High-stability modified Y-type molecular sieve and preparation method thereof
A molecular sieve and modification technology, applied in molecular sieve catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve the problem of low retention rate of crystallinity and specific surface area, poor thermal and hydrothermal stability, and retention of zeolite crystals. low coke selectivity, high thermal and hydrothermal stability, and high stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
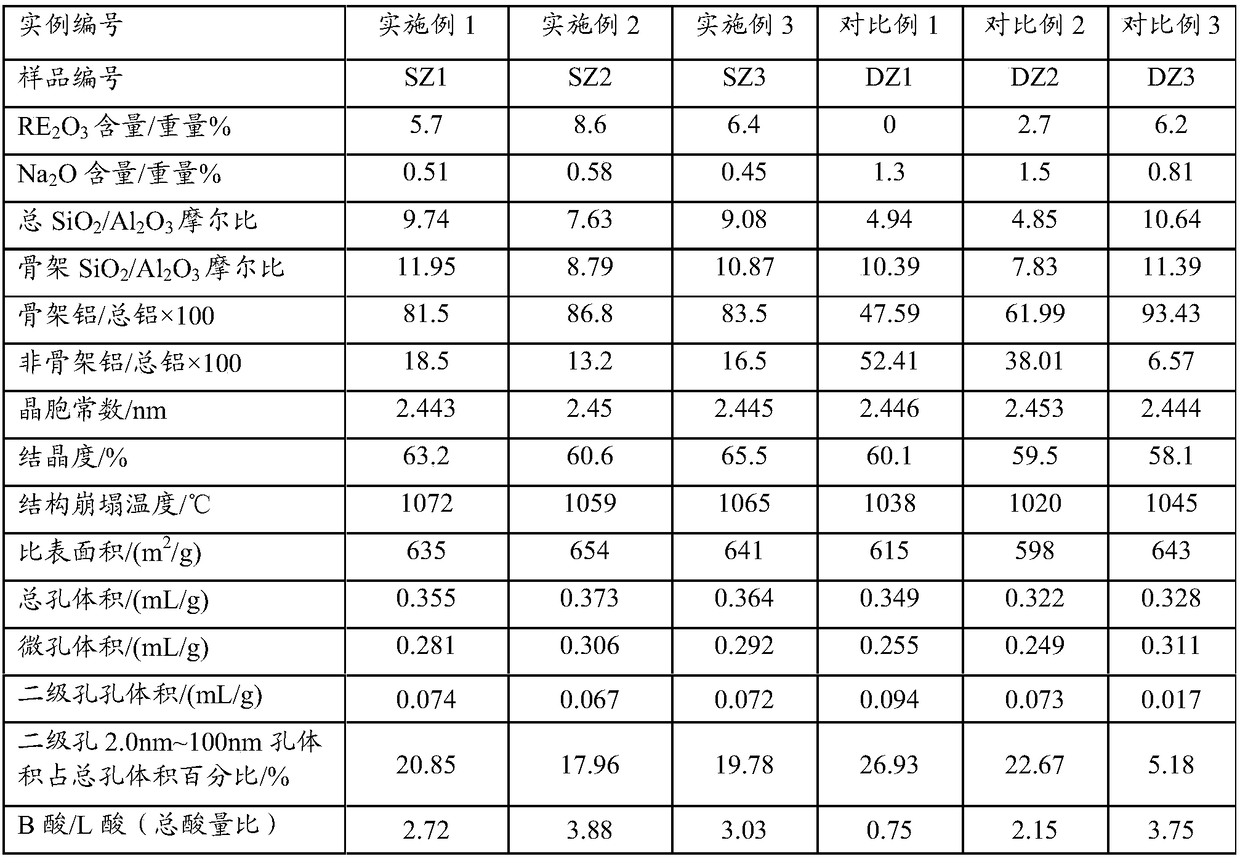
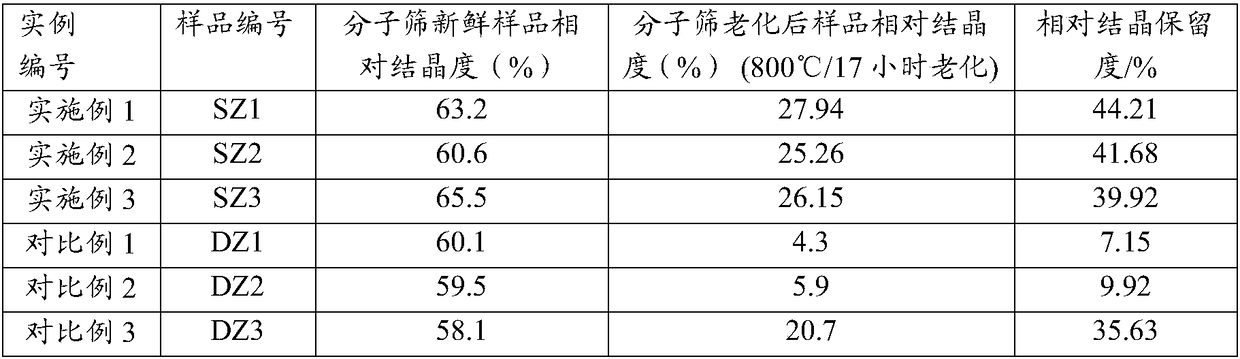
[0033] The preparation method of the modified Y-type molecular sieve provided by the invention, a kind of embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0034] (1) carry out ion exchange reaction with NaY molecular sieve (also claiming NaY zeolite) and rare earth solution, filter, wash, obtain the Y-type molecular sieve of the conventional unit cell size containing rare earth that sodium oxide content reduces; Said ion exchange is usually stirred, Exchange at a temperature of 15-95°C, preferably 65-95°C, for 30-120 minutes;
[0035] (2) The Y-type molecular sieve with the rare earth-containing conventional unit cell size whose sodium oxide content is reduced is roasted for 4.5 to 7 hours at a temperature of 350 to 480° C. in an atmosphere containing 30 to 90% by volume of water vapor, and dried to obtain water A Y-type molecular sieve with a reduced unit cell constant content of less than 1% by weight; the unit cell constant of the Y-type molecular sieve with a reduced unit cell ...
Embodiment 1
[0044] Get 2000 grams of NaY molecular sieves (calculated on a dry basis) and add them to 20 liters of decationized aqueous solution and stir to make them evenly mixed. Add 600ml of RE(NO 3 ) 3 Solution (rare earth solution concentration is RE 2 o 3 Calculated as 319g / L), stirred, heated to 90-95°C and kept for 1 hour, then filtered, washed, and the filter cake was dried at 120°C to obtain a unit cell constant of 2.471nm and a sodium oxide content of 7.0% by weight. 2 o 3 A Y-type molecular sieve with a total rare earth content of 8.8% by weight is then calcined for 6 hours at a temperature of 390°C in an atmosphere containing 50% by volume of water vapor and 50% by volume of air to obtain a Y-type molecular sieve with a unit cell constant of 2.455nm. After that, carry out Drying process, so that its water content is less than 1% by weight, and then according to SiCl 4 : Y-type molecular sieve (dry basis) = 0.5: 1 weight ratio, feed SiCl vaporized by heating 4 Gas, at a t...
Embodiment 2
[0047]Get 2000 grams of NaY molecular sieves (on a dry basis) and add them to 25 liters of decationized aqueous solution and stir to make them evenly mixed. Add 800 ml of RECl 3 solution (in RE 2 o 3 The calculated solution concentration is: 319g / L), stirred, heated up to 90-95°C for 1 hour, then filtered, washed, and the filter cake was dried at 120°C to obtain a unit cell constant of 2.471nm and a sodium oxide content of 5.5% by weight , with RE 2 o 3 A Y-type molecular sieve with a total rare earth content of 11.3% by weight is then calcined at a temperature of 450°C and 80% water vapor for 5.5 hours to obtain a Y-type molecular sieve with a unit cell constant of 2.461nm, and then dried to reduce its water content at 1 wt%, then follow SiCl 4 : Y-type zeolite = 0.6:1 weight ratio, feed SiCl vaporized by heating 4 The gas was reacted for 1.5 hours at a temperature of 480° C., and then washed with 20 liters of deionized water, and then filtered to obtain a modified Y-typ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com