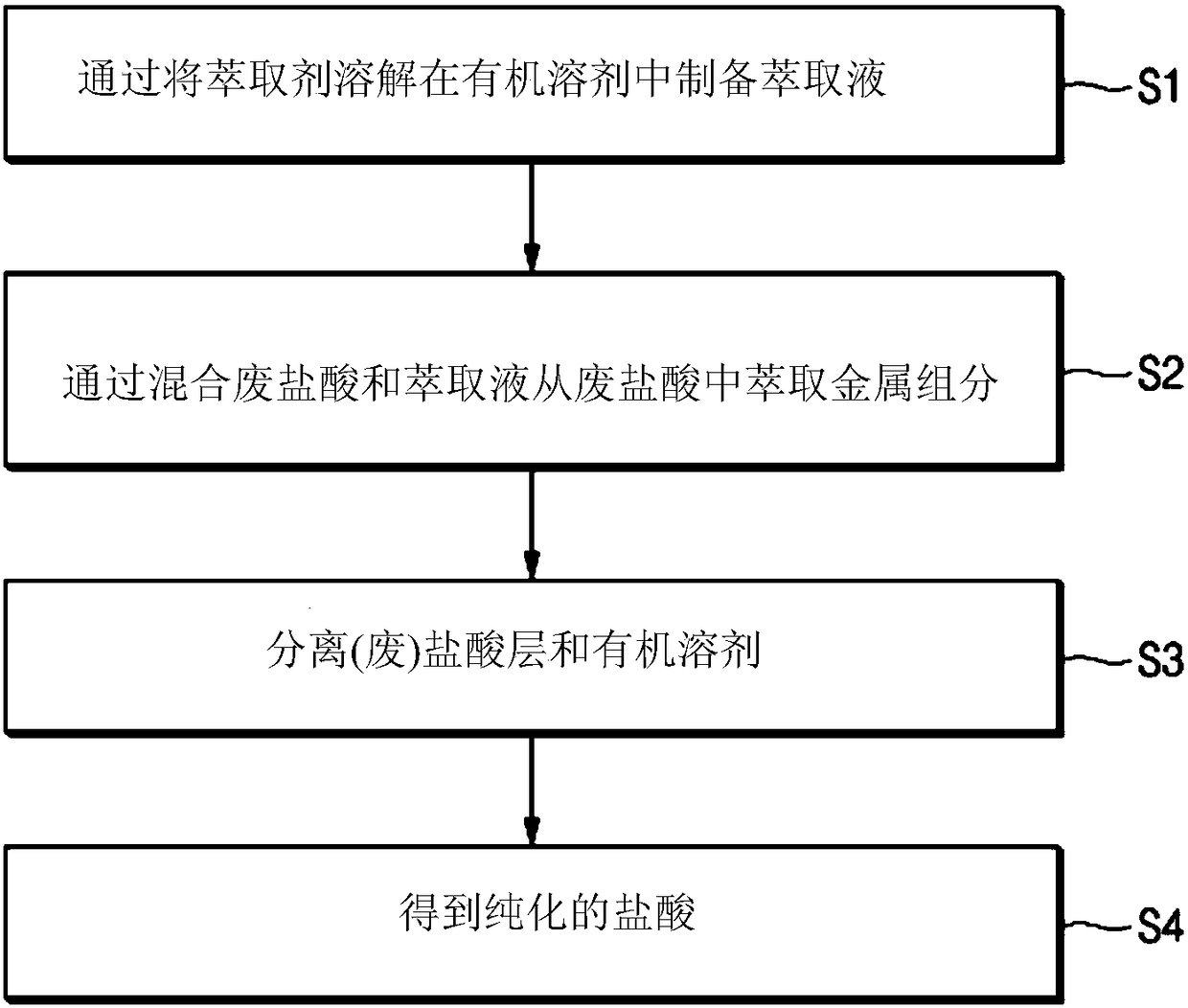
Method for purifying waste hydrochloric acid
A technology for waste hydrochloric acid and hydrochloric acid, applied in chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, preparation of iron compounds, etc., can solve problems such as energy consumption, complex process steps, difficulties, etc., to improve cycle efficiency, reduce manufacturing costs, and simplify processes. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0116] The concentration (S0) of iron (Fe) ions contained in 100 ml of waste hydrochloric acid was measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry.
[0117] Subsequently, trioctylamine (iron (Fe) ion component contained in waste hydrochloric acid: extractant = 1 mol: 40 mol) as an extractant was dissolved in 100 ml of toluene as an organic solvent to prepare an extract (S1 ).
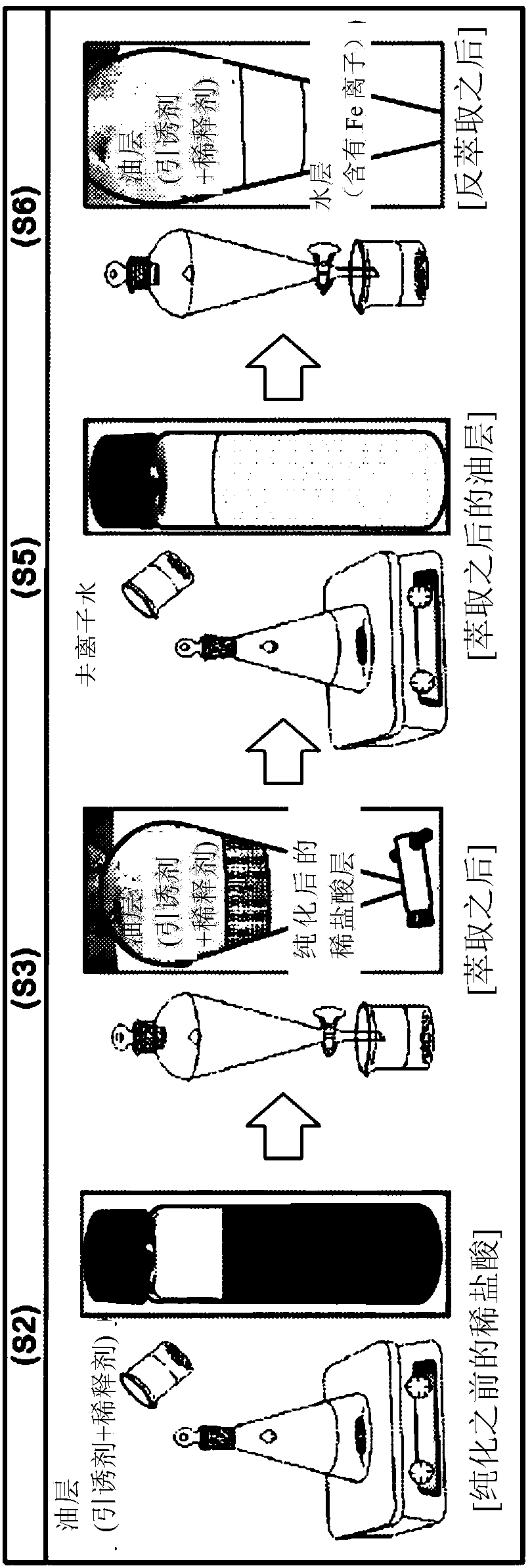
[0118] Next, the extract is added to 100 m of waste hydrochloric acid, and the metal components contained in the waste hydrochloric acid are extracted with an organic solvent while stirring at a speed of 200 rpm at normal temperature for 60 seconds (S2).
[0119] After stirring to reach equilibrium, the mixed liquid of organic solvent and waste hydrochloric acid is added to the separator, shaken for about 20 seconds, and then left to stand to separate (separate) the mixed liquid into organic solvent and waste hydrochloric acid layers containing metal components ( S3).
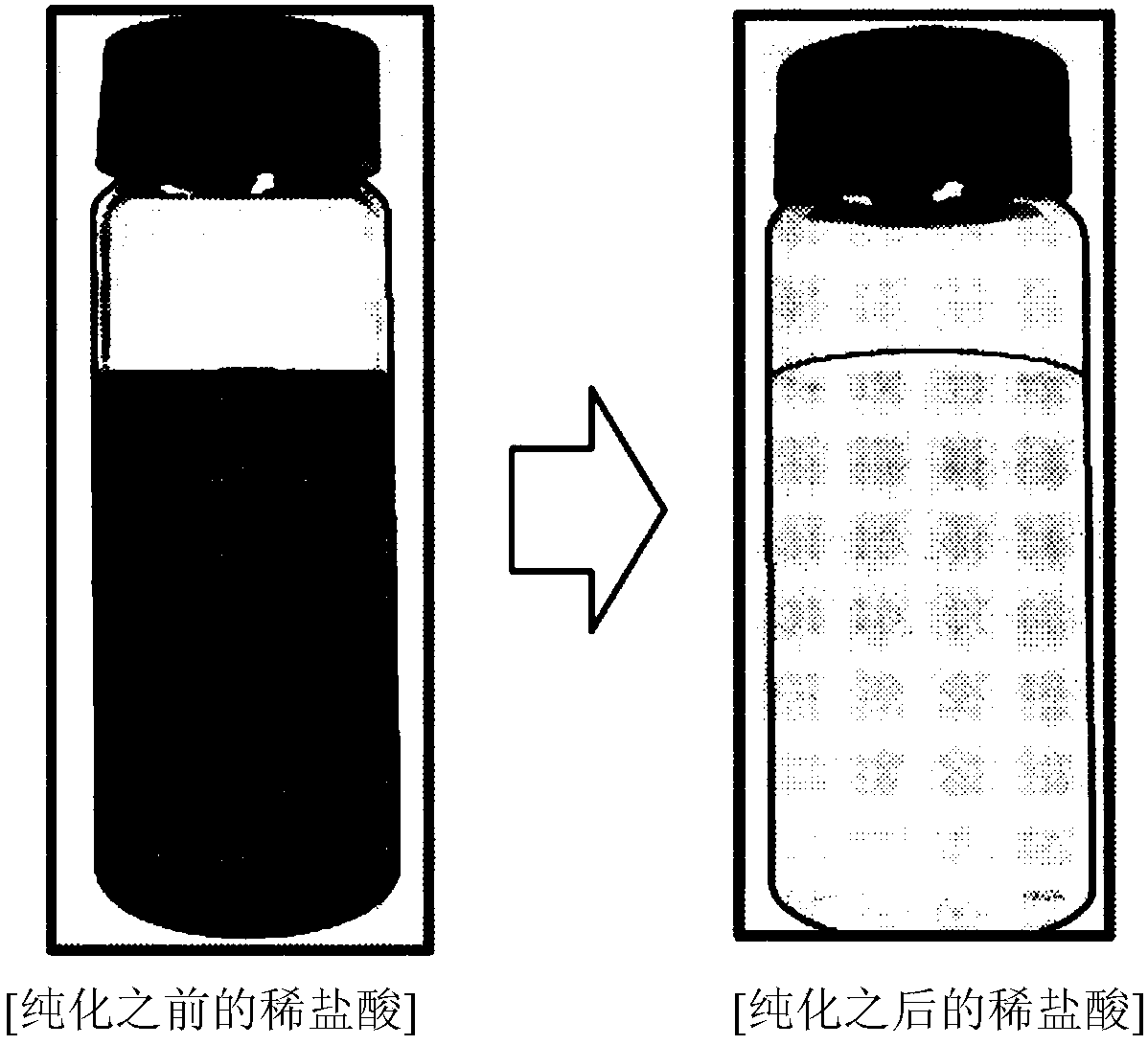
[0120] Subsequently, purified h...
Embodiment 2
[0124] The purified hydrochloric acid was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the amount of the extractant in step S1 of Example 1 was such that the molar ratio of Fe: extractant contained in the waste hydrochloric acid was 1:60. The residual metal concentration in the purified hydrochloric acid was measured, and the results are shown in Table 1 below.
Embodiment 3
[0126] Except that cyclohexane was used instead of toluene in Example 1, purified hydrochloric acid was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1. The residual metal concentration and TOC in the purified hydrochloric acid were measured, and the results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2 below.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com