Method for tracking depth of sound source autonomously in real time at deep sea under lower signal-to-noise ratio condition
A low signal-to-noise ratio, real-time tracking technology, applied in the fields of marine engineering, sonar, and underwater acoustic engineering, can solve the problem that the sound source depth tracking algorithm cannot work independently
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
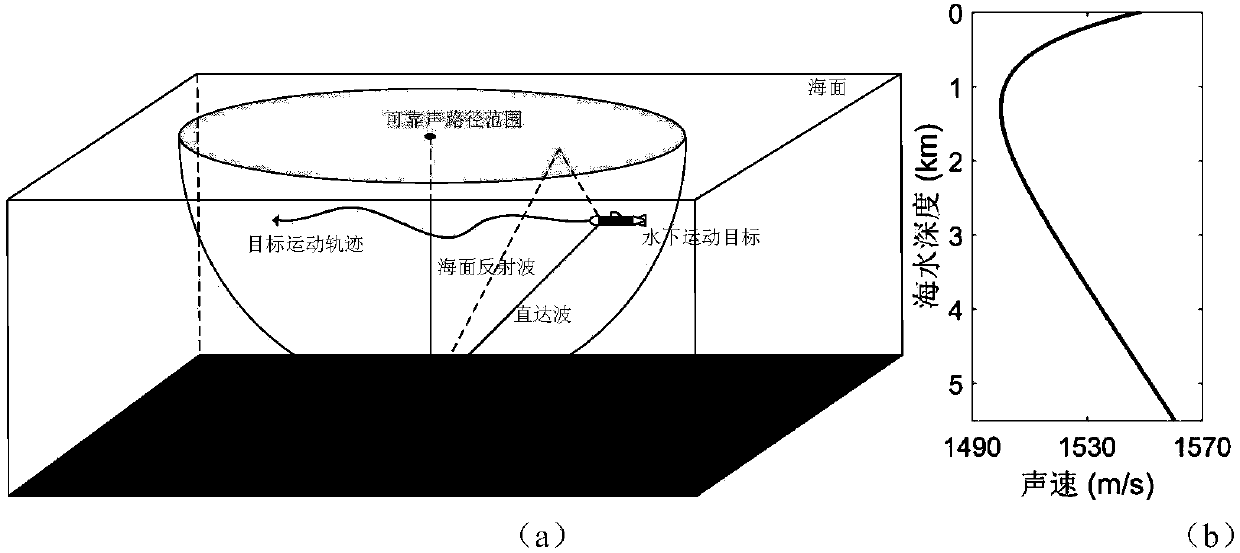
[0113] refer to figure 1 . Underwater acoustic channel modeling: the sound velocity profile of the simulation environment is a typical Munk sound velocity profile, the sea depth of the simulation environment is 5500m, the critical depth is 4800m, the seabed parameters are sound velocity 1600m / s, density 1.65g / cm 3 , the absorption loss is 0.1dB / λ, where λ is the wavelength. The receiving array is a 16-element vertical line array, the array element spacing is 5m, and the depth of the array center is 3700m.
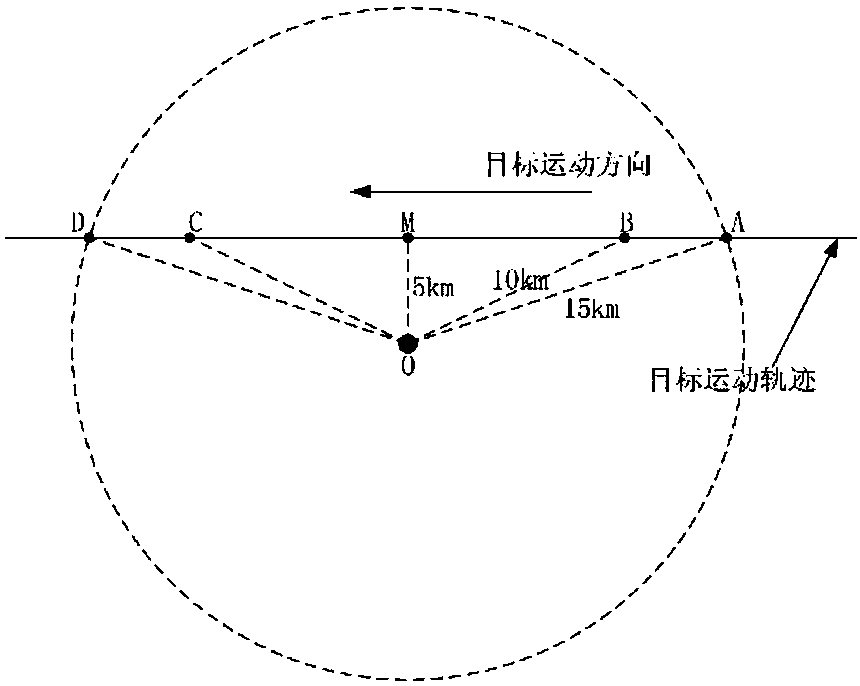
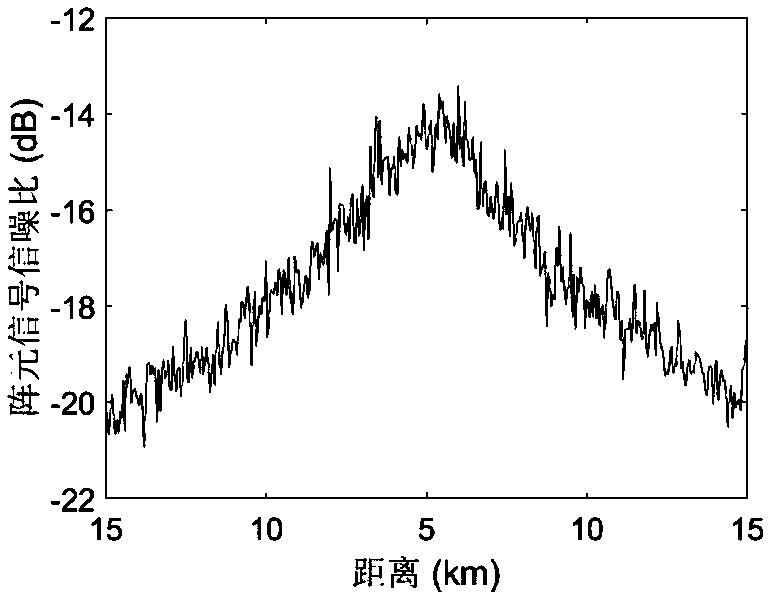
[0114] refer to figure 2 . Sound source motion modeling: The sound source moves from far to near, and the sound source depth tracking starts at 15km (point A). The horizontal distance from the nearest passing point of the sound source to the submerged buoy is 5km. After that, the sound source moves from near to far, and the tracking ends at 15km (point D). From point A to point B, the depth of the sound source is 100m; from point B to point C, the depth of the sound ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com