Construction method of gene knockout CHO cell line and application of gene knockout CHO cell line in expression of therapeutic recombinant proteins
A recombinant protein and gene knockout technology, applied in the direction of anti-receptor/cell surface antigen/cell surface determinant immunoglobulin, anti-animal/human immunoglobulin, and other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, etc. Reduced cell growth rate, blocked cell line selection process, slowed down cell mitosis, etc., to achieve the effect of improving expression yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
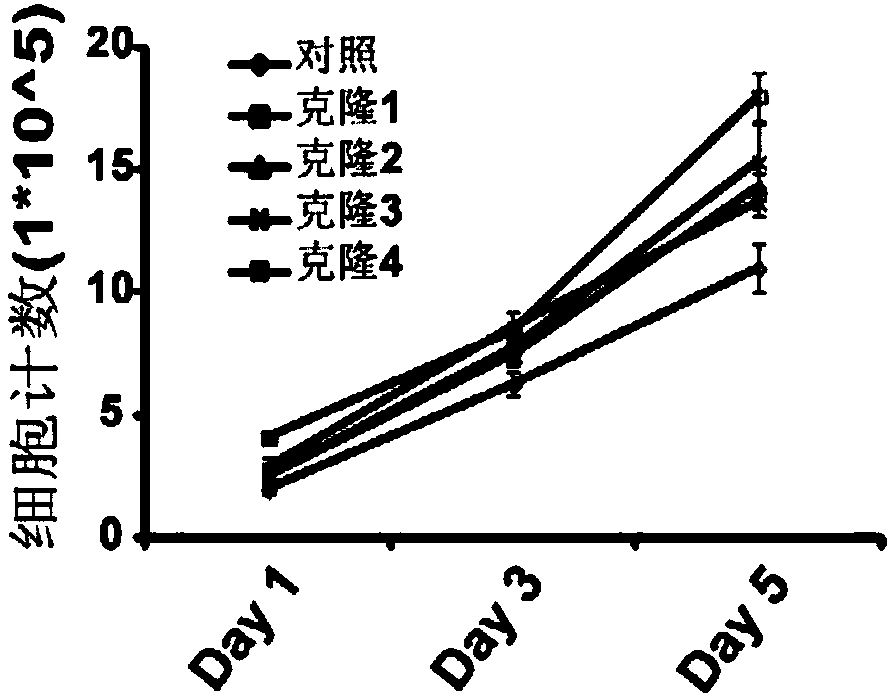
[0027] Embodiment 1, the preparation of CHO-K1-sgRNA3 cell
[0028] 1. sgRNA design
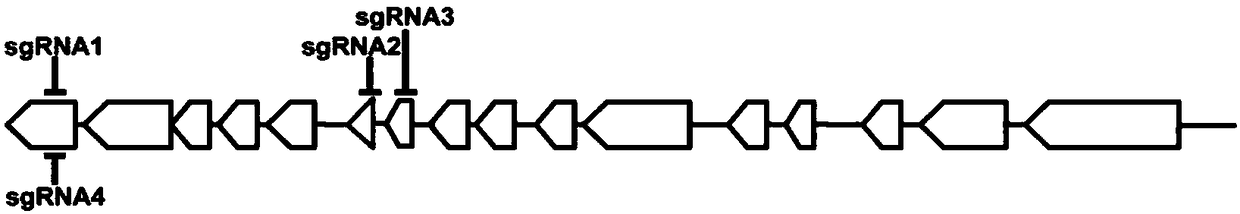
[0029] The open reading frame of the CYLD gene in CHO cells contains 16 exons. According to the CRISPR-Cas9 technical requirements and sequence homology comparison analysis, four sgRNAs (sgRNA1-4) were screened and designed, and sgRNA1 and sgRNA4 simultaneously targeted Exon 1, sgRNA2 and sgRNA3 target exons 6 and 7, respectively. The target sequences of the four sgRNAs are shown in Table 1 below, and the positions on the CYLD exons are shown in the results figure 1 shown.
[0030] Table 1 Four sgRNA target sequences
[0031] name
Sequence (5'-3')
sgRNA1
CCAGGAGTTGTACGCTTCAG
sgRNA2
TATGGGGTTATCCGTTGGAT
sgRNA3
GCTGTACGGACGGAACTTTC
sgRNA4
CCTCTGAAGCGTACAACTCC
[0032] 2. Construction of recombinant plasmids
[0033] Further, the DNA sequences in Table 1 and their complementary pairs were synthesized according to the requirements...
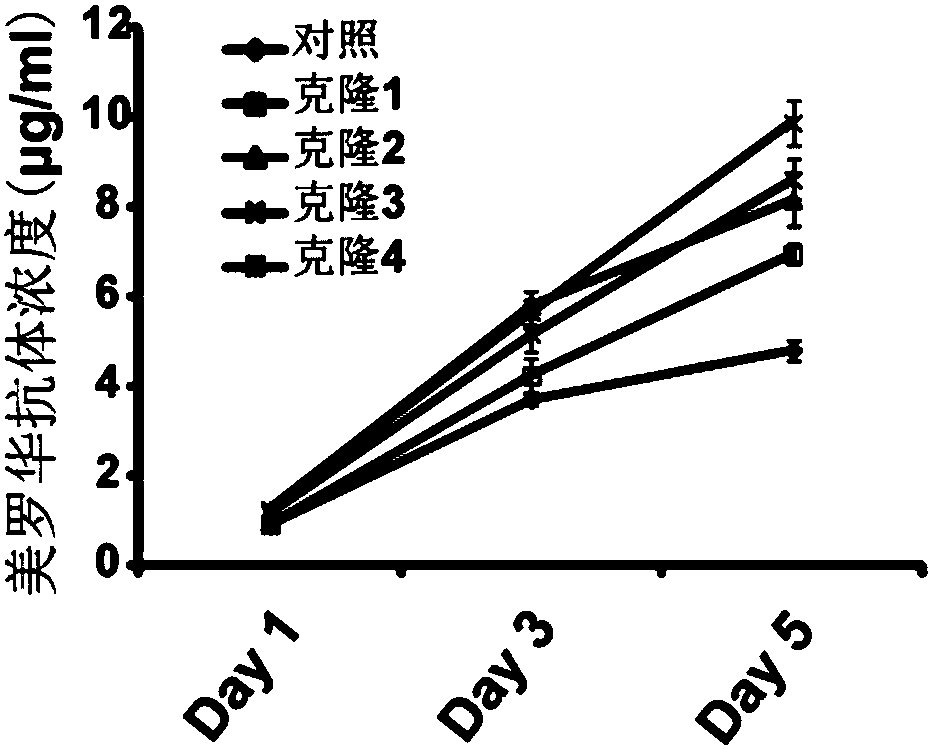
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2, the preparation of CHO-IgG-sgRNA3 cell
[0049] A CHO-K1 suspension cell stably expressing anti-EGFR humanized antibody L4H3 was used to verify the effect of inhibiting CYLD on antibody expression. The cell construction process for stably expressing the anti-EGFR humanized antibody is as follows:
[0050] 1. Recombine the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in sequence 7 of the sequence listing between the HindIII and NotI restriction sites of the pcDNA-3.3 vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pcDNA3.3-L4.
[0051] 2. The complete sequence 8 of the sequence listing was recombinantly cloned between the HindIII and NotI restriction sites of the pOptiVEC vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pOptiVEC-H3.
[0052] 3. The recombinant plasmid pcDNA3.3-L4 and the recombinant plasmid pOptiVEC-H3 were co-transfected into CHO-K1 cells, and the recombinant cells stably expressing the heavy and light chains of the antibody were screened and domesticated into su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com