Watermelon stick seed gene SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) molecular marker as well as screening method and application thereof
A technology of molecular markers and watermelons, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of unobtained molecular markers, improve accuracy and selection efficiency, accelerate improvement process, and scientifically The effect of practical detection and identification technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Determination of the sticky seed gene of watermelon seeds and the development of molecular markers
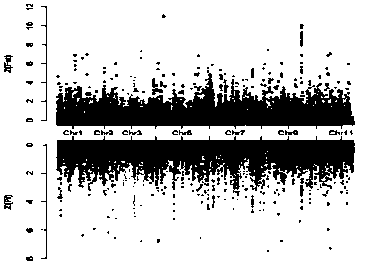
[0035] Simplified genome sequencing of different types of watermelon materials, combined with differences in population polymorphisms to determine the selected regions between populations, and obtaining chromosomal intervals related to sticky-seeded watermelon types, using deep resequencing of sticky-seeded watermelon materials and common watermelon materials The SNP sites in the target chromosome interval were screened, and the CAPS / dCAPS molecular marker primers were designed, and then the CAPS / dCAPS molecular marker primers and watermelon genomic DNA were used for PCR amplification, and finally the amplified products were digested and verified by electrophoresis.
[0036] Specific steps are as follows:
[0037] (1) Choose different types of watermelon materials, including sticky watermelon, common watermelon and wild watermelon;
[0038] (2) Using the meth...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2: Watermelon DNA Molecular Marker Analysis
[0045] 1. Select 5 parts of sticky watermelon, 5 parts of ordinary watermelon and 5 parts of wild watermelon, and use the CTAB method to extract the total DNA of watermelon leaves. Three parallel experiments are set up for each sample. The specific steps are as follows:
[0046] (1) Put 1 g of fresh leaves into a mortar, add liquid nitrogen to grind into powder, then transfer to a centrifuge tube with 1 ml of CTAB extraction solution, mix the two thoroughly, and then place in a constant temperature water bath at 65°C 60 min, during which the mixture was inverted 2 to 3 times;
[0047] (2) After taking it out from the water bath, centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 1 min;
[0048] (3) Take the supernatant and put it in another centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (24:1, V / V), invert gently to mix well;
[0049] (4) Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 5 min, and take the supernatant;
[0050](5) Add 0...
Embodiment 3
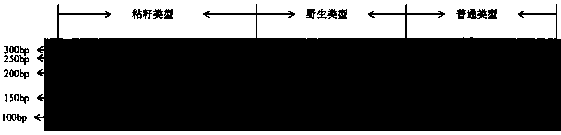
[0071] Embodiment three: identify and assist the germplasm type of screening watermelon
[0072] Carry out Npr372 molecular marker in 5 parts of sticky watermelon, 5 parts of wild watermelon and 5 parts of common watermelon genotype identification after carrying out embodiment 2, check the distribution situation of two genotypes of Npr372 molecular marker in 93 different types of watermelon materials .
[0073] Table 1 Identification and verification of NPr372 in 93 different types of watermelon materials
[0074] material code
breed name
Germplasm type
NPr372
S001
PI 248178
Sticky Seed Watermelon
A
S002
PI 494527
Sticky Seed Watermelon
A
S003
PI 559992
Sticky Seed Watermelon
A
S004
PI 559993
Sticky Seed Watermelon
A
S005
PI 559994
Sticky Seed Watermelon
A
S006
PI 559996
Sticky Seed Watermelon
A
S007
PI 559999
Sticky Seed Watermelon
A
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com