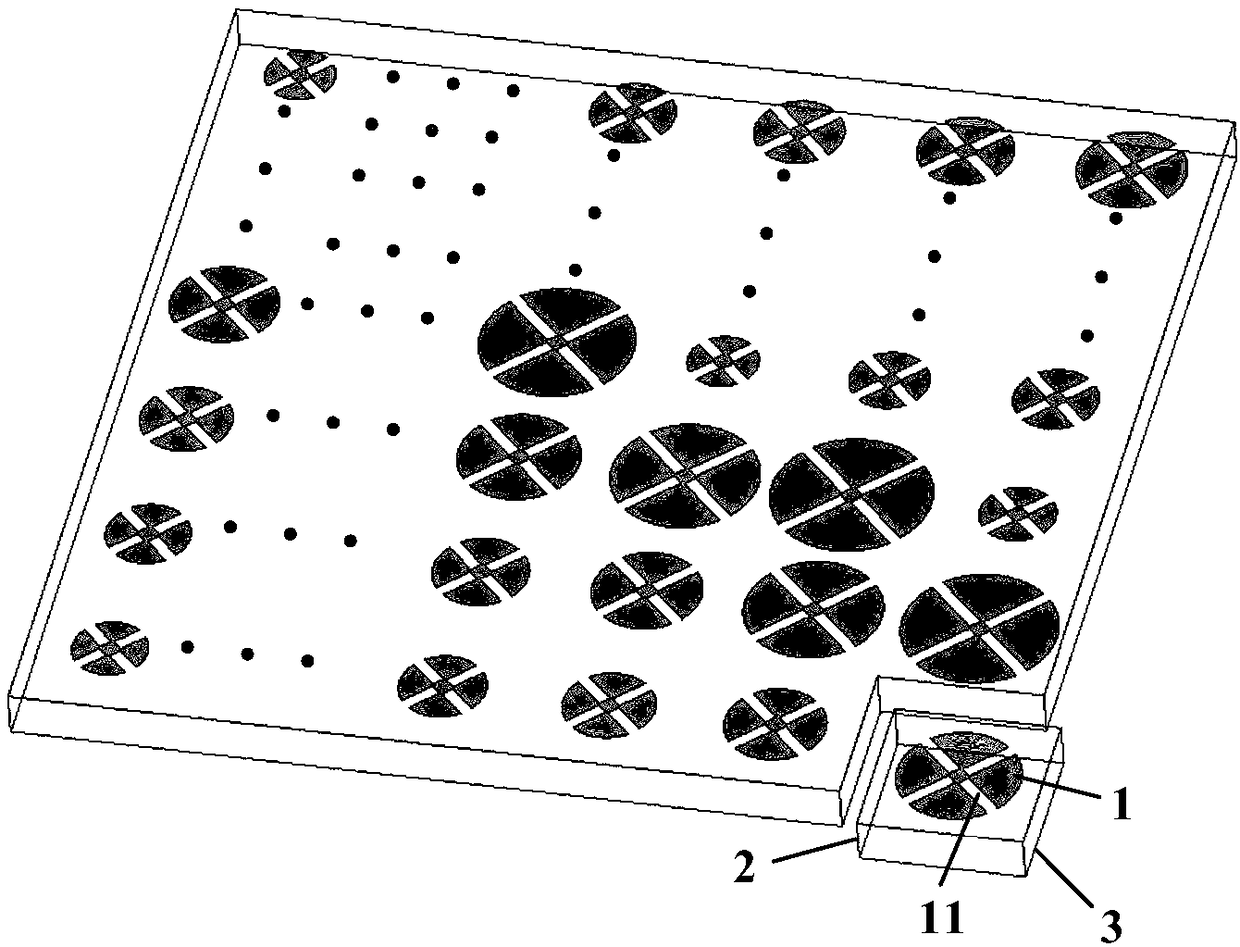
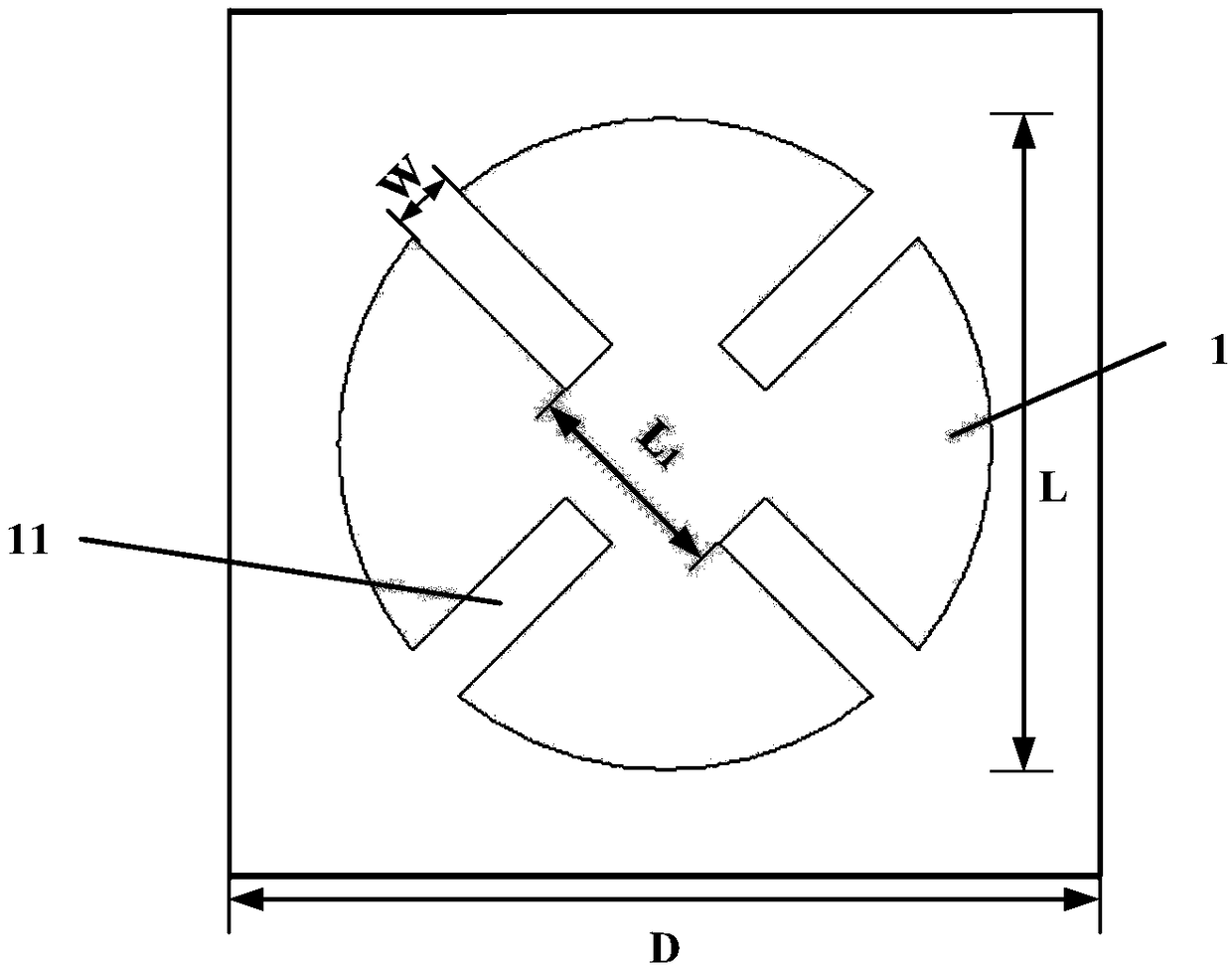
[0040] refer to Figure 4 , in this embodiment, the aperture distribution of the microstrip reflectarray is 40mm×40mm, and it is composed of 100 reflectarray units of 10×10 arranged according to the interval D of 4mm. The diameter L of each unit is different, that is, it is set within 1 mm to 4 mm according to the change curve of reflection phase and diameter, the width W of each slit is 0.3 mm, and the distance L between two slits 1 is 0.4mm; the relative permittivity ε of the dielectric substrate is 3.66, and the thickness h is 1.118mm; the coordinates of the reflective array unit (x i ,y i ,z i ) range of values: -4.5D≤x i ≤4.5D, -4.5D≤y i ≤4.5D, zi =0, where D is the arrangement period of each unit; incident wave angle Reflected wave angle
example 2
[0041] Example 2: Microstrip reflectarray antenna with an aperture distribution of 28mm×28mm
[0042] refer to Figure 5 In this example, the microstrip reflectarray antenna with a caliber distribution of 28mm×28mm is composed of 64 reflectarray units of 8x8 arranged according to the interval D of 3.5mm. The diameter L of each unit is different, that is, it is set within 0.875mm to 3.5mm according to the change curve of reflection phase and diameter, the width W of each slit is 0.22mm, and the distance L between two slits 1 is 0.375mm; the relative permittivity ε of the dielectric substrate is 3.4, and the thickness h is 0.25mm; the coordinates of the reflective array unit (x i ,y i ,z i ) range of values: -3.5D≤x i ≤3.5D, -3.5D≤y i ≤3.5D, z i =0, where D is the arrangement period of each unit; incident wave angle Reflected wave angle
example 3
[0043] Example 3: Microstrip reflectarray antenna with an aperture distribution of 60mm×60mm
[0044] refer to Figure 6 , in this embodiment, the aperture distribution of the microstrip reflectarray is 60mm×60mm, and it is composed of 12×12 100 reflectarray units arranged according to the interval D of 5mm. The diameter L of each unit is different, that is, according to the change curve of reflection phase and diameter, it is set within 1.25mm~5mm, the width W of each slit is 0.36mm, and the distance L between two slits 1 is 0.5mm; the relative permittivity ε of the dielectric substrate is 3.8, and the thickness h is 2mm; the coordinates of the reflective array unit (x i ,y i ,z i ) range of values: -5.5D≤x i ≤5.5D, -5.5D≤y i ≤5.5D, z i =0, where D is the arrangement period of each unit; incident wave angle Reflected wave angle
[0045] Effect of the present invention can be further illustrated by following simulation:
[0046] 1. Simulation conditions
[0047] I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com