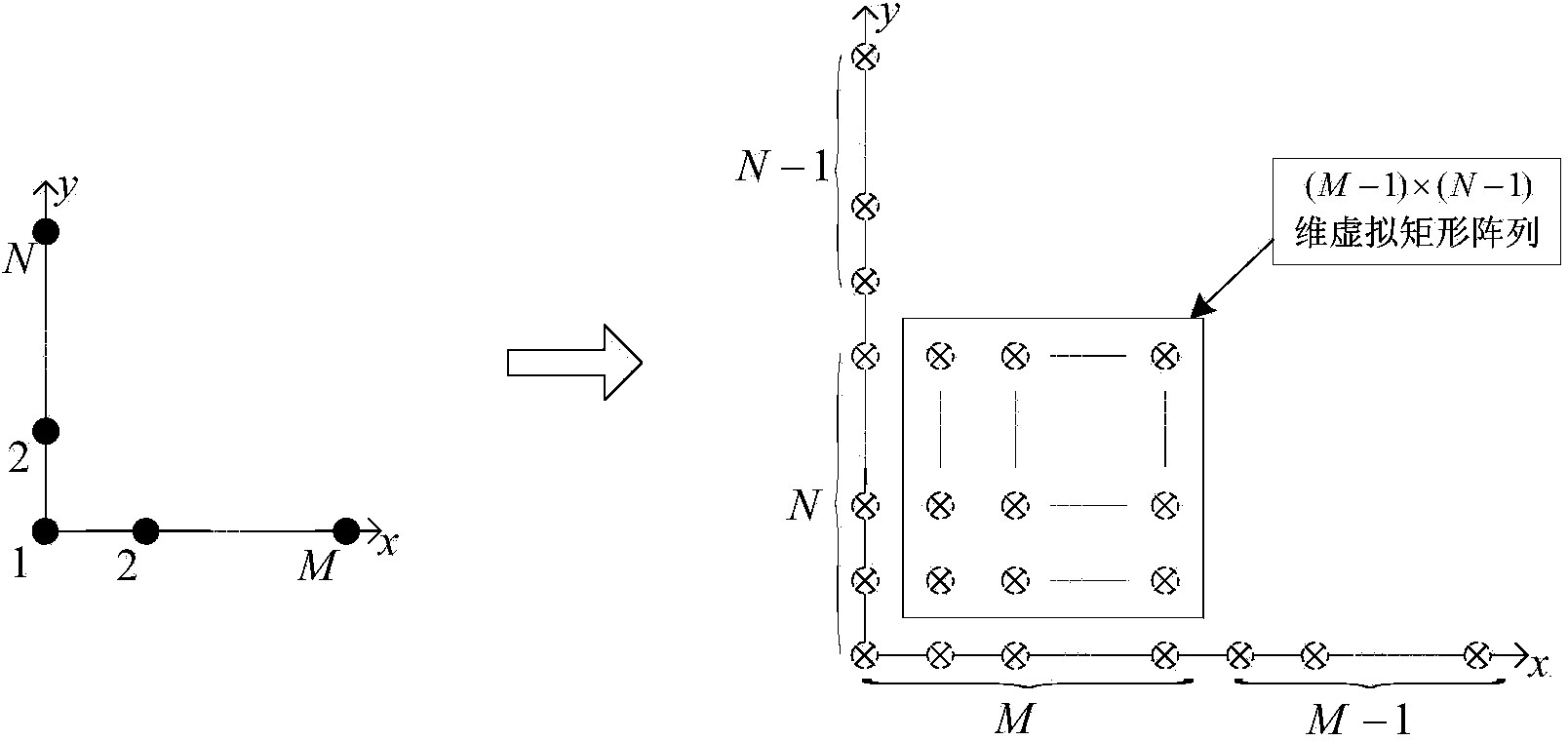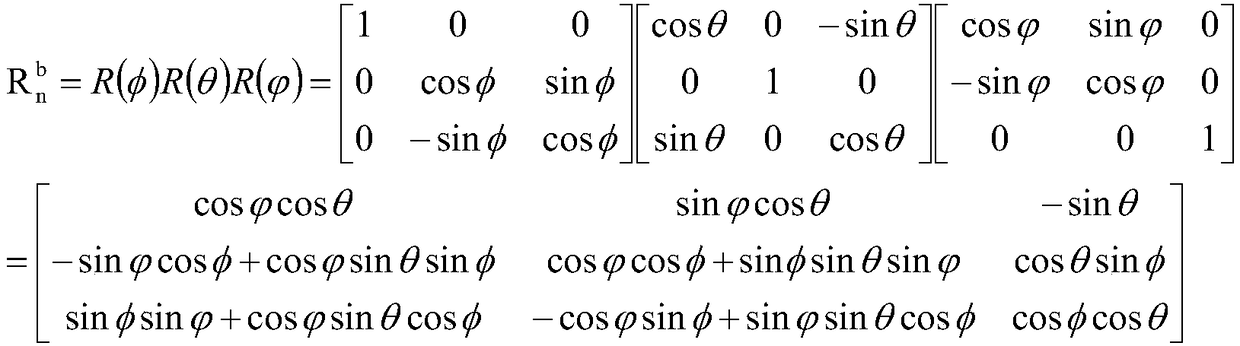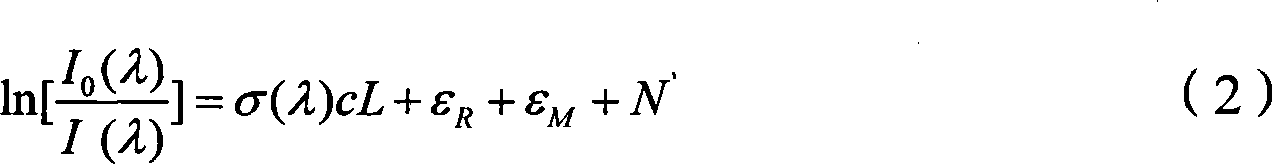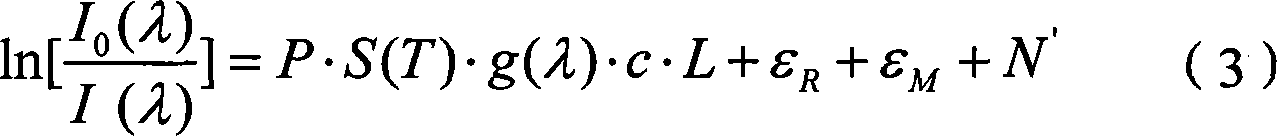Patents
Literature
128results about How to "Easy to process in real time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Self-adaptive low-illuminance or non-uniform-brightness image enhancement method
ActiveCN104156921AImprove processing efficiencyEasy to process in real timeImage enhancementIlluminanceColor saturation
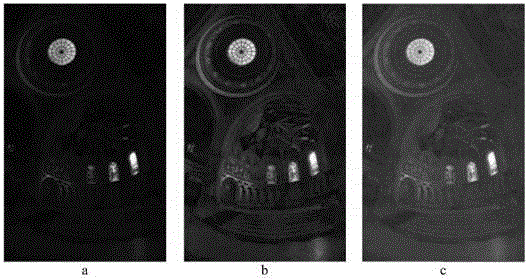
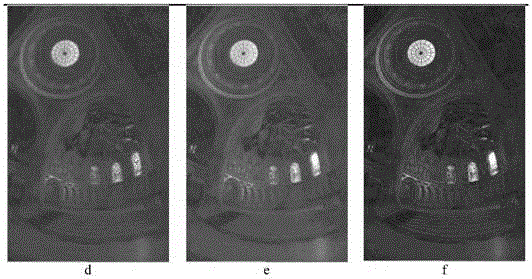
The invention relates to a self-adaptive low-illuminance or non-uniform-brightness image enhancement method. The method comprises the following steps: 1), preprocessing is performed on a low-illuminance and non-uniform-brightness image, wherein the preprocessing includes brightness preprocessing on the low-illuminance and non-uniform-brightness image, and edge enhancement is performed on the image after brightness preprocessing, so that the preprocessed image is obtained; 2), region segmentation is performed according to the brightness of the preprocessed image, corresponding mapping functions are selected according to the different characteristics of all segmented regions and corresponding self-adaptive brightness enhancement is performed; 3), saturation enhancement processing is performed on the image subjected to self-adaptive brightness enhancement segment by segment through the change characteristics of initial saturation and brightness. According to the invention, the steps are adopted to process the image, therefore, the color saturation of the image is improved, the image is enabled to be bright in color and have a better visual effect. The self-adaptive image enhancement method can be widely popularized in the fields of biomedicine, real-time monitoring, satellite remote sensing and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
True color high definition night vision imaging method
InactiveCN107563971AHigh resolutionPreserve high-frequency information of brightness changesImage enhancementTelevision system detailsNight visionColor image
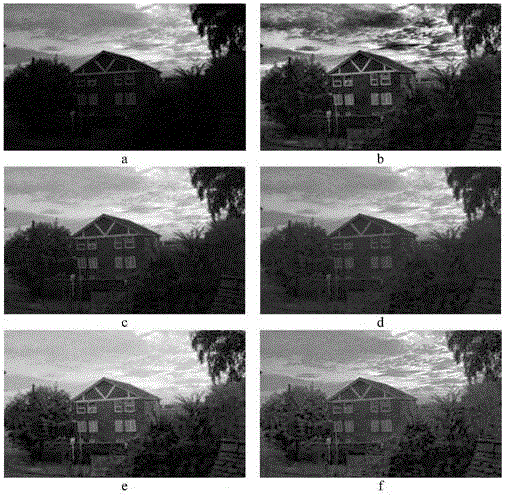
An existing night vision imaging method is hard to obtain a true color high definition night vision image; the true color high definition night vision imaging method can solve said problems, and is featured by comprising the following steps: obtaining a high resolution gray scale image and a low resolution high signal to noise ratio color image of the same scene; using the low resolution high signal to noise ratio color image to colorize the high resolution gray scale image so as to obtain a true color high definition night vision image. Compared with the prior arts, the method can greatly reduce the imaging system cost, and can improve the color night vision imaging quality.
Owner:四川精视科技有限公司
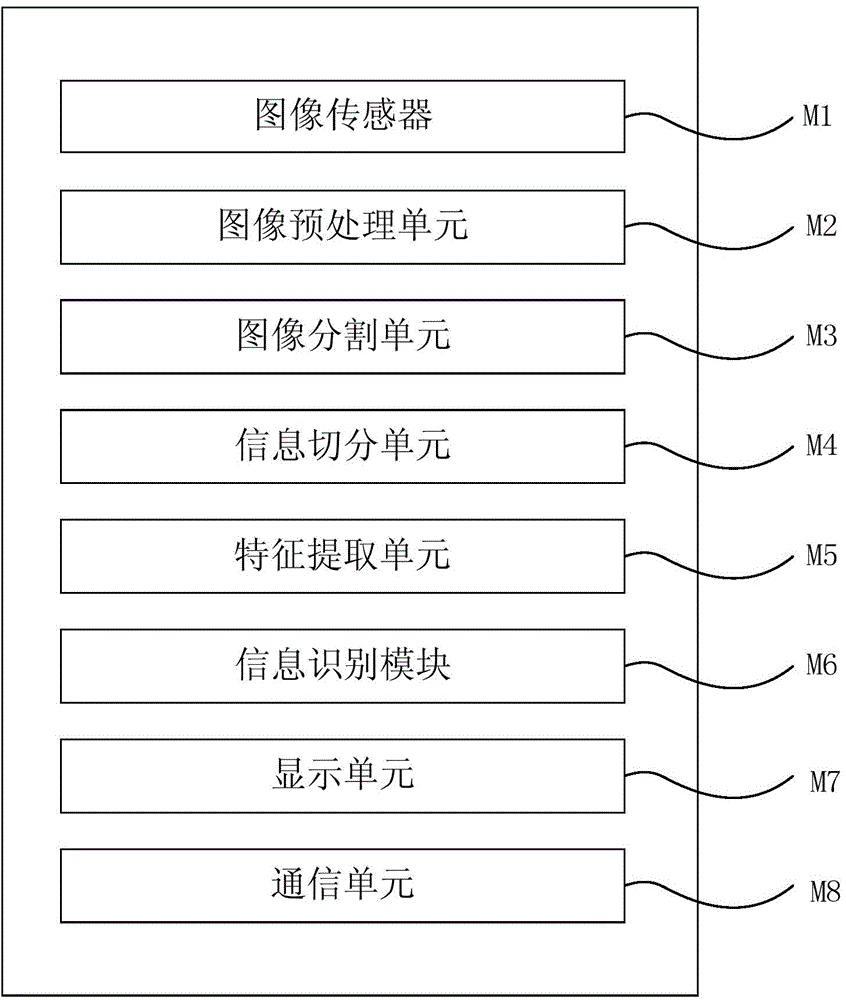
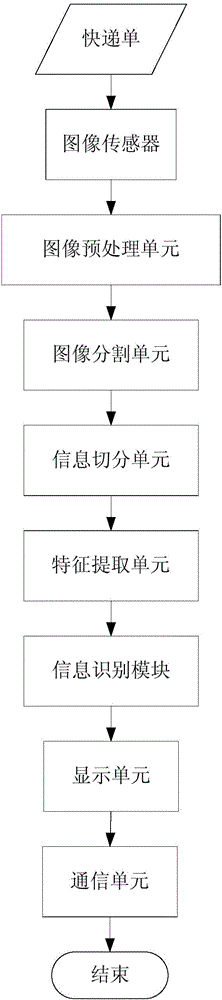
Express bill information identification system and express bill information identification method
The invention relates to an express bill information identification system and an express bill information identification method. The system comprises an image processing module used to acquire and preprocess an express bill image, an information extraction module used to extract the features of the express bill image, an information identification module used to identify numeric information, text information and graphic information, and a display module used to display an information identification result and derivative information. By adopting the system and the method of the invention, the labor efficiency of the express industry is improved, the labor force is liberated greatly, the labor cost and transport cost of the express industry are lowered, the material cost of the express industry is lowered, the business boundary of express enterprises is expanded, and the quality of express service is improved greatly.
Owner:秦志勇
Multi-target positioning method of bistatic multi-input multi-output radar
InactiveCN102135617AAvoid decompositionFast convergenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti inputComputation complexity
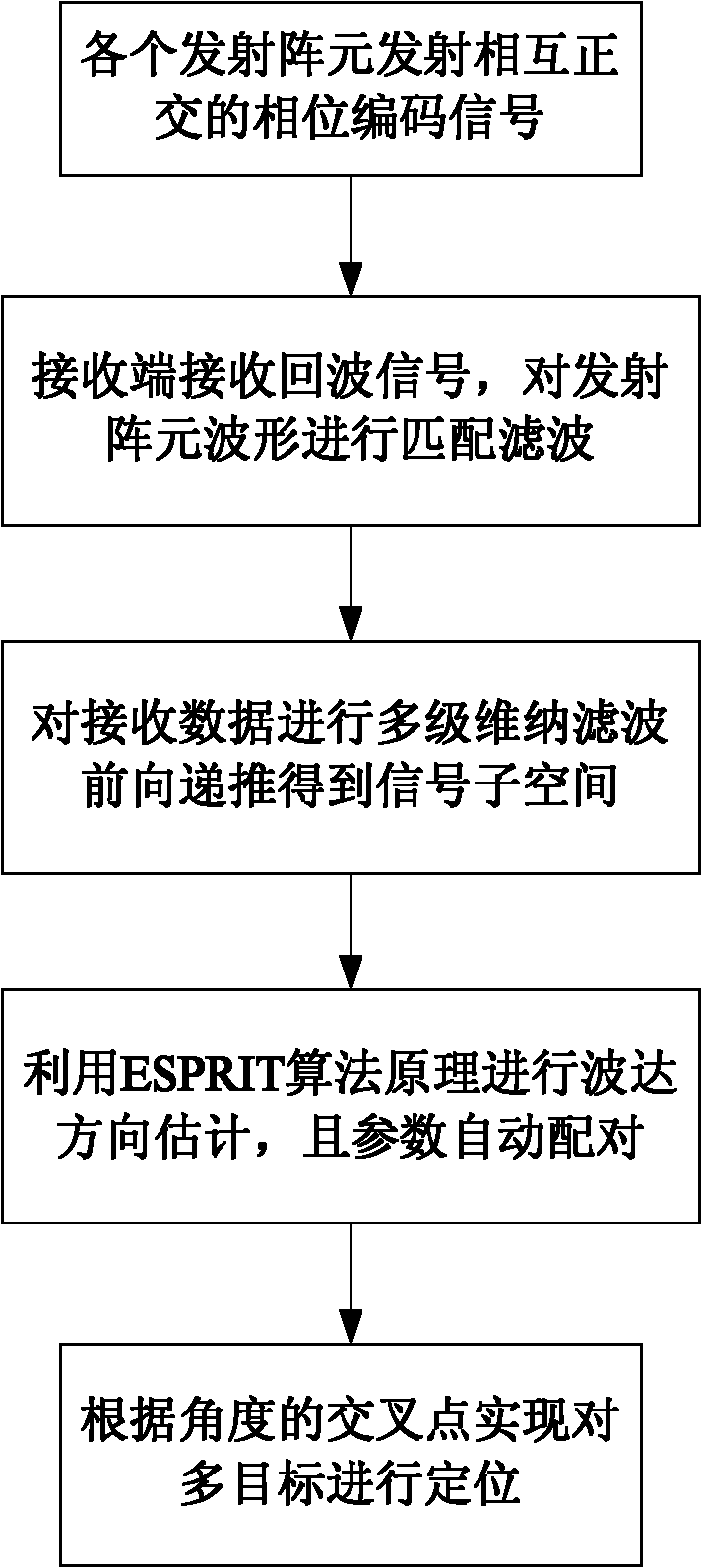
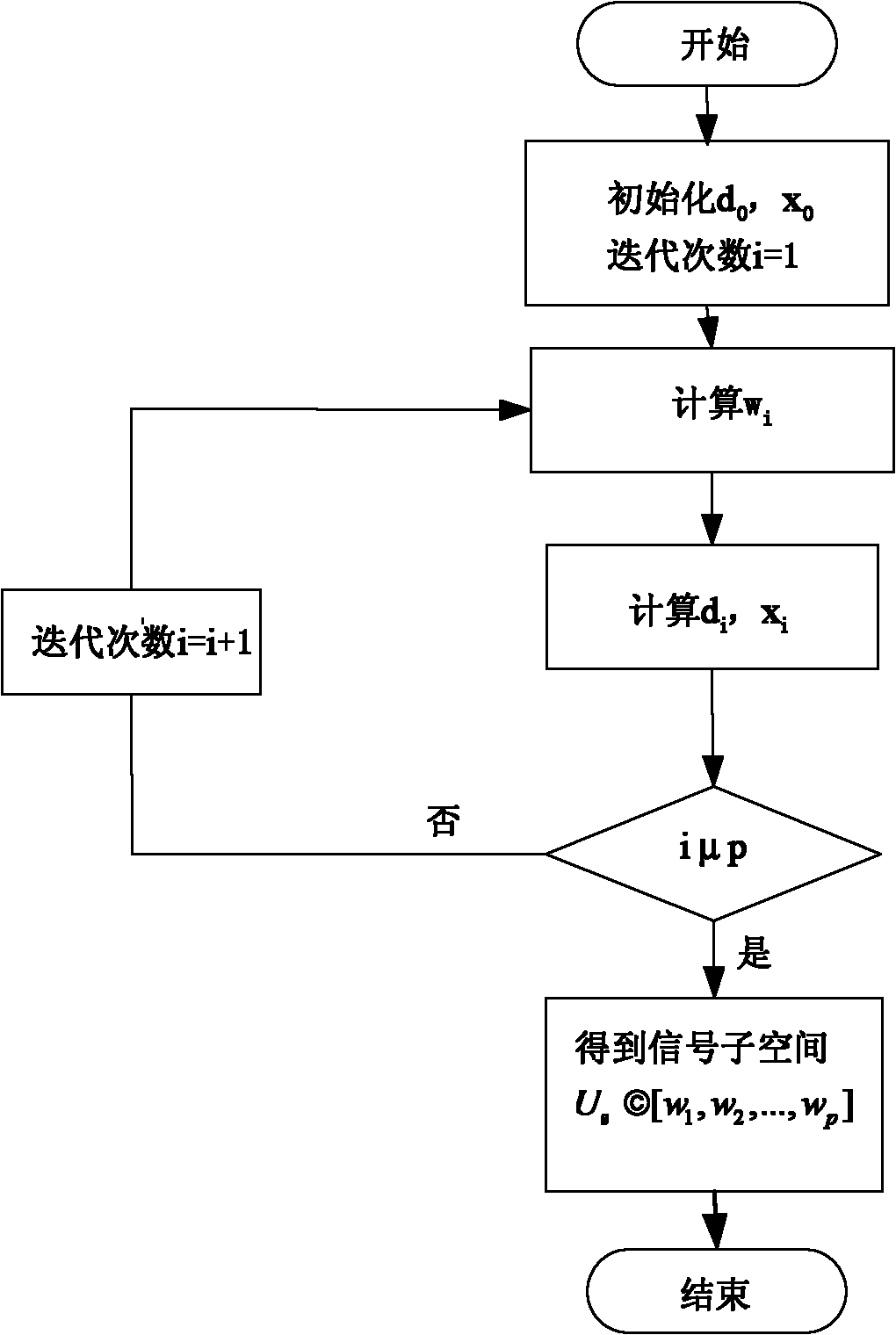
The invention provides a multi-target positioning method of a bistatic multi-input multi-output radar, comprising the following steps of: (1) transmitting mutually orthogonal phase-coded signals by M transmitting array elements, and receiving the phase-coded signals by N receiving array elements, wherein the distances of the M transmitting array elements and the N receiving array elements are all of half wavelengths; (2) carrying out matched filtering on the received phase-coded signals by a matched filter of a receiver of each receiving array element; (3) carrying out multistage Wiener filtering on a matched signal data covariance matrix space, and carrying out forward recursion to obtain a signal subspace; (4) carrying out high-resolution DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation by using an ESPRIT algorithm, wherein a pairing algorithm is used for carrying out the automatic pairing on two-dimensional parameters; and (5) realizing multi-target positioning according to cross points at two angles so as to obtain the positions of space targets. The multi-target positioning method provided by the invention has the advantages of low computation complexity, high computation speed, high estimation accuracy and can be used for positioning the sea-surface or low-altitude targets during tracking and guidance.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Multiple-target and send-receive angle estimation method of double-base multiple-input and multiple-output radar
InactiveCN102981152AImprove estimation accuracyGood angle estimation performanceWave based measurement systemsMatched filterEcho signal
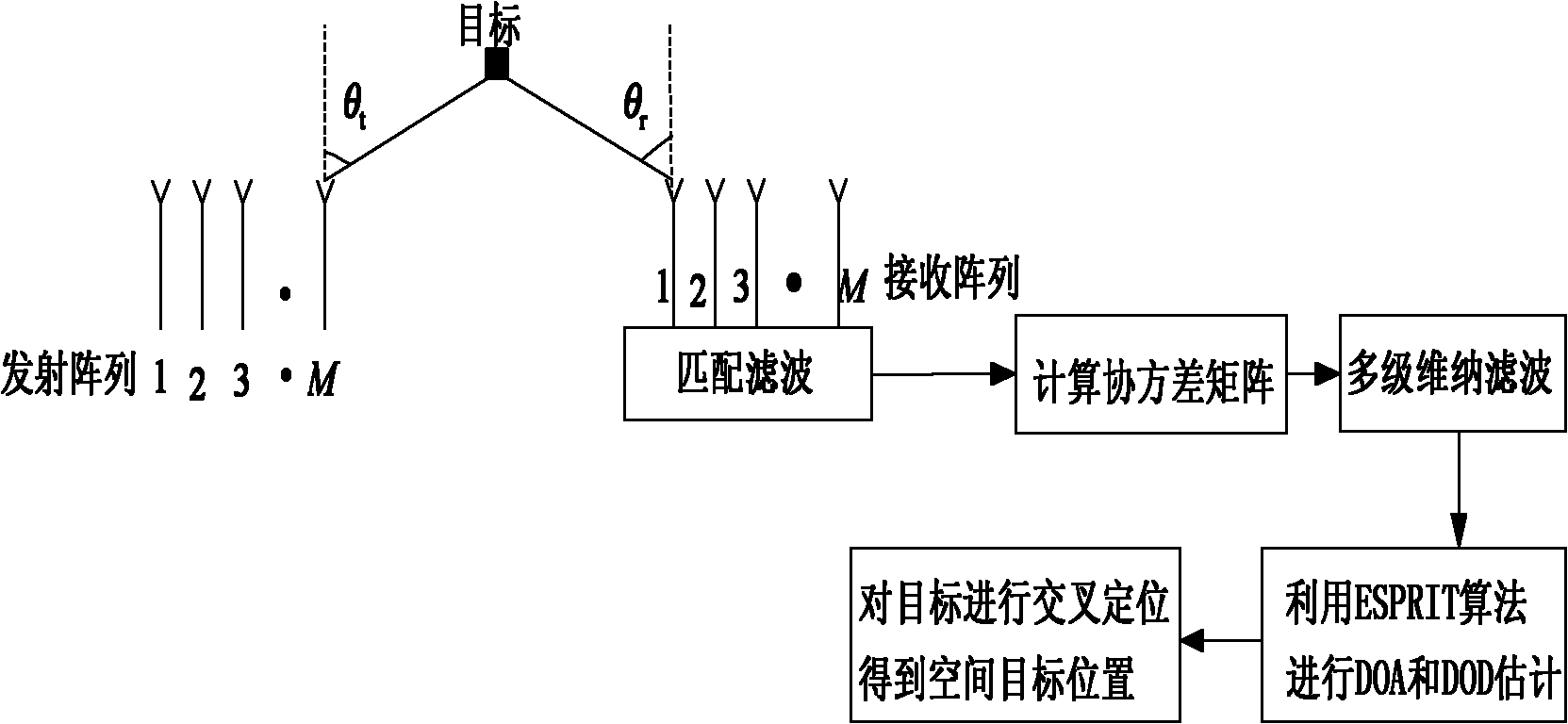
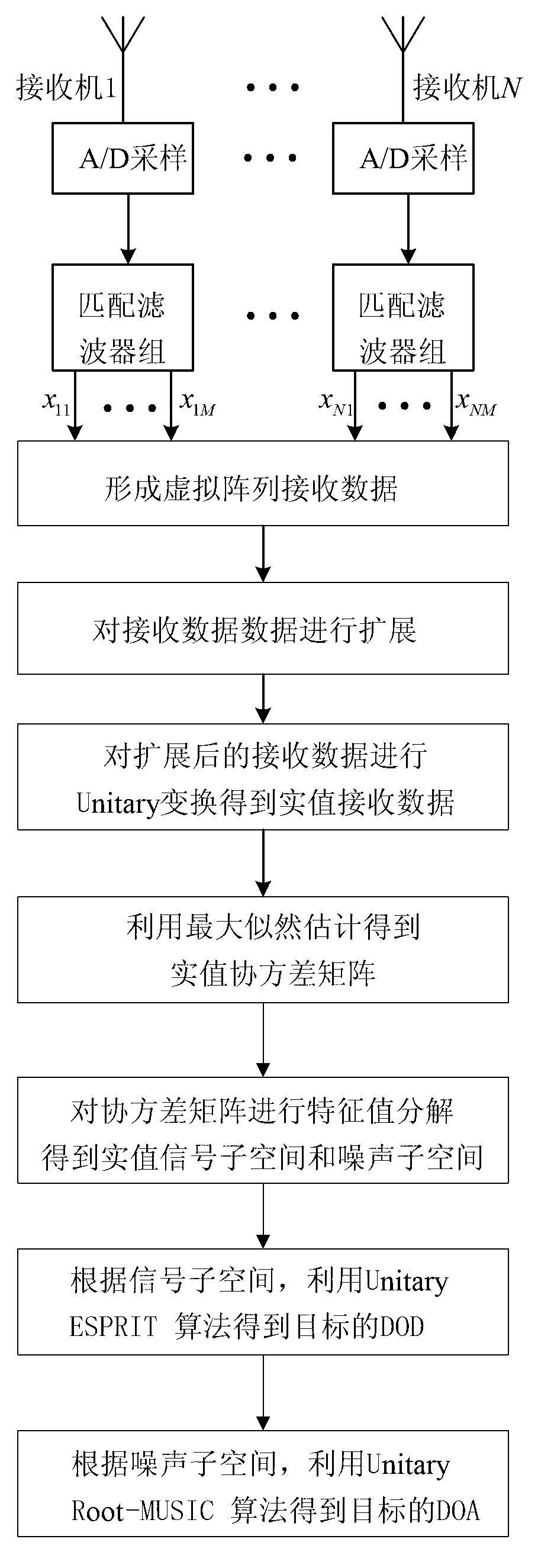
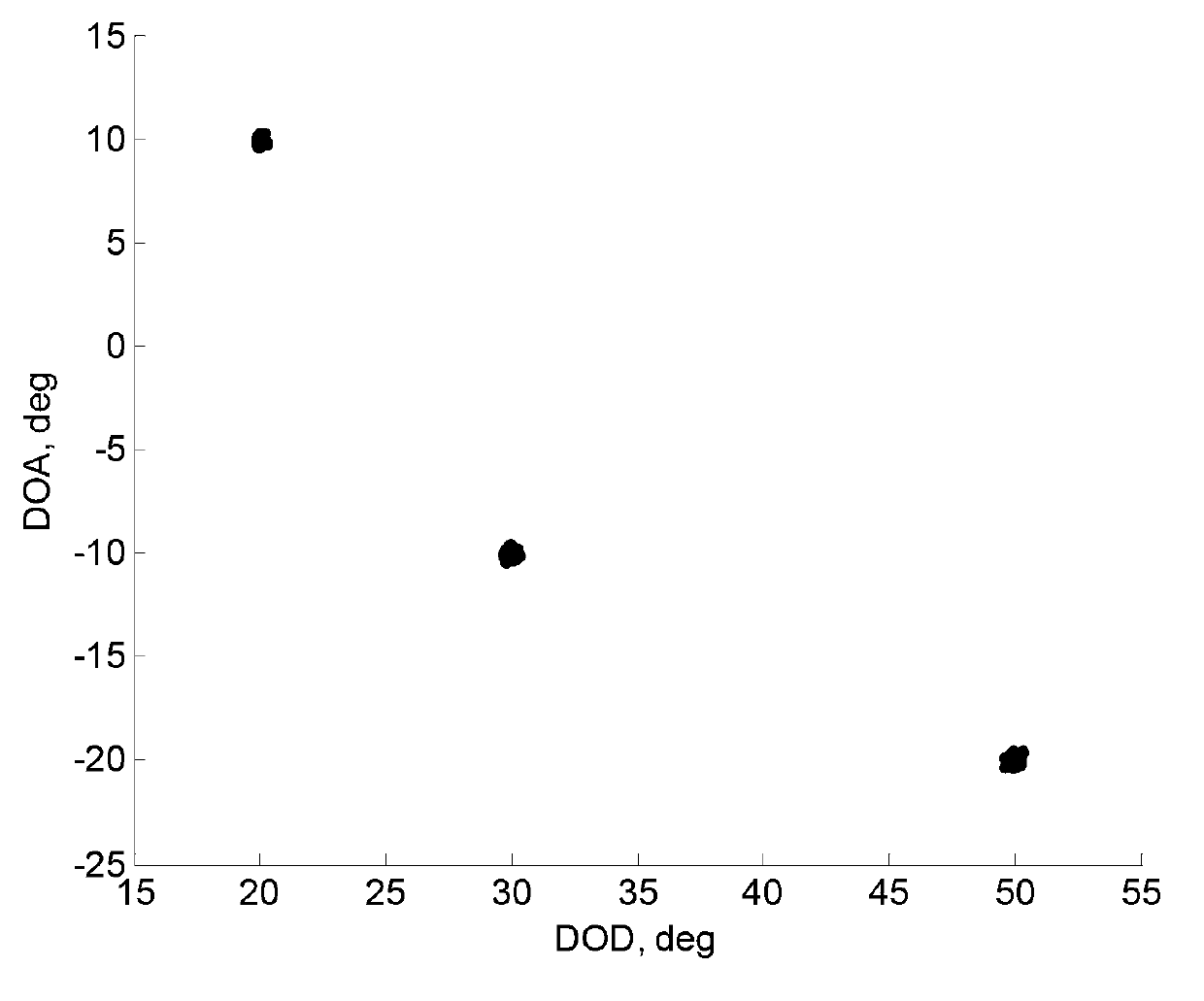
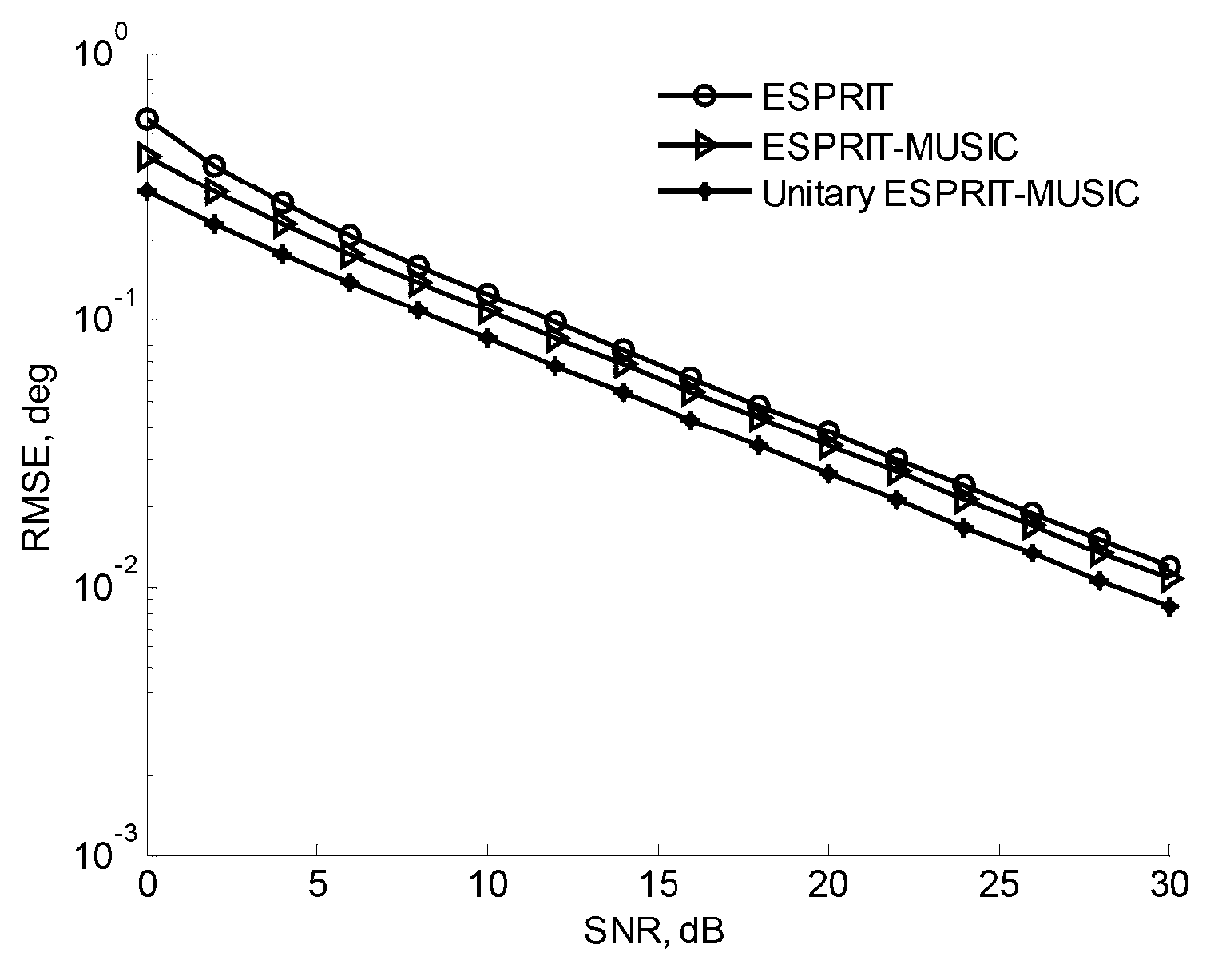
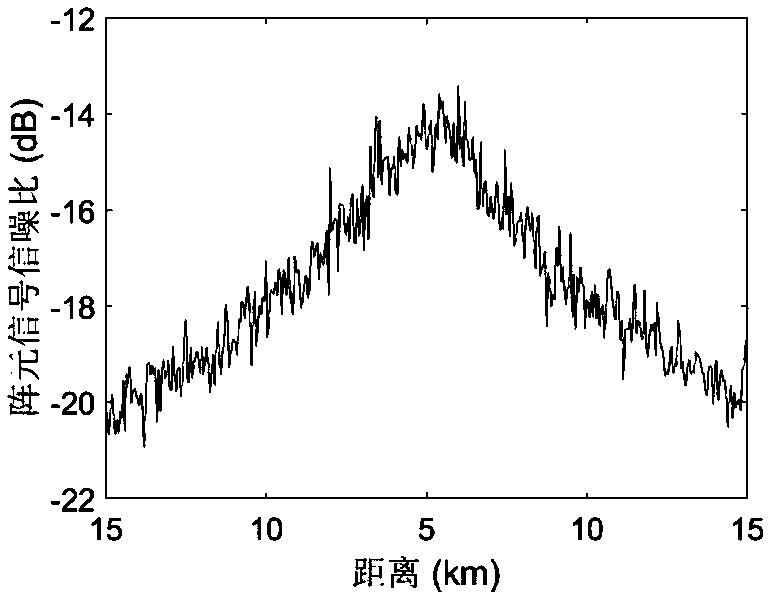
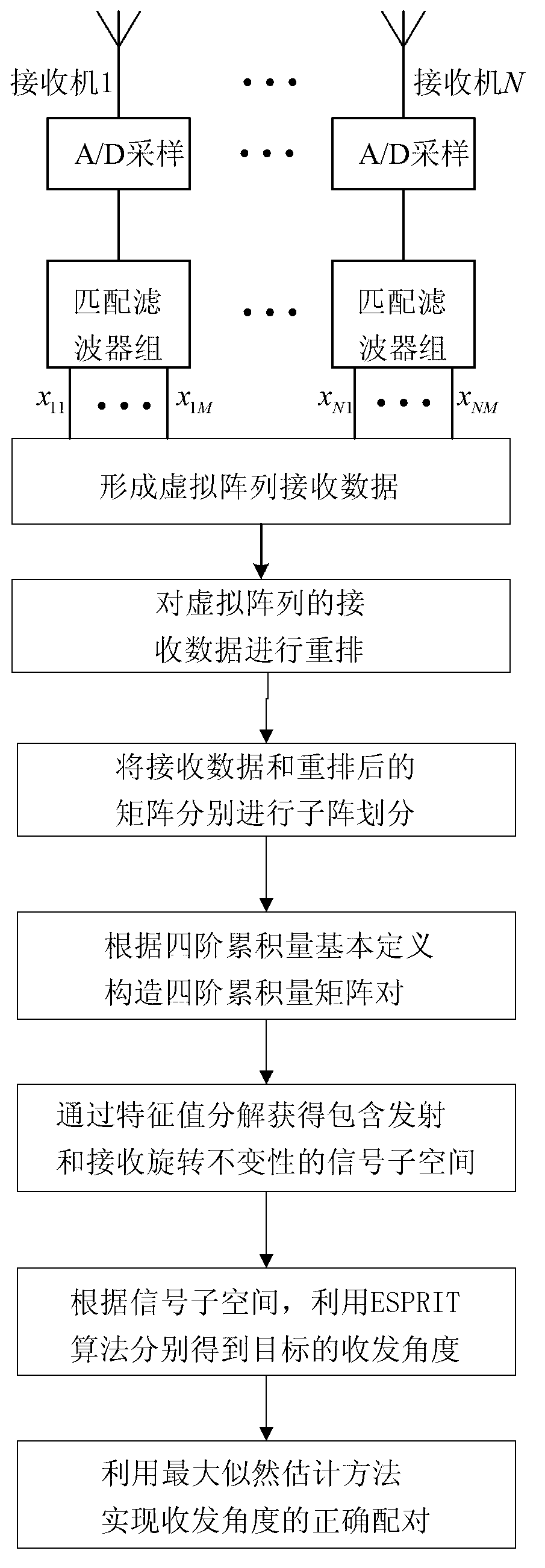
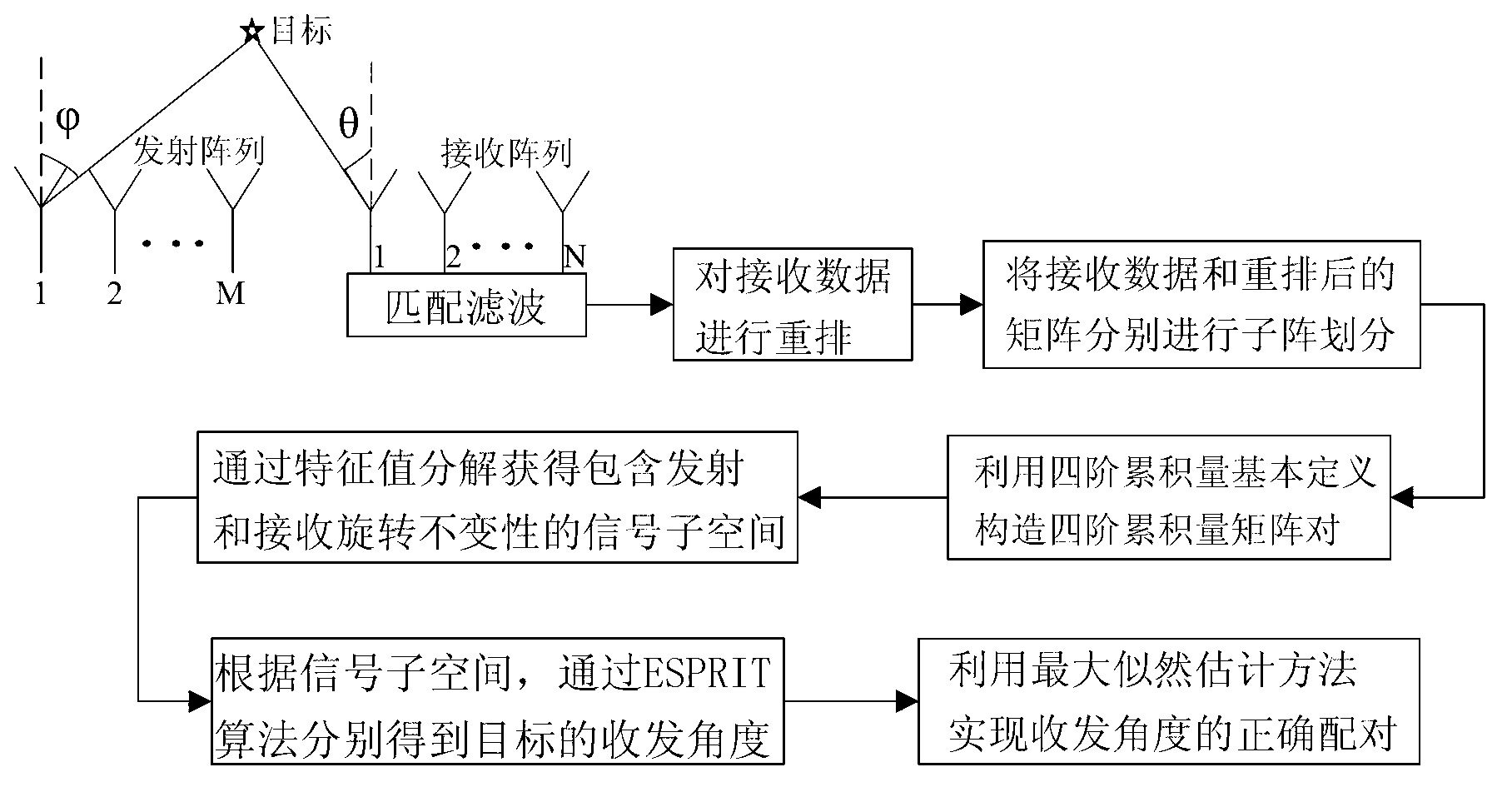
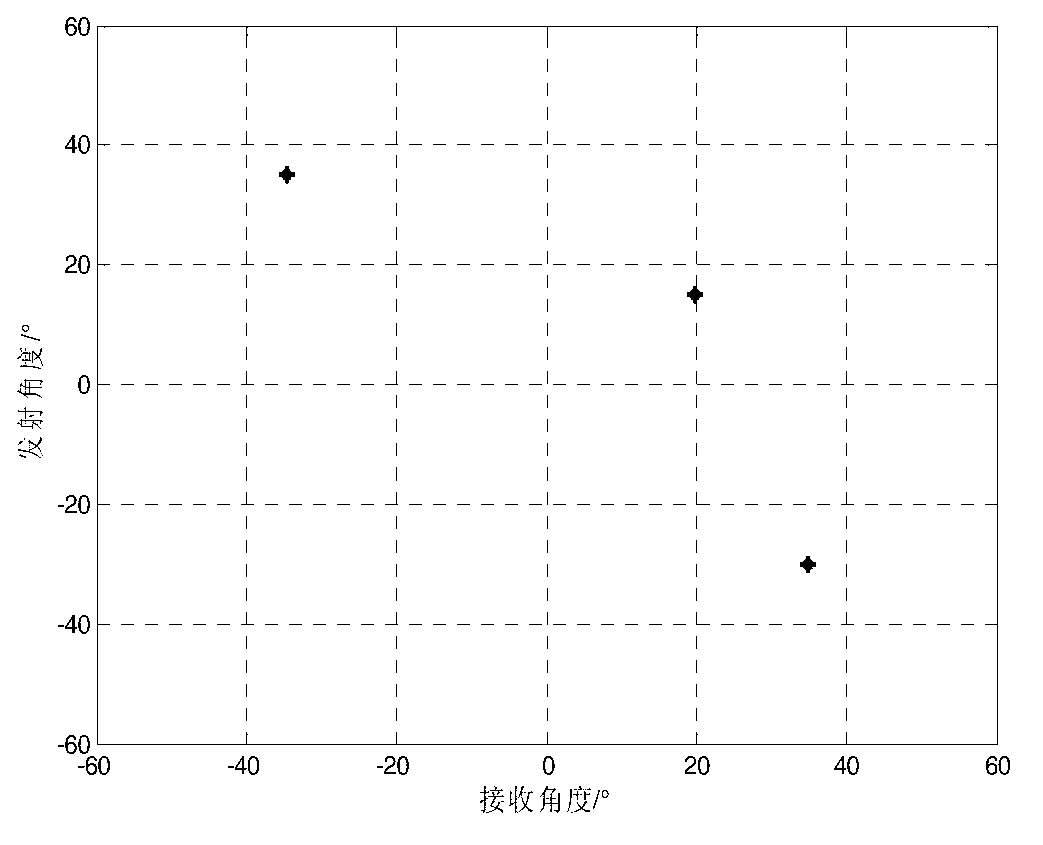
The invention provides a multiple-target and send-receive angle estimation method of a double-base multiple-input and multiple-output radar. A receiving end collects echo signals of every receiving antenna through an analog to digital (A / D) sampling module. The collected signals passes through a matched filter group, signals corresponding to every launching channel are separated, and receiving data of a virtual array is obtained, wherein the number of array elements is MN. The receiving data is expanded and is transformed into a real number field by utilizing Unitary transformation. A covariance matrix is calculated and is disassembled by utilizing characteristic value to obtain an actual value signal subspace and an actual value signal subspace. In the end, a target DOD is obtained by utilizing Unitary ESPRIT, and a target DOA is obtained by utilizing Unitary Root-MUSIC. According to the multiple-target and send-receive angle estimation method of the double-base multiple-input and multiple-output radar, the send-receive angle is automatically paired, extra pairing operation is not needed, and cross bearing of the target is achieved by utilizing the send-receive angle of the target. The multiple-target and send-receive angle estimation method of the double-base multiple-input and multiple-output radar has the advantages of being high in estimated accuracy and low in computing complexity.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
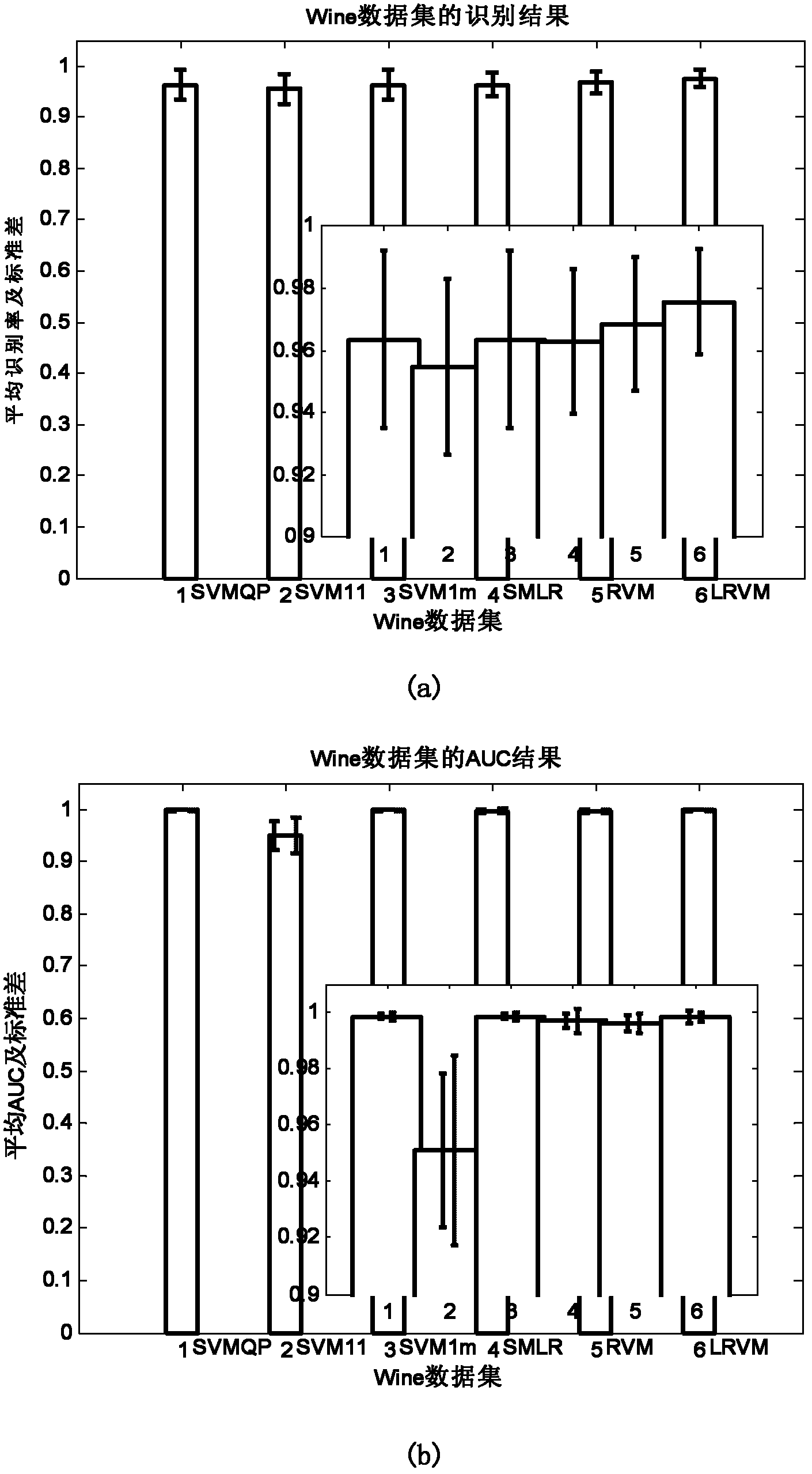
Relevance vector machine-based multi-class data classifying method
InactiveCN102254193AAvoid Category OverlapAvoid approximationCharacter and pattern recognitionValue setData set
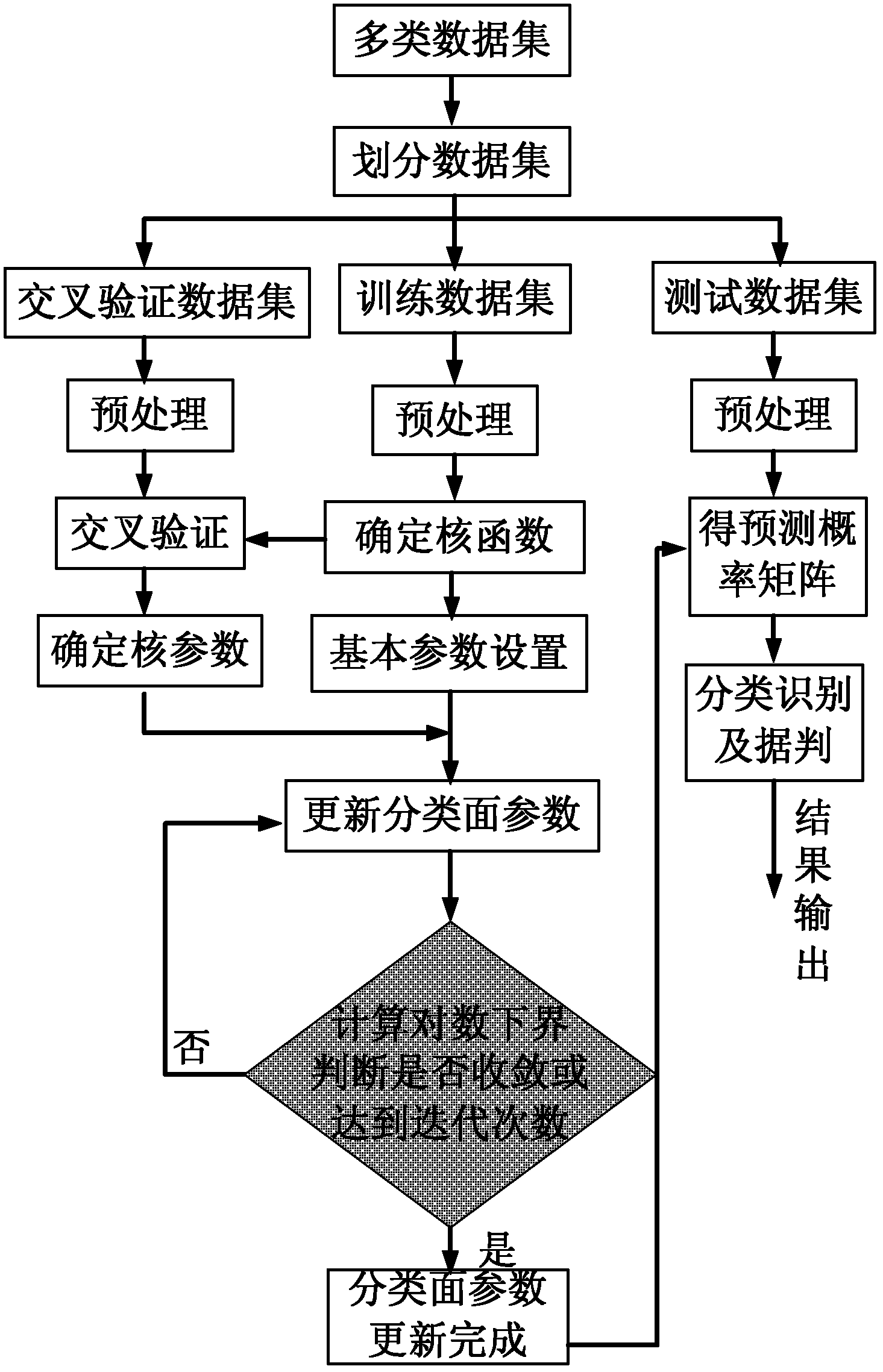
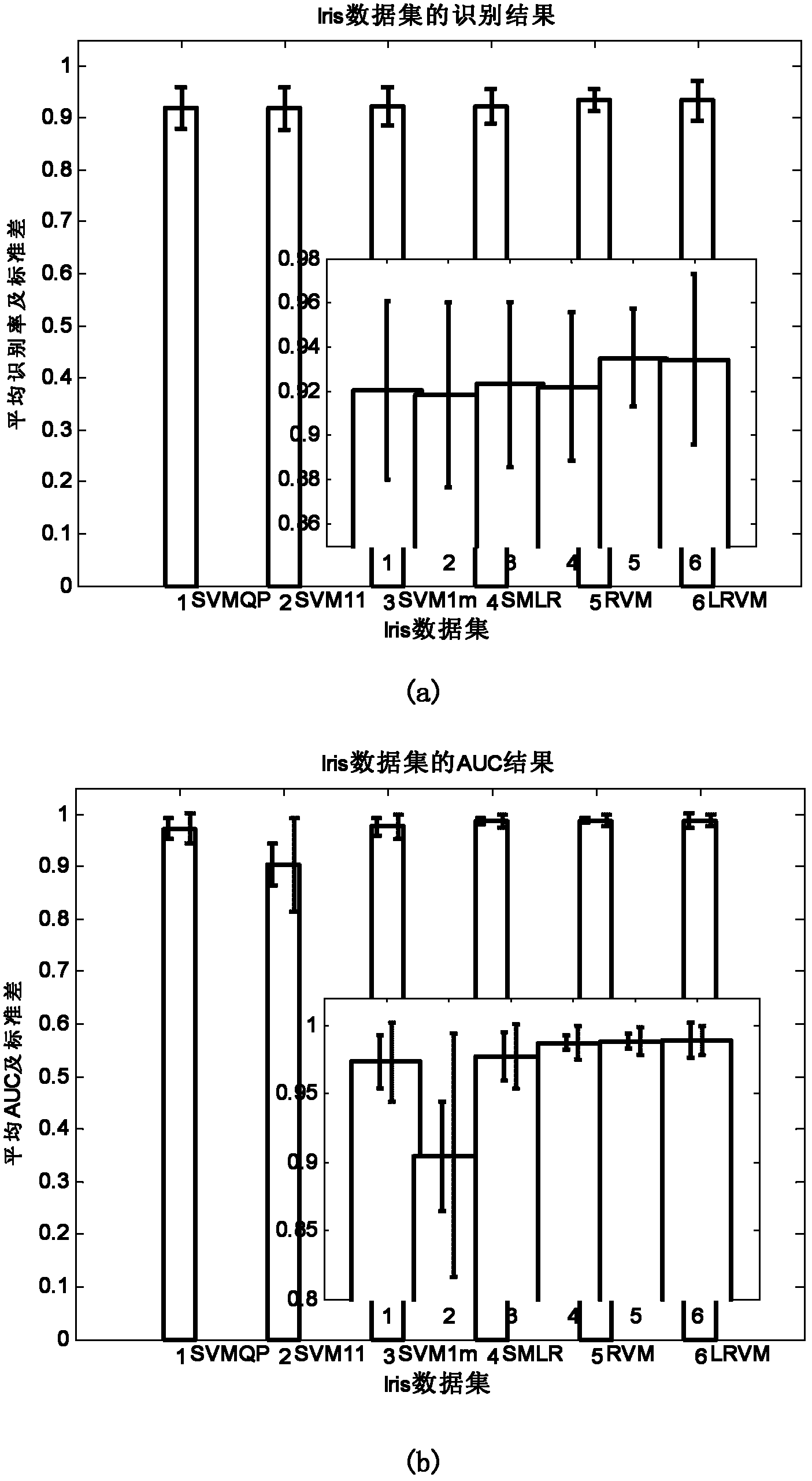
The invention provides a relevance vector machine-based multi-class data classifying method, which mainly solves the problem that the traditional multi-class data classifying method cannot integrally solve classifying face parameters and needs proximate calculation. The relevance vector machine-based multi-class data classifying method comprises a realizing process comprising the following steps of: partitioning a plurality of multi-class data sets and carrying out a normalizing pretreatment; determining a kernel function type and kernel parameters; setting basic parameters; calculating the classifying face parameters; calculating lower bounds of logarithms and solving variant values of the lower bounds of the logarithms and adding 1 to an iterative number; if the variant values of the lower bounds of the logarithms are converged or the iterative number reaches iterating times, finishing updating the classifying face parameters, and otherwise, continuing to updating; and obtaining a prediction probability matrix according to the updated classifying face parameters, wherein column numbers corresponding to a maximum value of each row of the matrix compose classifying classes for testing the data sets, and samples which have the prediction probability less than a false-alarm probability and the detection probability corresponding to a false-alarm probability value set in a curve are rejected. The relevance vector machine-based multi-class data classifying method has the advantages of obtaining classification which is comparable to that of an SVM (Support Vector Machine) by using less relevant vectors and rejecting performance and can be used for target recognition.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
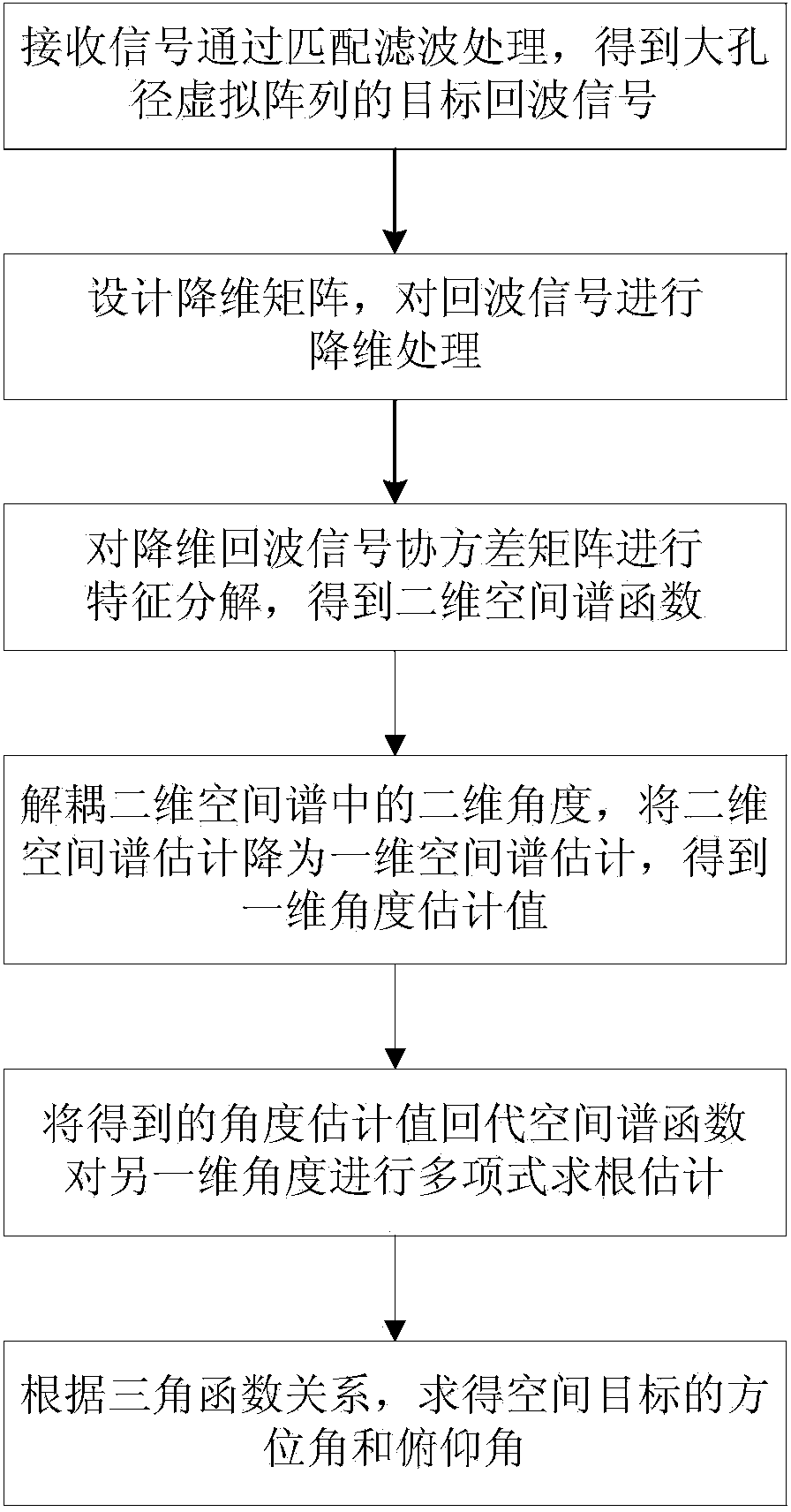
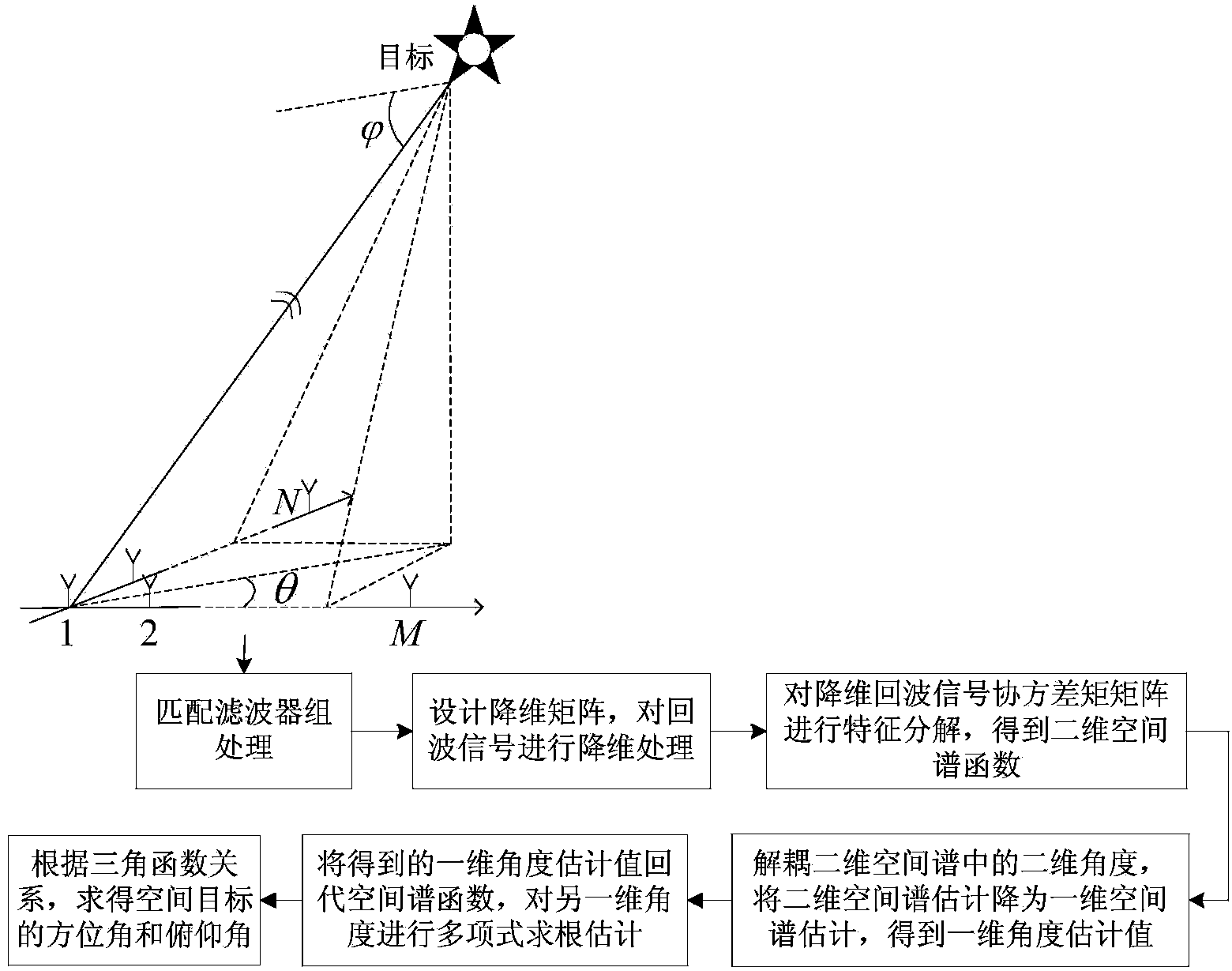
Low-complexity space target two-dimensional angle estimation method of L-shaped array MIMO radar
ActiveCN103901417ARealize two-dimensional positioningReduce operational complexityWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsDecomposition
The invention aims to provide a low-complexity space target two-dimensional angle estimation method of L-shaped array MIMO radar. The method comprises the following steps that an L-shaped array is composed of two uniform linear arrays perpendicular to each other, the distance between every two adjacent array elements is a half of a wavelength, one linear array has M array elements, the other linear array has N array elements, all the array elements are receiving and sending co-located array elements, orthogonal narrow-band signals are sent, received signals are processed by means of matched filtering, and echo signals of a large-aperture virtual array are obtained; a dimensionality reduction array is designed, and dimensionality reduction is conducted on the echo signals; characteristic decomposition is conducted on a covariance matrix of dimensionality reduction signals, and a two-dimensional space spectrum function is obtained; a two-dimensional angle in the two-dimensional space spectrum function is decoupled, and space spectrum estimation is conducted on the angle of one dimension; an obtained space spectrum estimated value is substituted into the space spectrum function, and polynomial rooting estimation is conducted on the angle of the other dimension; according to the relation of trigonometrical functions, the azimuth angle and pitching angle of a target are obtained. The method greatly reduces computational complexity of algorithm, and is beneficial to real-time processing of a radar system.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
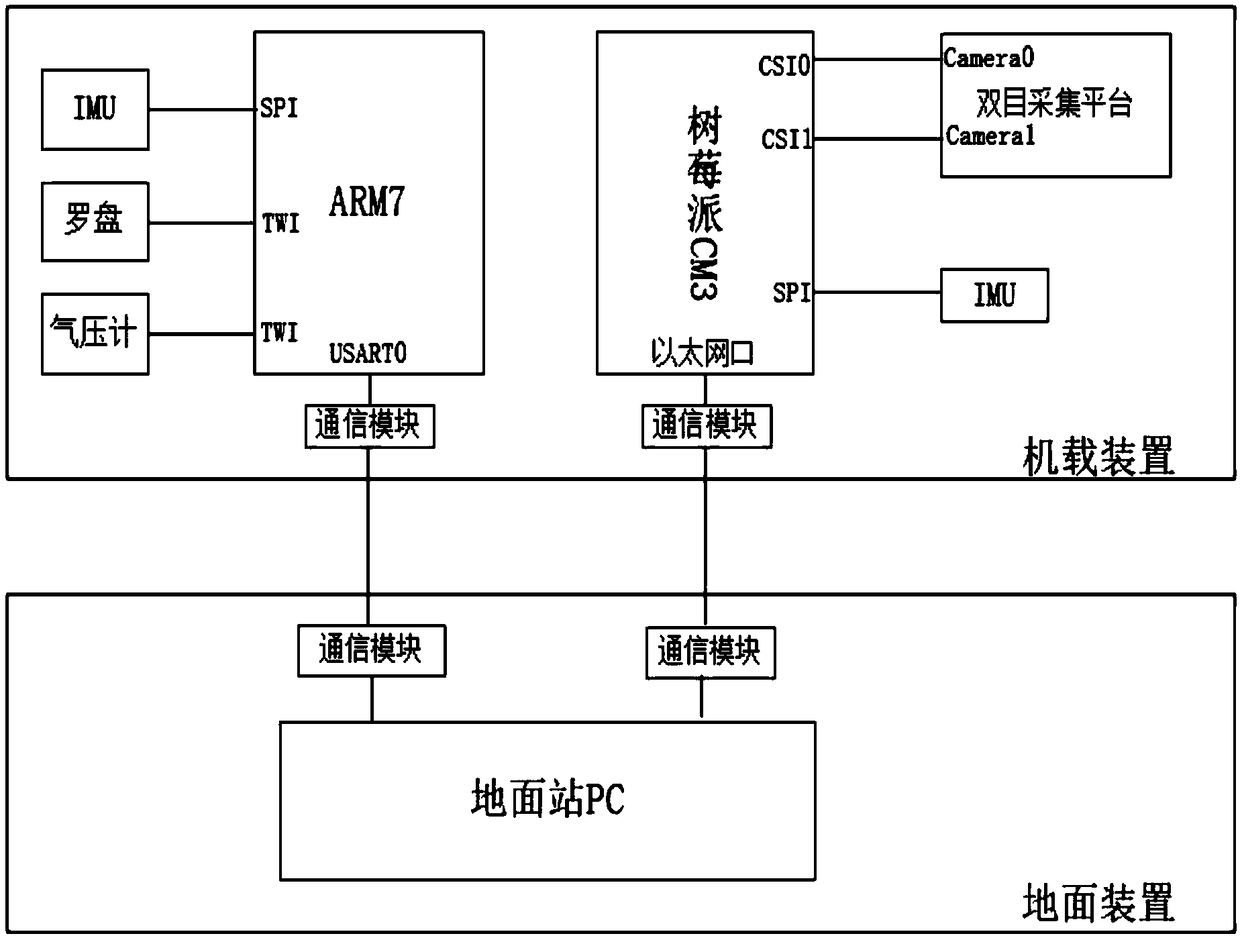
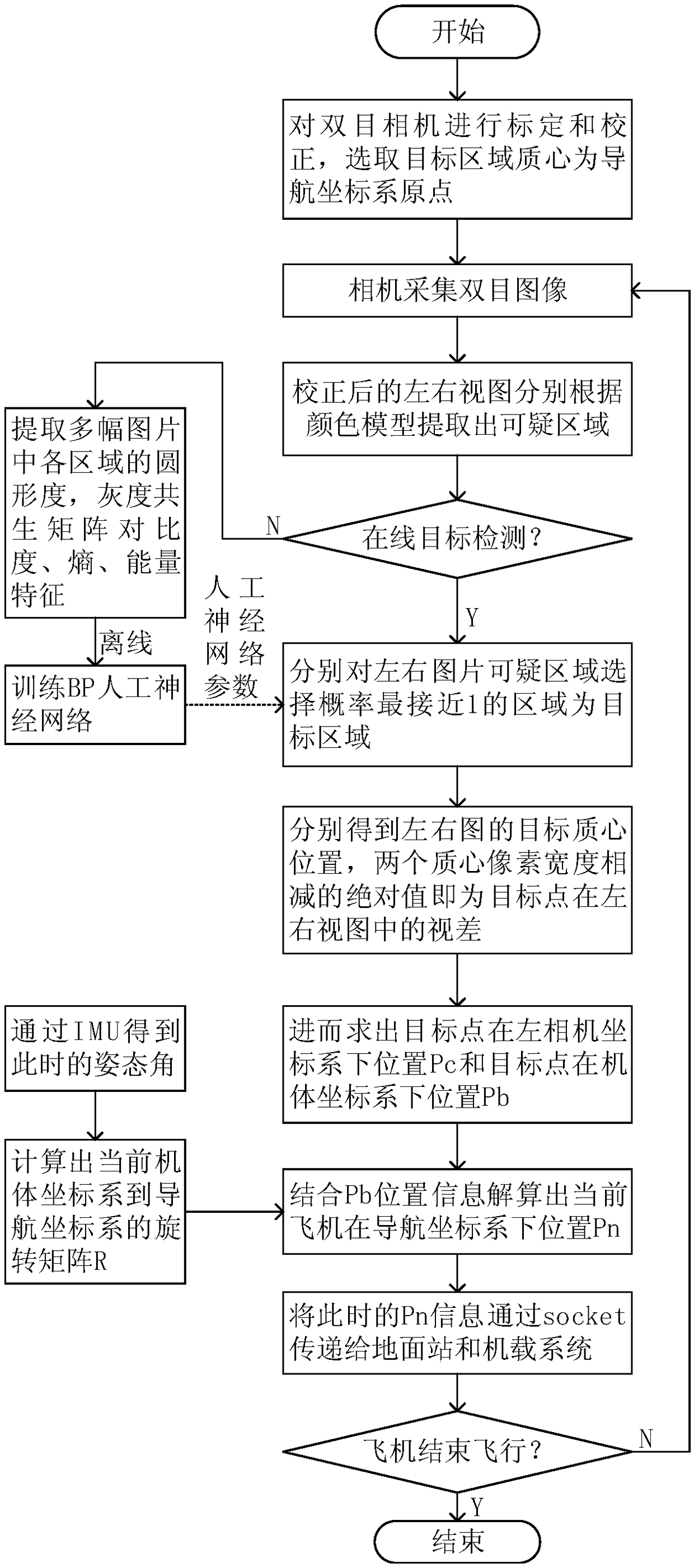
A positioning method of small unmanned aerial vehicle based on binocular vision
The invention discloses a positioning method of a small unmanned aerial vehicle based on binocular vision, which includes the following steps: using a ground target as a reference, selecting the target centroid as the origin of the navigation coordinate system, wherein the binocular camera fixed on the computer is based on the V4L2 interface to collect the image of the object in real time; By means of the object detection algorithm based on color model and artificial neural network algorithm to remove the disturbance region in the image, extracting the target area from the left and right viewsprecisely, the difference in the width of the target centroid pixel between the two images is the parallax of the target point; combined with binocular ranging and camera calibration parameters, theposition of the target point in the left camera coordinate system is calculated, and then the rotation matrix from the current airframe coordinate system to the initial airframe coordinate system is calculated based on the attitude angle information obtained by IMU, so as to calculate the coordinates of the UAV in the navigation coordinate system. The method effectively shortens the positioning time of the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and is beneficial to the real-time processing of the aircraft position.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
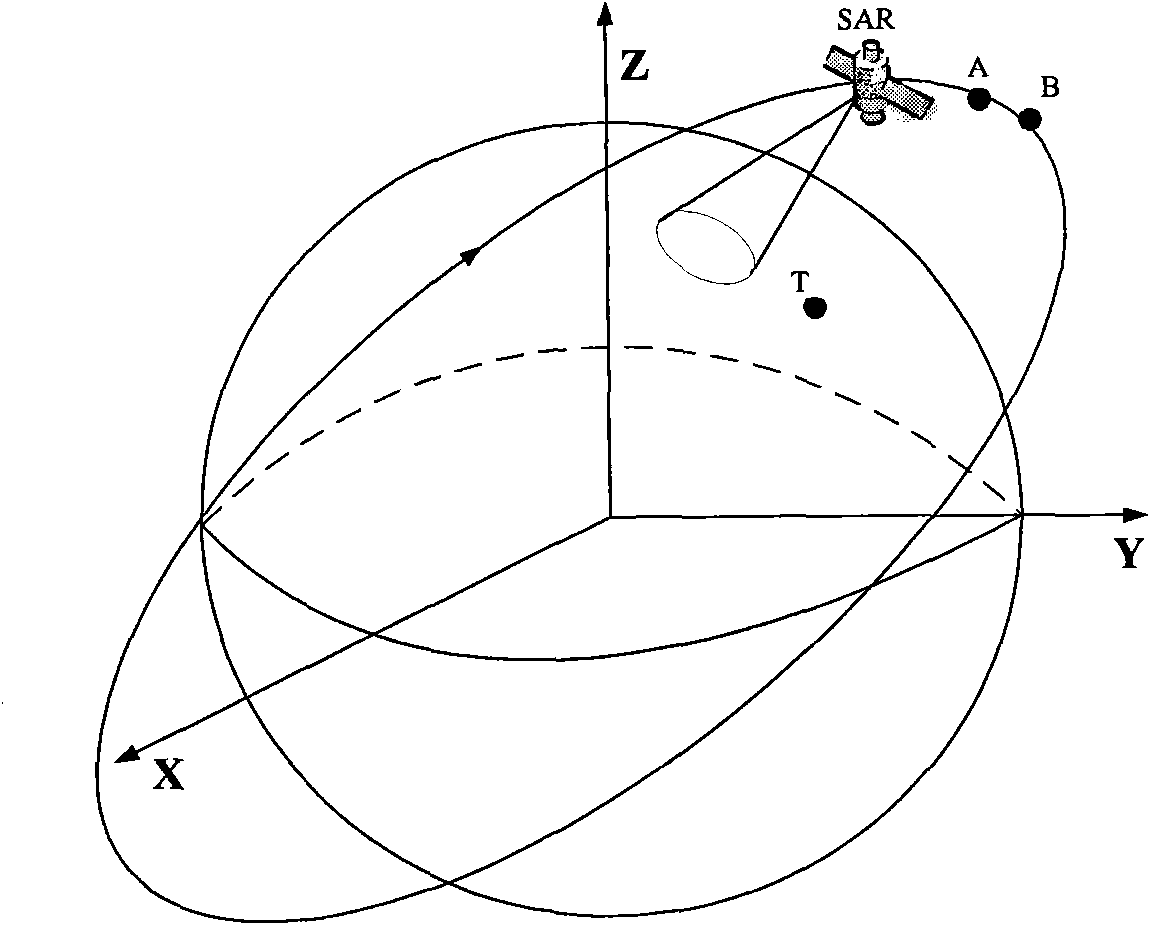
Space-borne SAR image target positioning method capable of eliminating ground elevation errors
InactiveCN101887122AEliminate positioning errorsAvoid solving difficult problemsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEphemerisEnvironmental geology
The invention discloses a space-borne SAR image target positioning method capable of eliminating ground elevation errors, comprising the following steps: (1) acquiring needed ephemeris parameters; (2) respectively calculating target slant-range parameters, Doppler parameters and state vectors of a satellite; (3) substituting the target slant-range parameters, the Doppler parameters and the state vectors in step (2) into a target positioning equations set, and then solving the equations set to obtain a ground target position; and (4) taking the x, y and z coordinates solved in step (3) as the coordinates under an inertial coordinate system, transforming the coordinates into a geocentric rotating coordinate system xc, yc and zc by a coordinate transformation mode, transforming the geocentric rotating coordinate system into geocentric longitude and latitude Lc and Deltac, and finally transforming the geocentric longitude and latitude into geographical longitude and latitude lon and lat. In the method, the target positioning equations set does not contain an earth model equation, thus eliminating positioning errors caused by the ground elevation errors, avoiding the difficult problem of solving a Range-Doppler (R-D) positioning equations set, and being beneficial to real-time processing of ground target positioning.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Restraining device and restraining method for burst impulse noise of power line communication channel
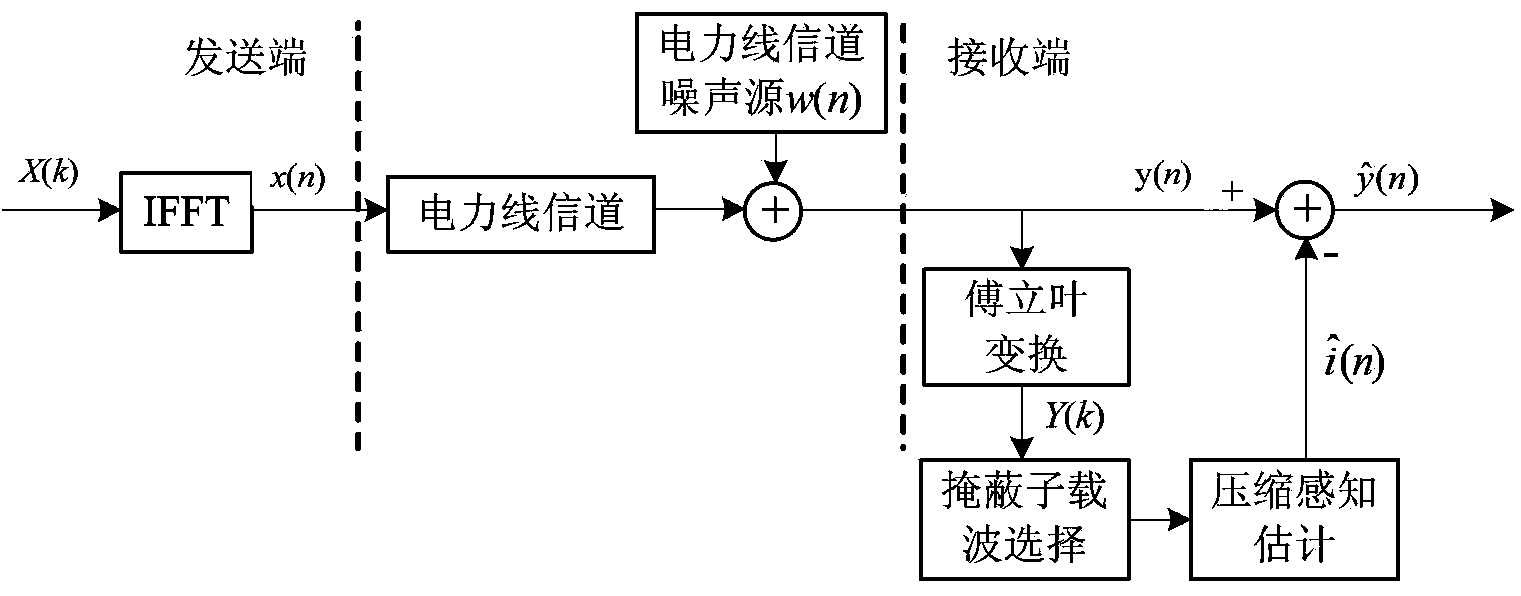
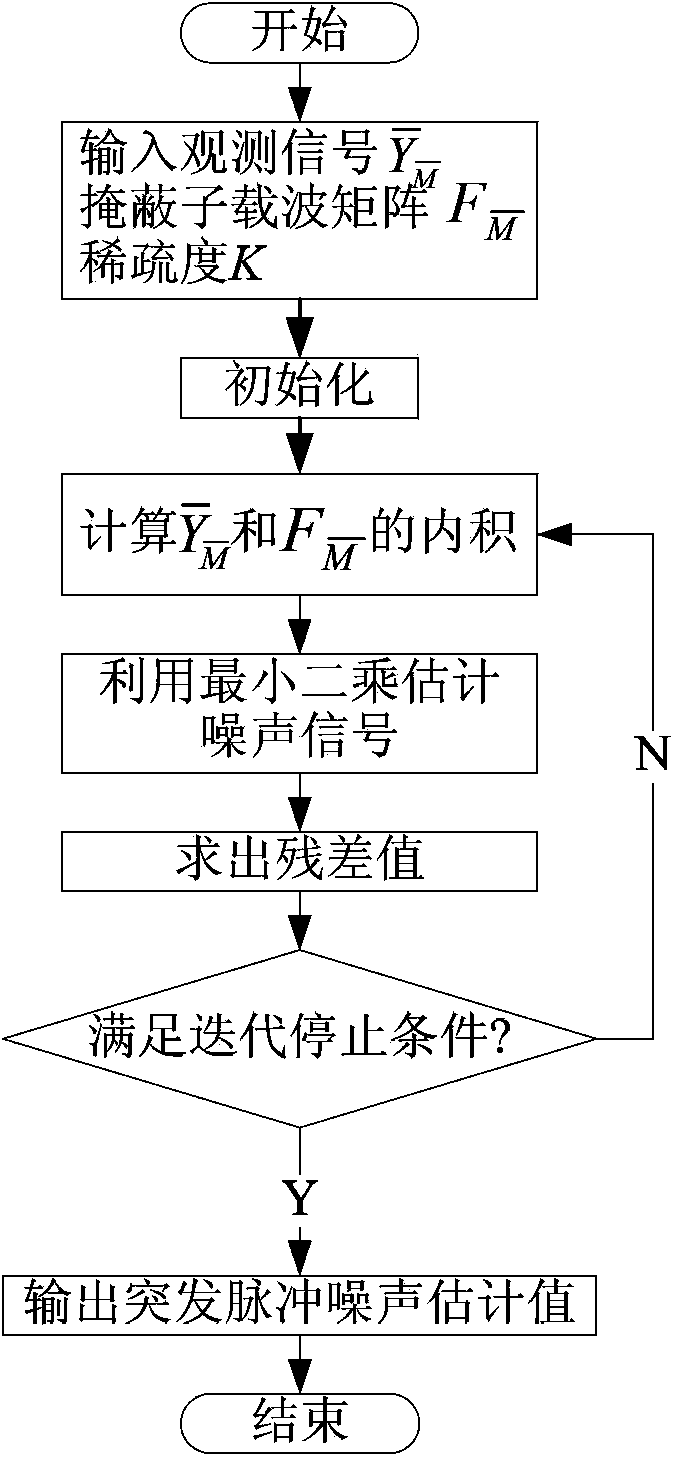
InactiveCN103457638AImprove performanceKeep signal informationPower distribution line transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsFourier transform on finite groupsCarrier signal
The invention discloses a restraining device and restraining method for burst impulse noise of a power line communication channel. The restraining device comprises a Fourier transformation module, a masking subcarrier selection module and a compressed sensing estimation module. The restraining method for the burst impulse noise of the power line communication channel is based on compressed sensing and comprises the steps of carrying out Fourier transformation on a received signal to obtain a frequency domain signal, carrying out masking subcarrier selection to obtain a subcarrier only comprising background noise and the burst impulse noise, estimating the burst impulse noise in the power line communication channel by using a signal recover method based on compressed sensing, and finally, removing the impulse noise from the received signal to obtain a signal with noise removed. Due to the facts that the burst impulse noise in the power line communication channel has the characteristic of sparsity, and the OFDM masking subcarrier selection and compressed sensing technologies are applied, the effect of restraining the noise can be remarkably improved, and signal information of positions interfered by burst impulse can be effectively kept.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
License plate recognition system based on artificial neural network and method
InactiveCN104156731ARun fastEasy to process in real timeCharacter and pattern recognitionCommunication interfaceLiquid-crystal display
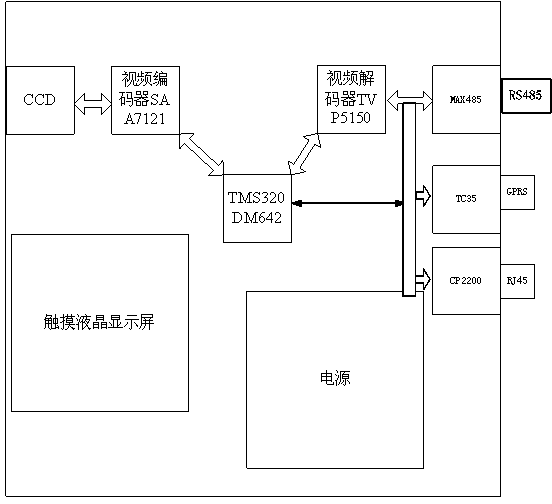
The invention discloses a license plate recognition system based on an artificial neural network. The license plate recognition system comprises an image sensor, a video encoder, a video decoder and a touch liquid crystal display, and is characterized by further comprising a digital signal processor, wherein the model of the digital signal processor is TMS320DM642; the image sensor is connected with the video decoder; the video encoder is connected with the digital signal processor; the digital signal processor is connected with the video decoder; the video decoder and the digital signal processor are connected with a communication interface module. The license plate recognition system is high in running speed, high in recognition precision, simple, and high in robustness, and can accurately recognize various license plates with hazier ground colors under poor illumination conditions.
Owner:成都易默生汽车技术有限公司
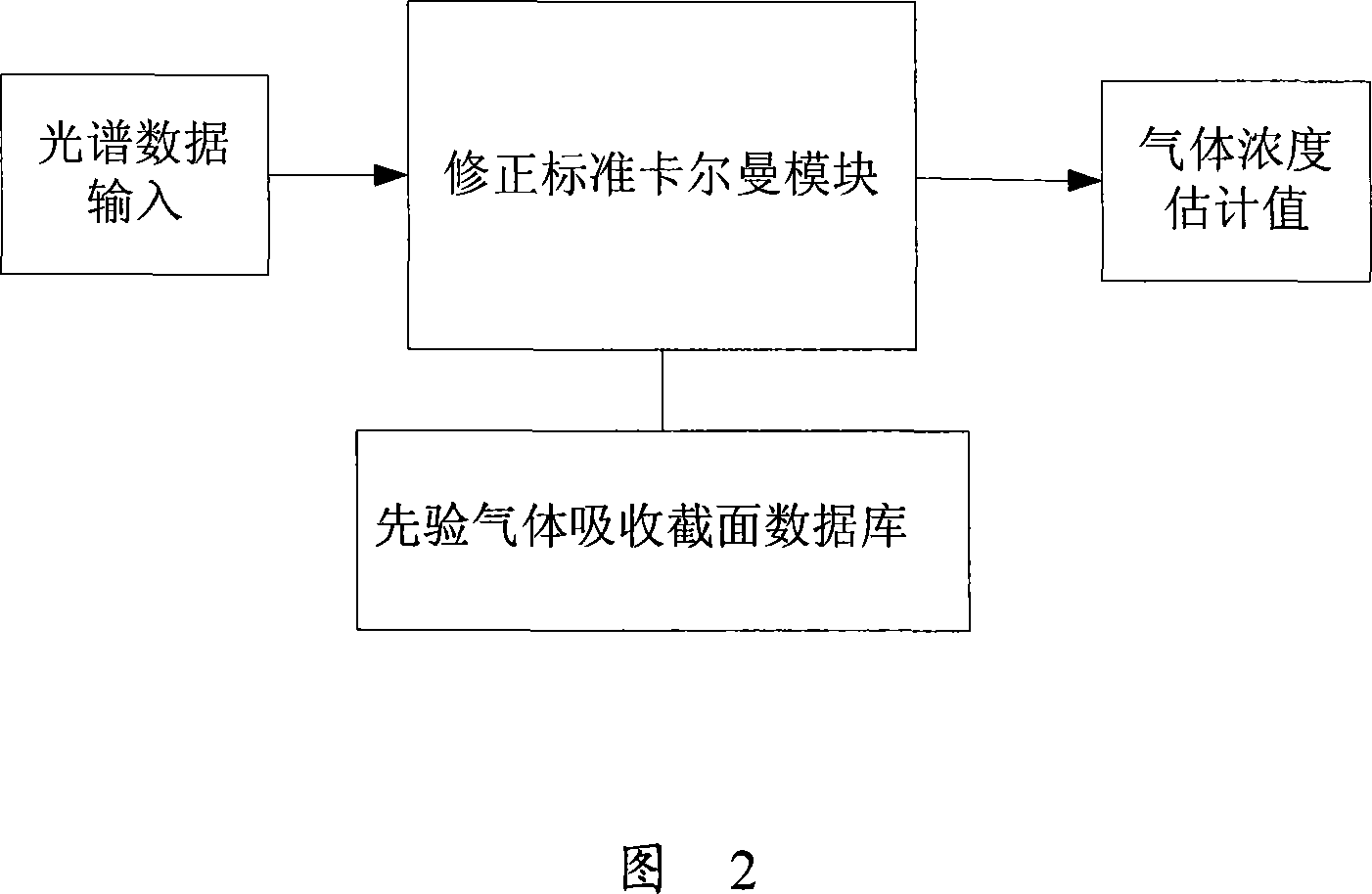
Gas density quantitative analysis instrument based on corrected kalman filtering theory
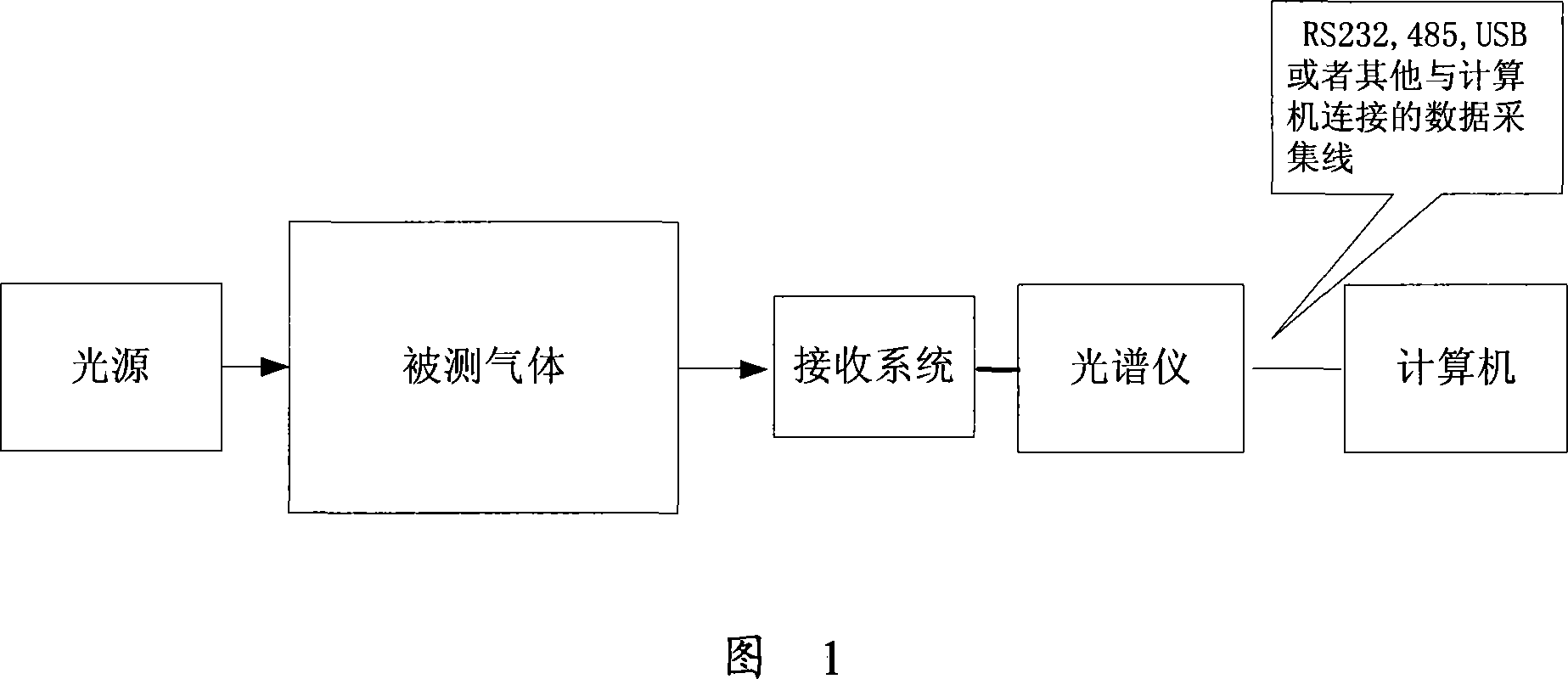
InactiveCN101059428AImprove robustnessEliminate the effects ofColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsFiltering theorySpectrometer
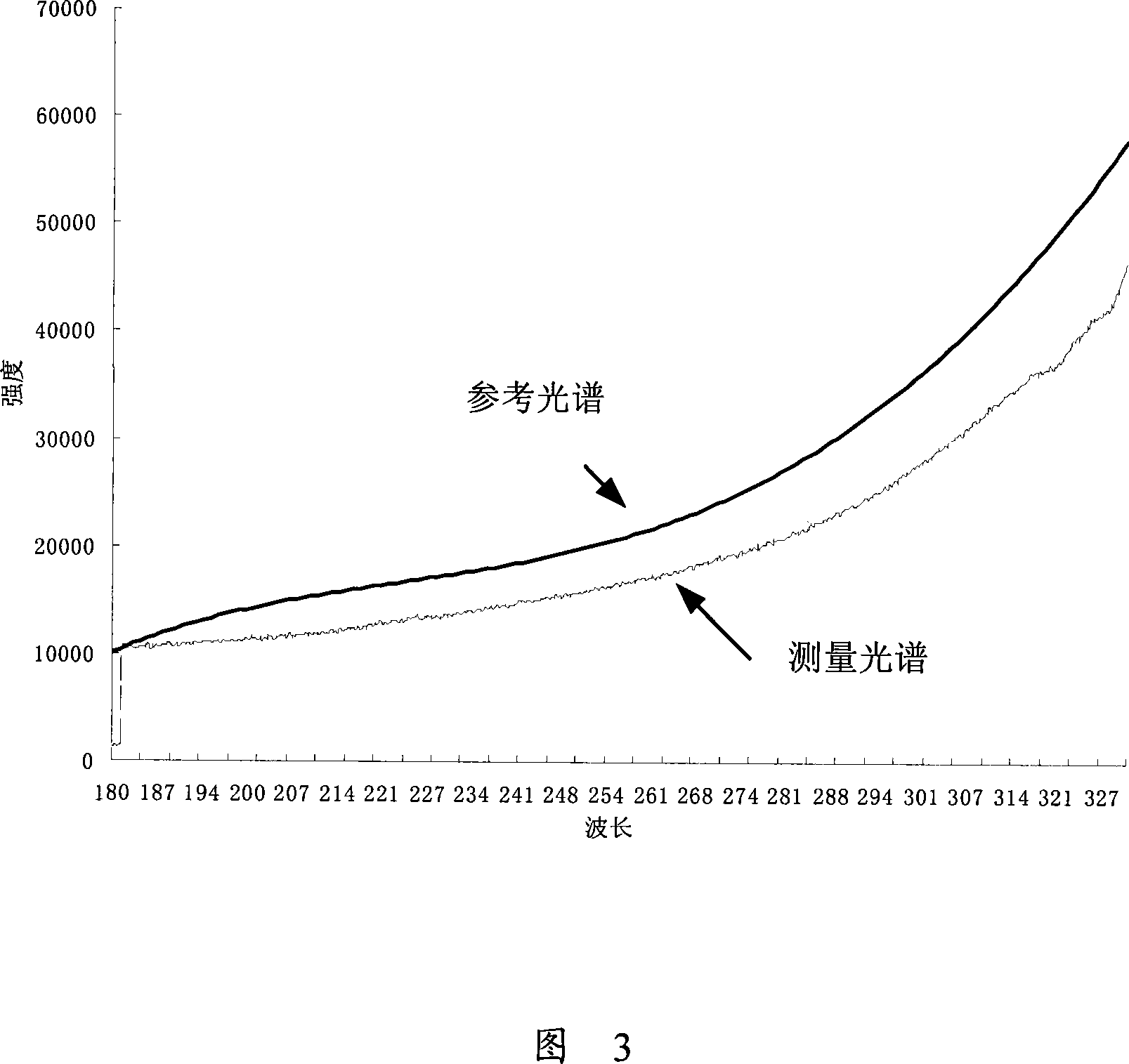
The invention discloses a gas density quantitative analyzer based on correct Kalman filter theory, wherein the hardware part is composed of a light source, a receiving system, a spectrum device, a data line and a computer, the correct Kalman filter algorism of the software part is composed of a standard Kalman filter algorism and a noise parameter self-adaptive evaluation algorism. The light of light source is absorbed by object gas into the receiving system to enter into the spectrum device which obtains the transmissivity relative to the wavelength, to output spectrum data via the data line to be fed into the computer. The spectrum data in the computer is built into a measurement equation, which density distribution changes along time, to build a gas density equation, to be treated by correct Kalman filter algorism, to reversely obtain the gas density.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Gas status quantitative analyzer based on extended kalman filter theory
InactiveCN101216426AImprove robustnessImprove inversion accuracyTransmissivity measurementsThermometers using physical/chemical changesFiltering theoryData modeling
The invention discloses a gas state quantitative analyzer based on the extended Kalman filtering theory for simultaneous online estimation of concentration and temperature of gas to be detected. The hardware portion is composed of a light source, a receiving system, an optical detection system and a computer, and the software portion is composed of a gas state space model and an extended Kalman filtering portion. Light wave emitted from the light source passes through the gas to be detected and enters the optical detection system through a receiving system, and the optical detection system acquires transmittance corresponding to each wavelength of the light wave and transmits corresponding light intensity spectral data to the computer. The computer constructs a measurement equation based on gas absorption intensity data by gas state analysis software to obtain a gas state equation, thus inversing the concentration and the temperature of the gas by using the extended Kalman filtering algorithm.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
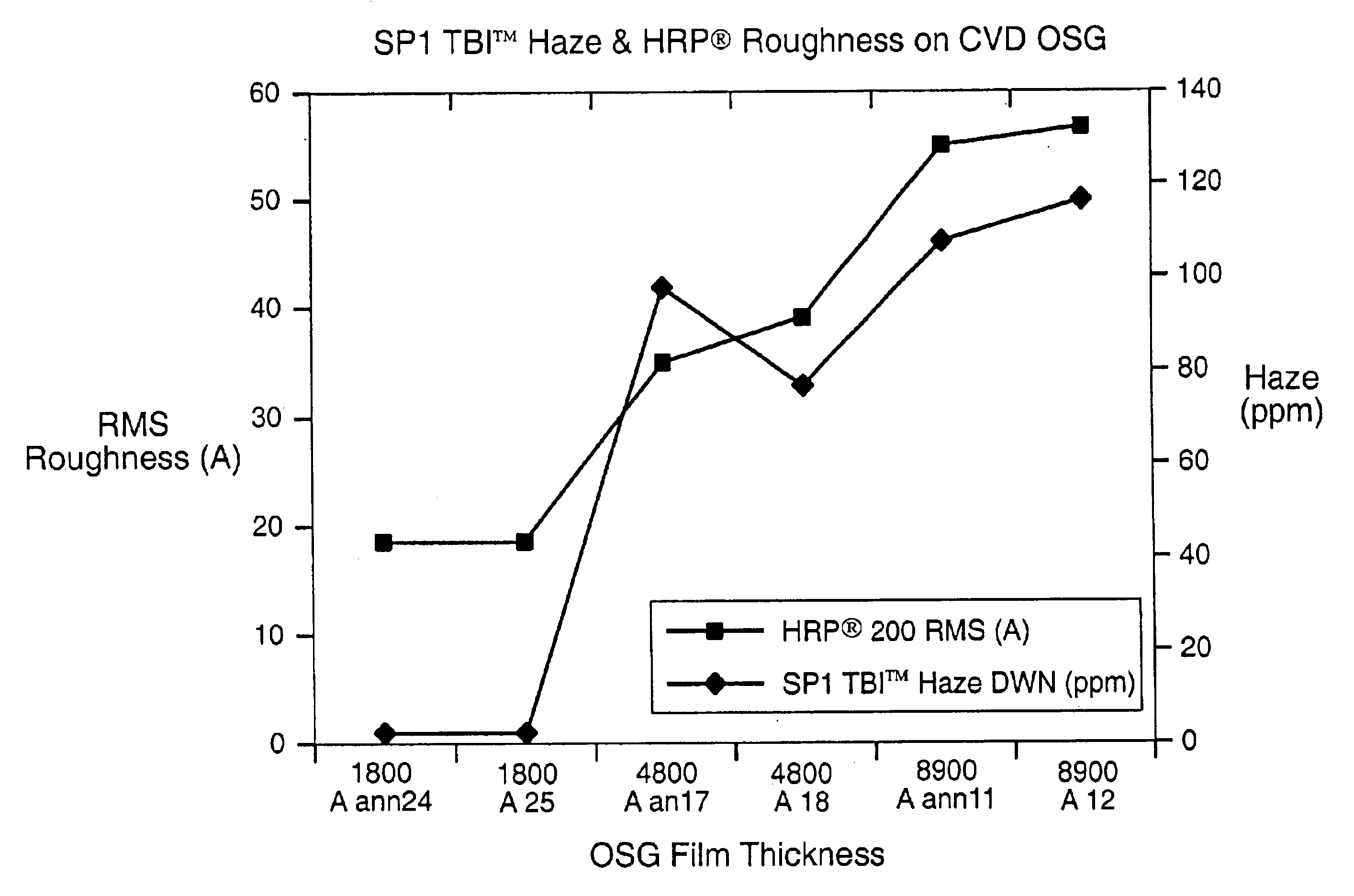
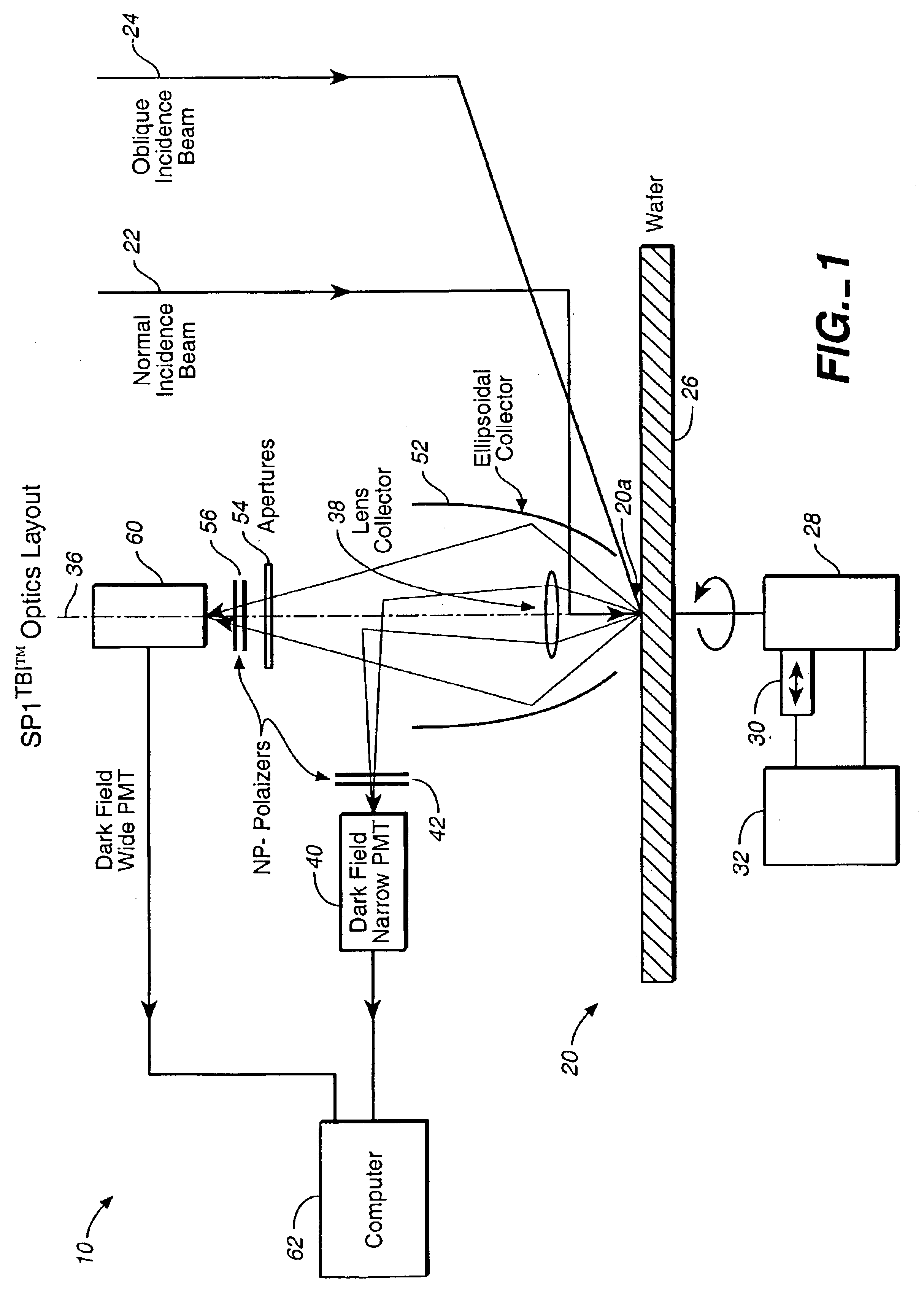
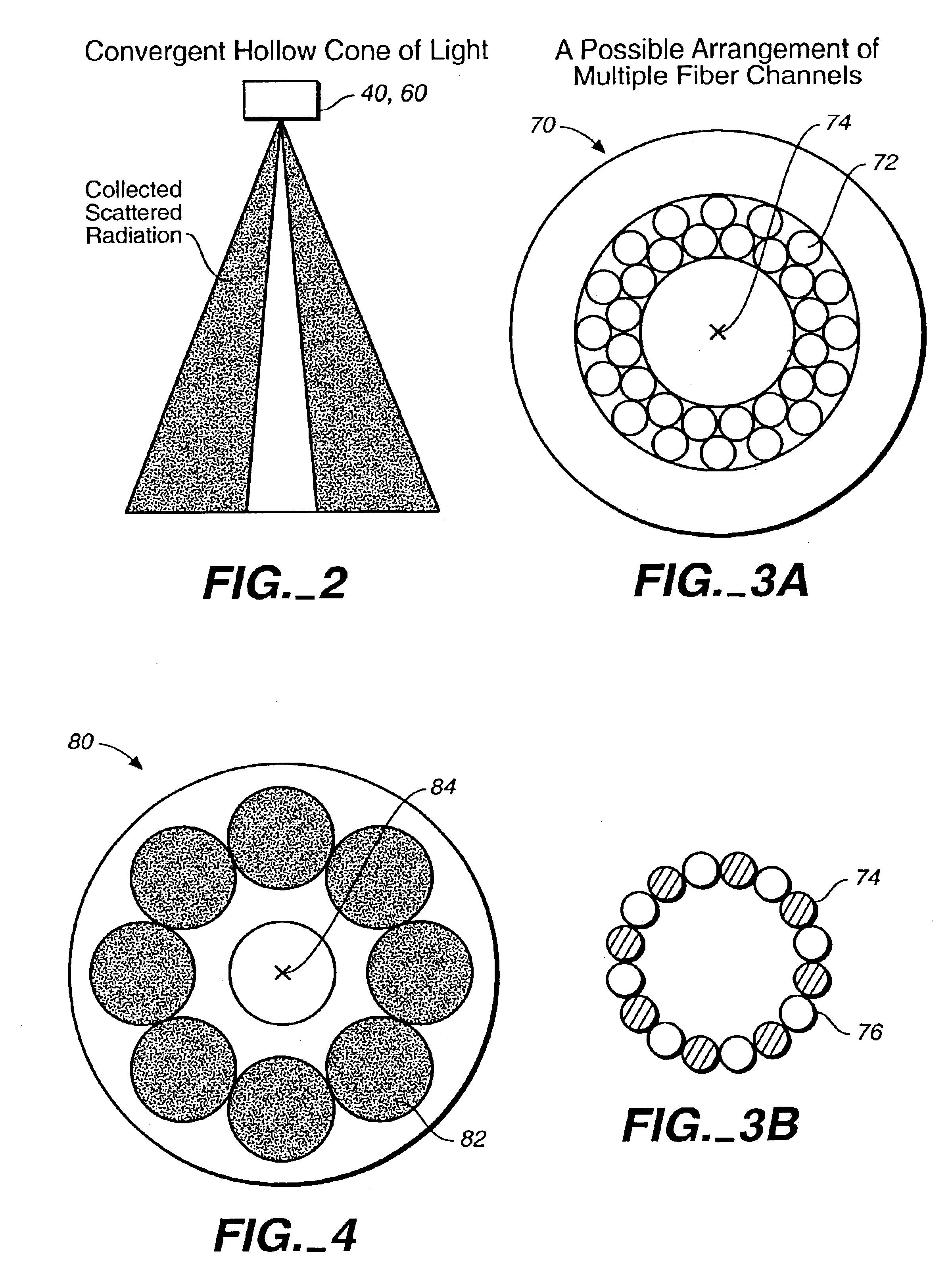
Defect detection system
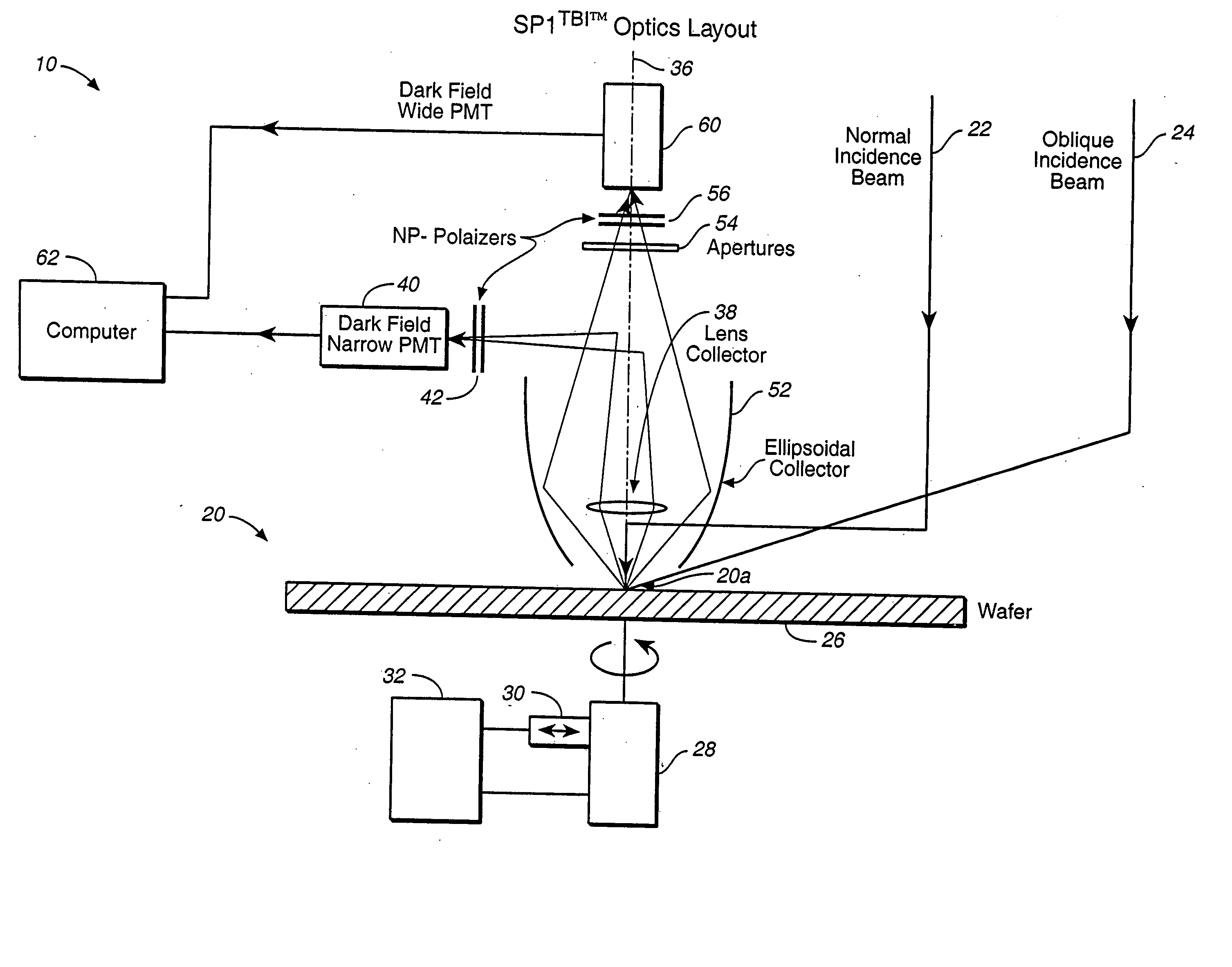
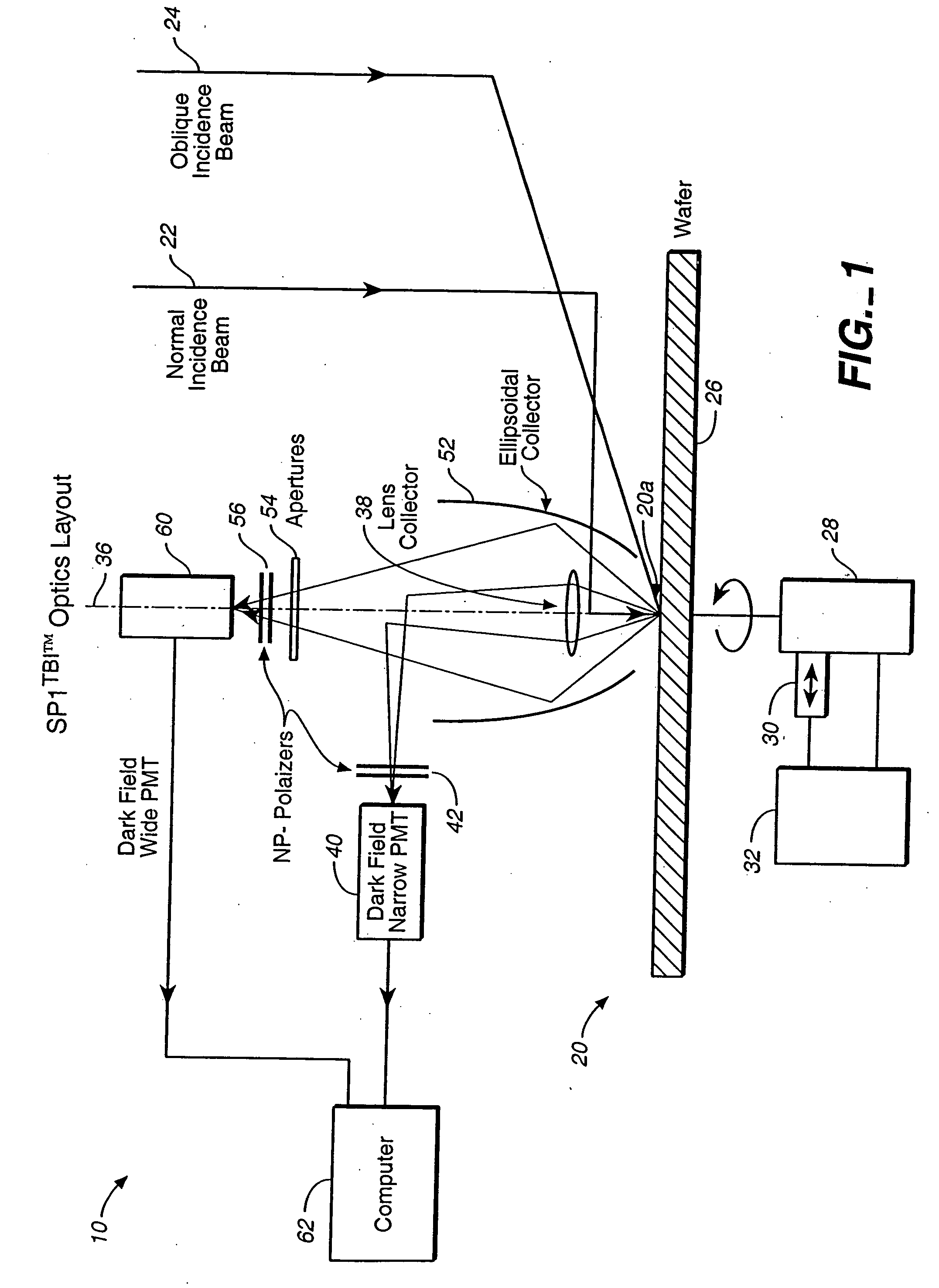
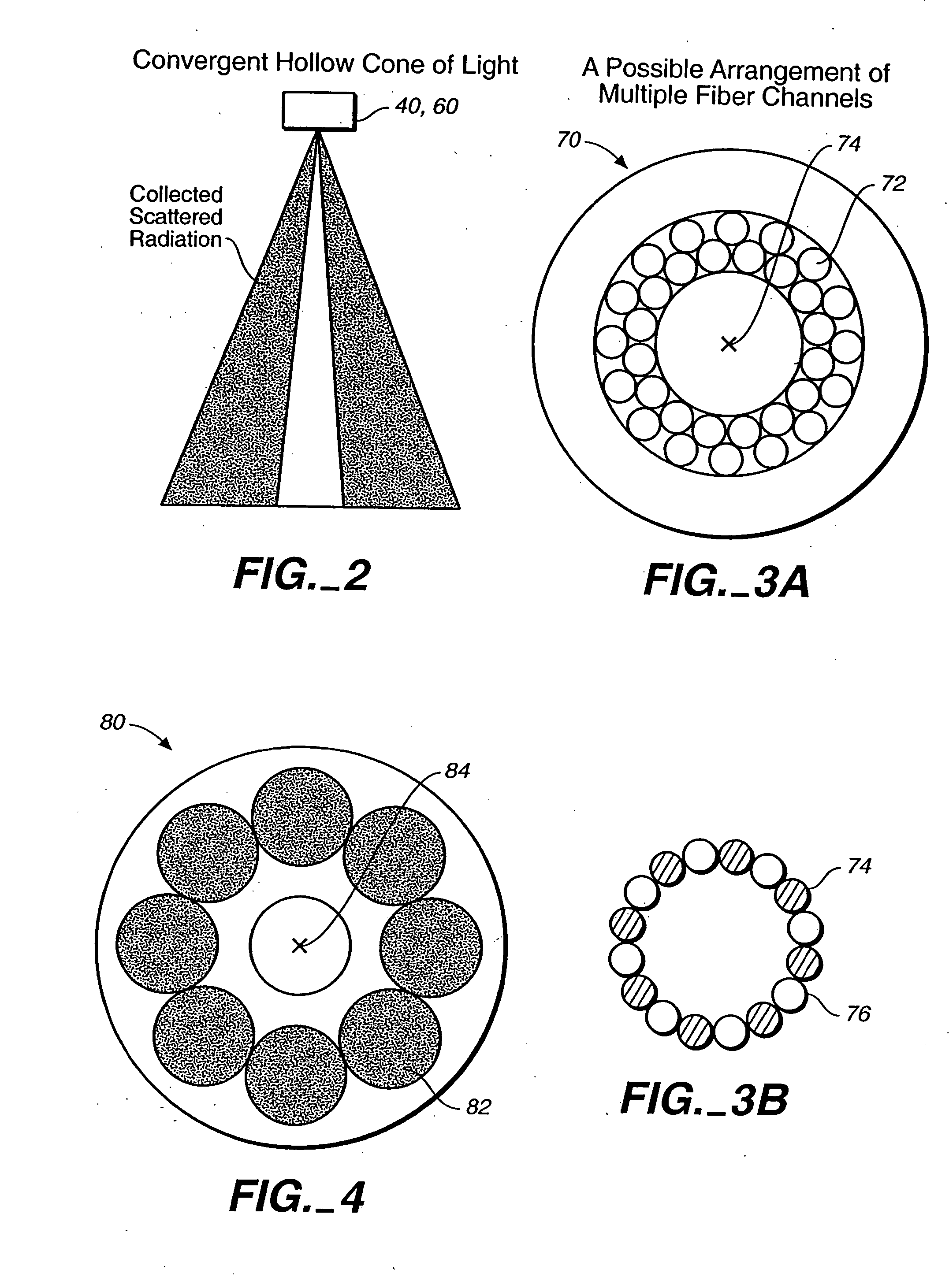
InactiveUS6862096B2Easy to detectReduce crosstalkPhotometry using reference valuePolarisation-affecting propertiesScanning probe microscopyOptical polarization
Scattered radiation from a sample surface is collected by means of a collector that collects radiation substantially symmetrically about a line normal to the surface. The collected radiation is directed to channels at different azimuthal angles so that information related to relative azimuthal positions of the collected scattered radiation about the line is preserved. The collected radiation is converted into respective signals representative of radiation scattered at different azimuthal angles about the line. The presence and / or characteristics of anomalies are determined from the signals. Alternatively, the radiation collected by the collector may be filtered by means of a spatial filter having an annular gap of an angle related to the angular separation of expected pattern scattering. Signals obtained from the narrow and wide collection channels may be compared to distinguish between micro-scratches and particles. Forward scattered radiation may be collected from other radiation and compared to distinguish between micro-scratches and particles. Intensity of scattering is measured when the surface is illuminated sequentially by S- and P-polarized radiation and compared to distinguish between micro-scratches and particles. Representative films may be measured using profilometers or scanning probe microscopes to determine their roughness and by the above-described instruments to determine haze in order to build a database. Surface roughness of unknown films may then be determined by measuring haze values and from the database.
Owner:KLA CORP
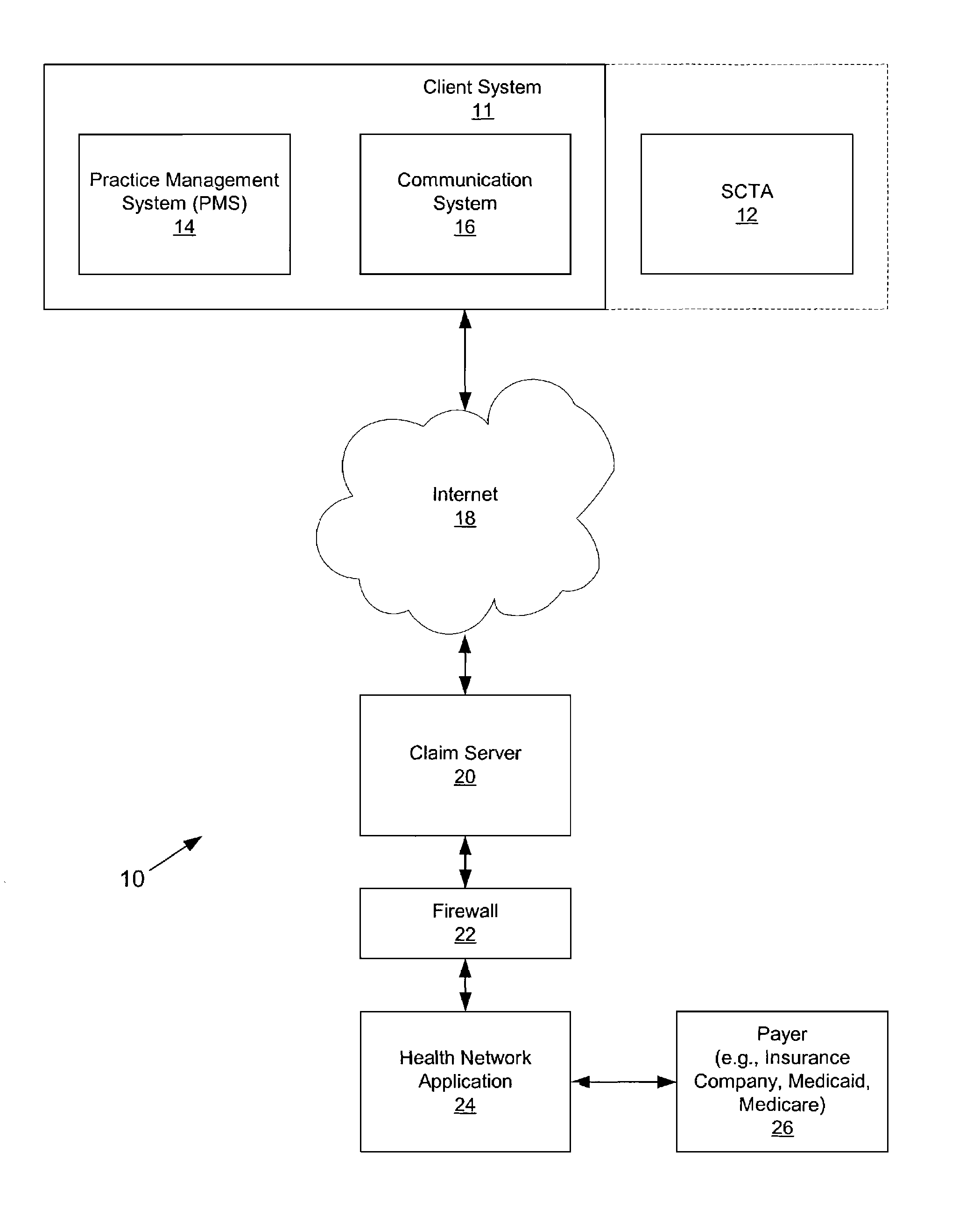
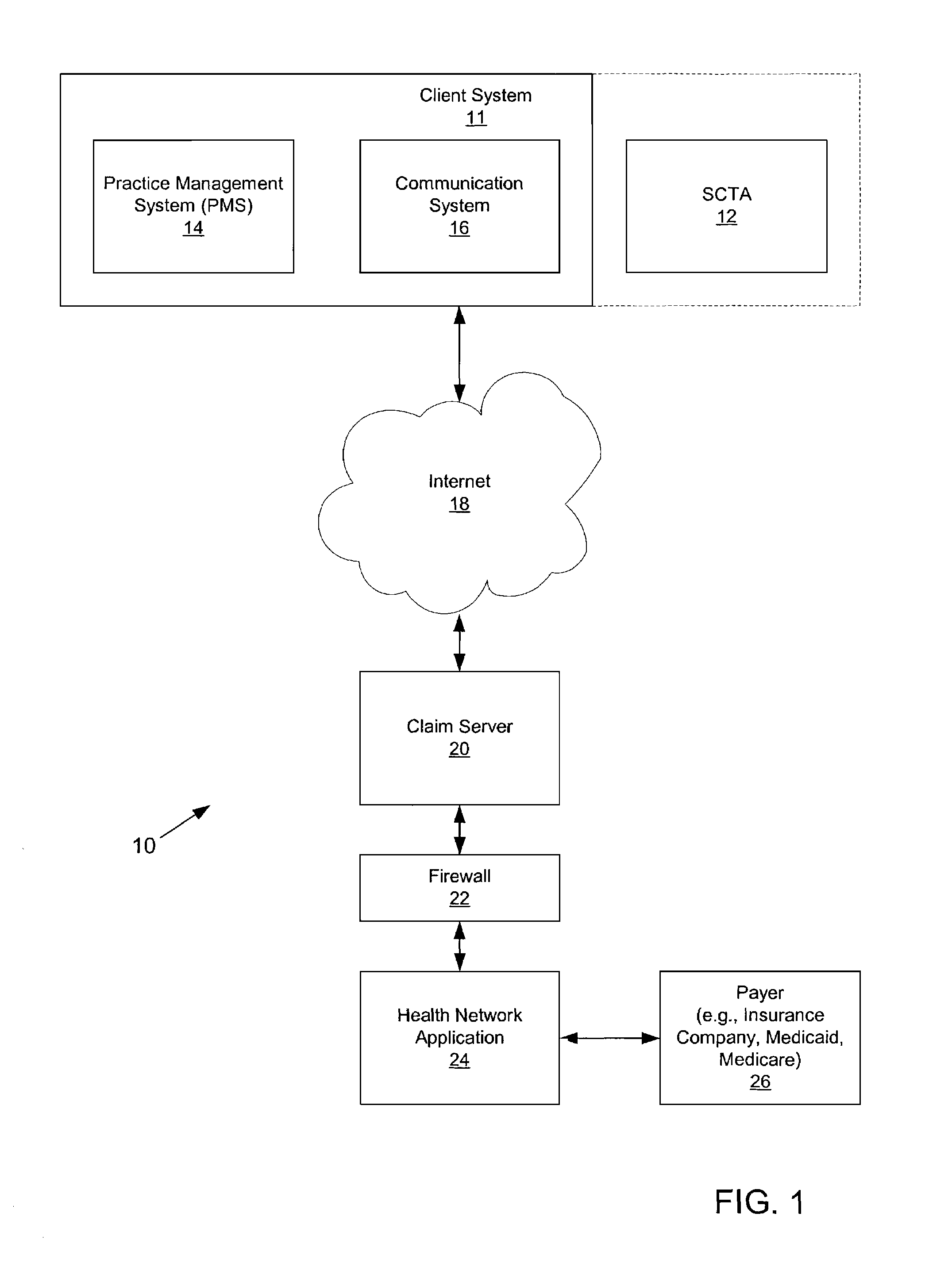
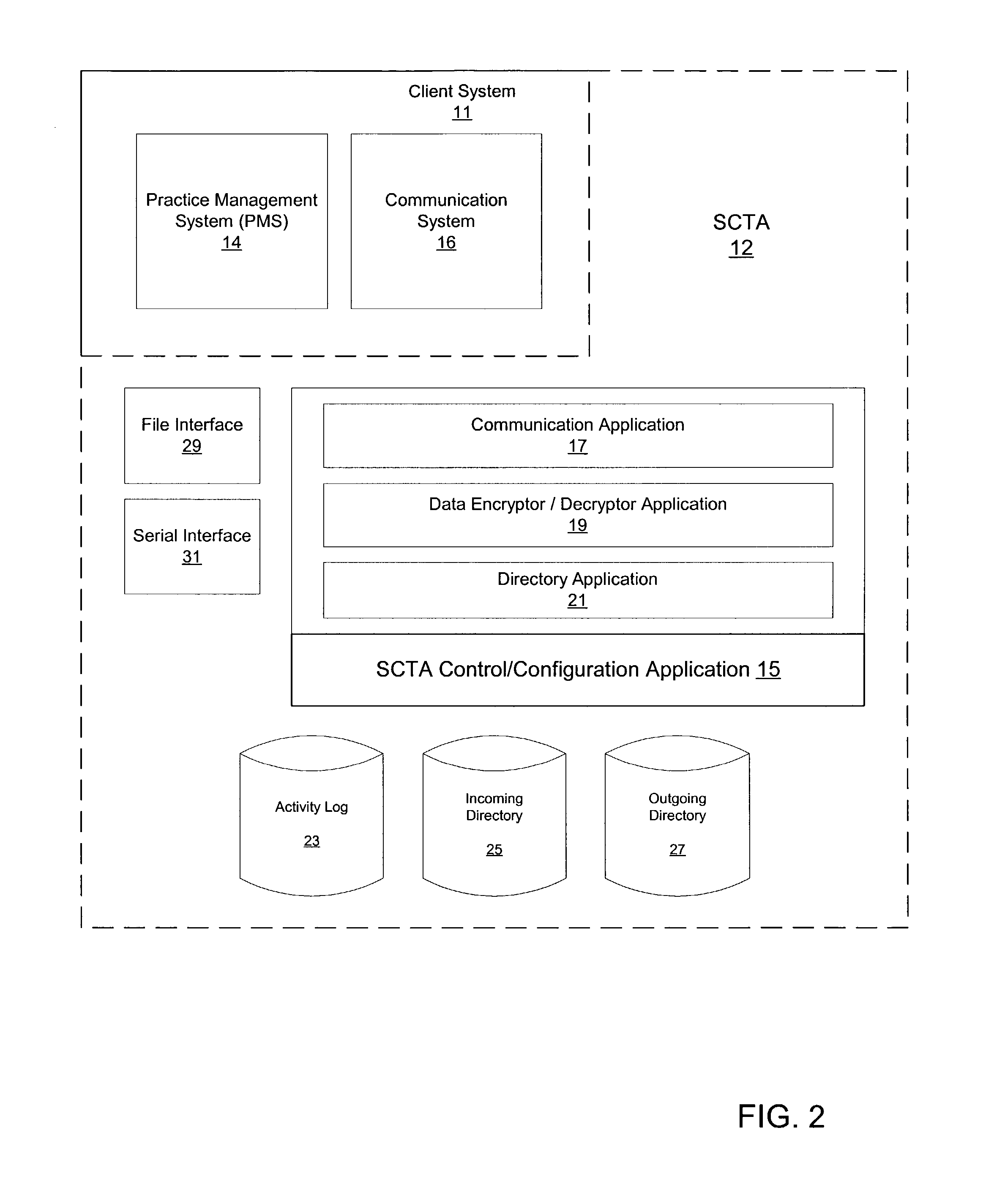
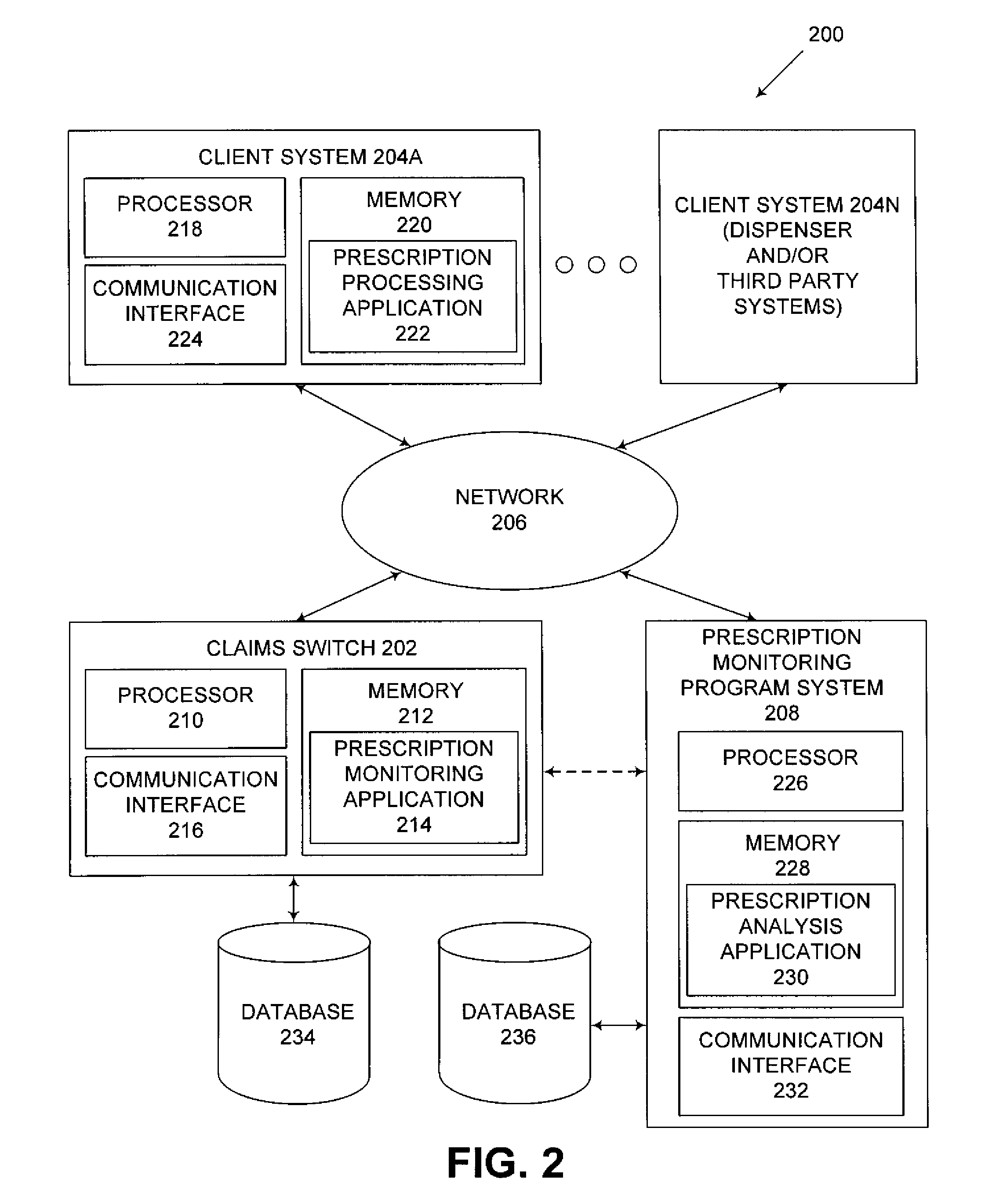
Systems and methods for processing claims in real-time
Claim processing system providing an interface to permit pharmacy and medical management systems to use the Internet to transmit third-party insurance claims on a claim-by-claim basis in real-time or near-real-time to one or more claim servers that receive insurance claim requests over the Internet in an encrypted form. The one or more claim servers decrypt the claim requests and forward them to a health network application which facilitates the submission of the claims to insurance payers and the response of the insurance payers to the requests. Payer responses are received by the claim servers, encrypted and forwarded to the pharmacy and medical management systems in real-time or near real-time.
Owner:MCKESSON FINANCILA HLDG LTD +1
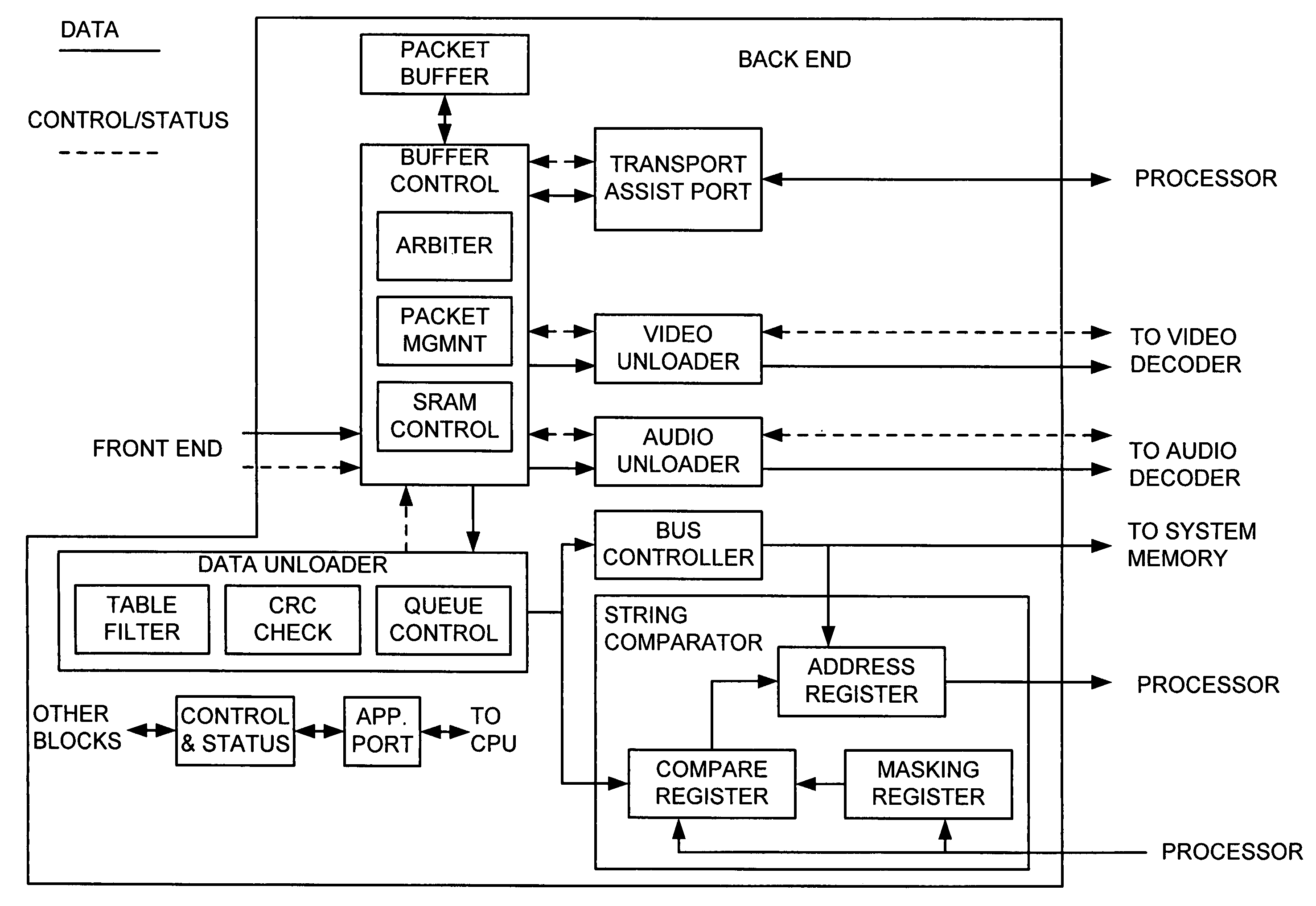
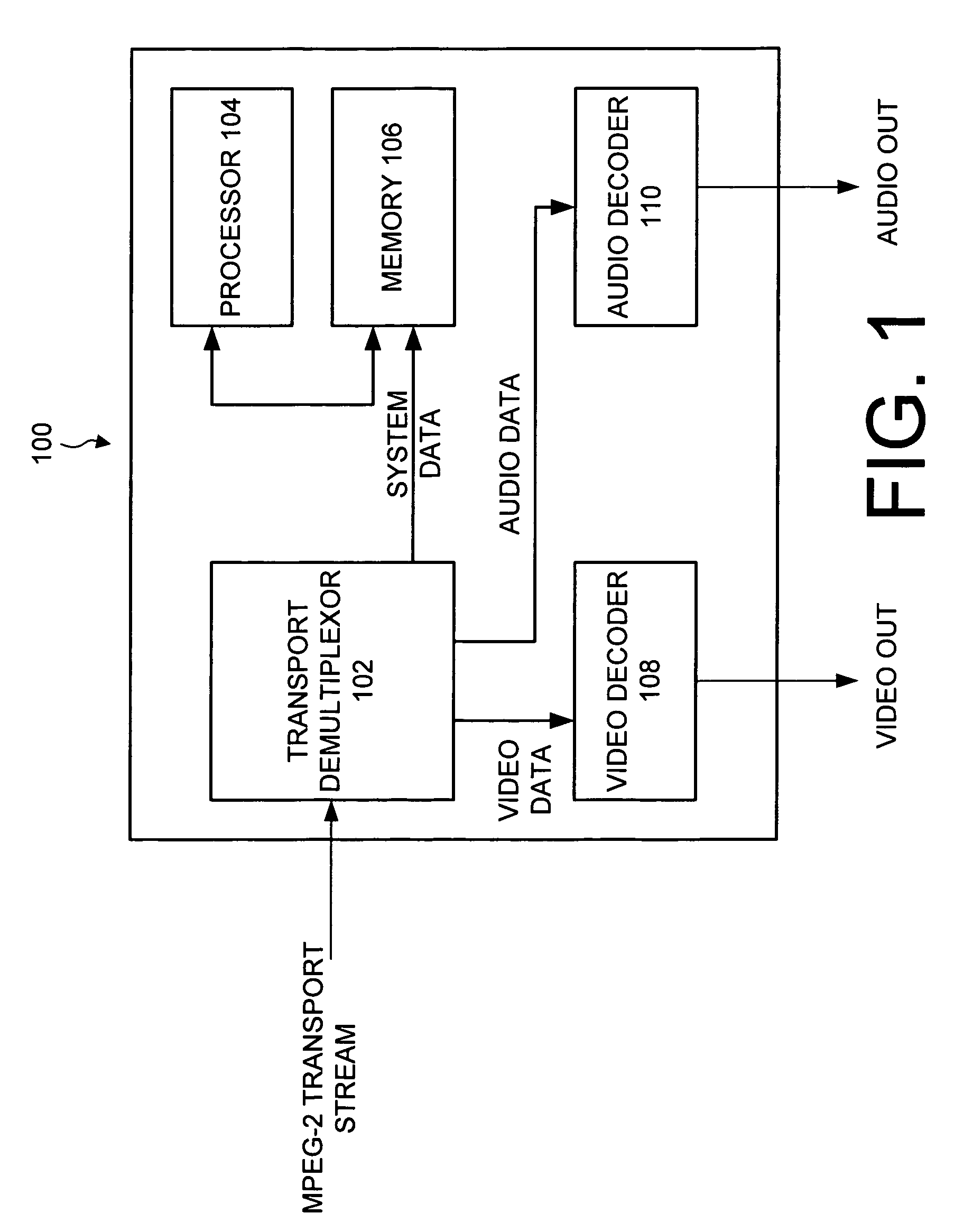
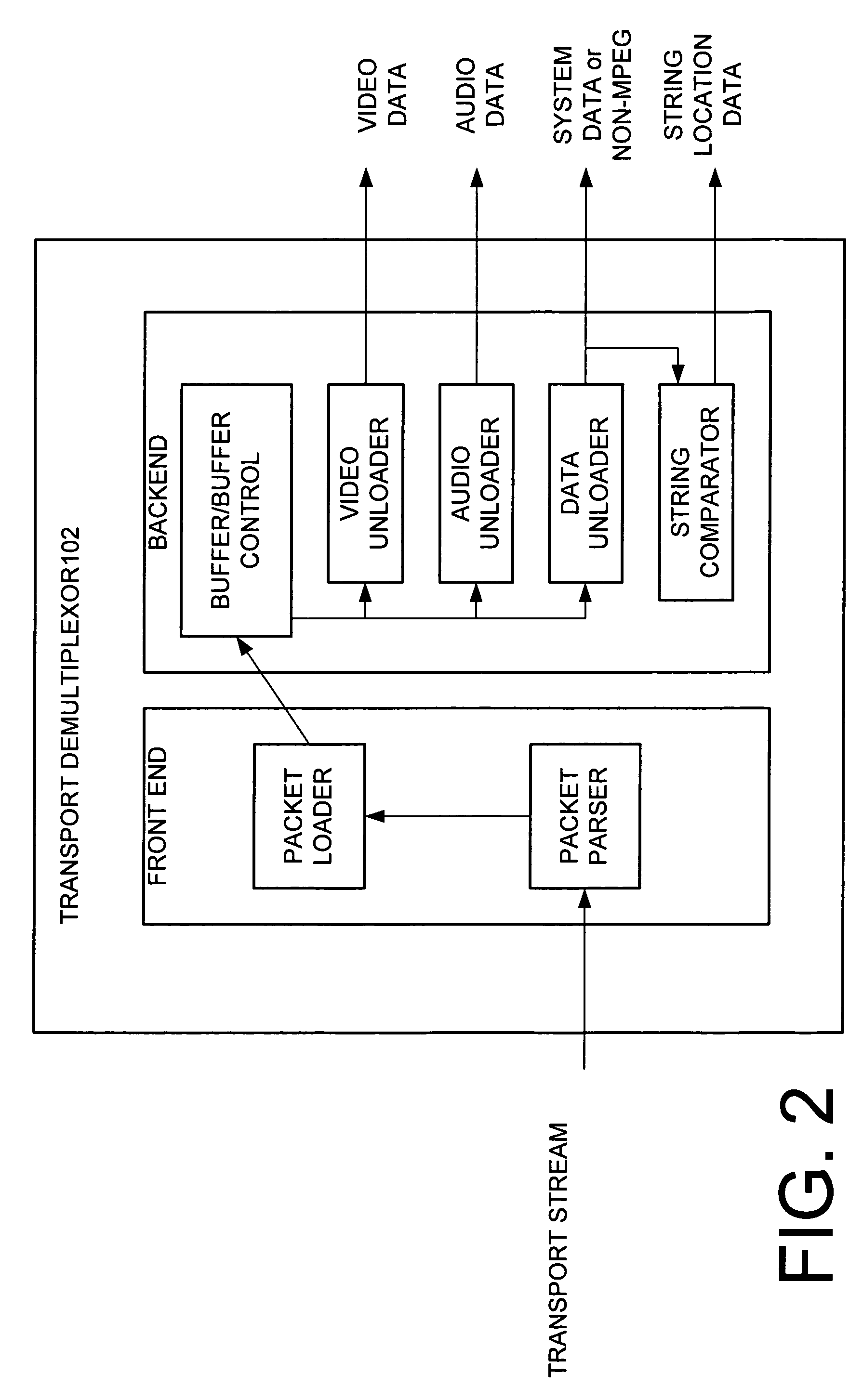
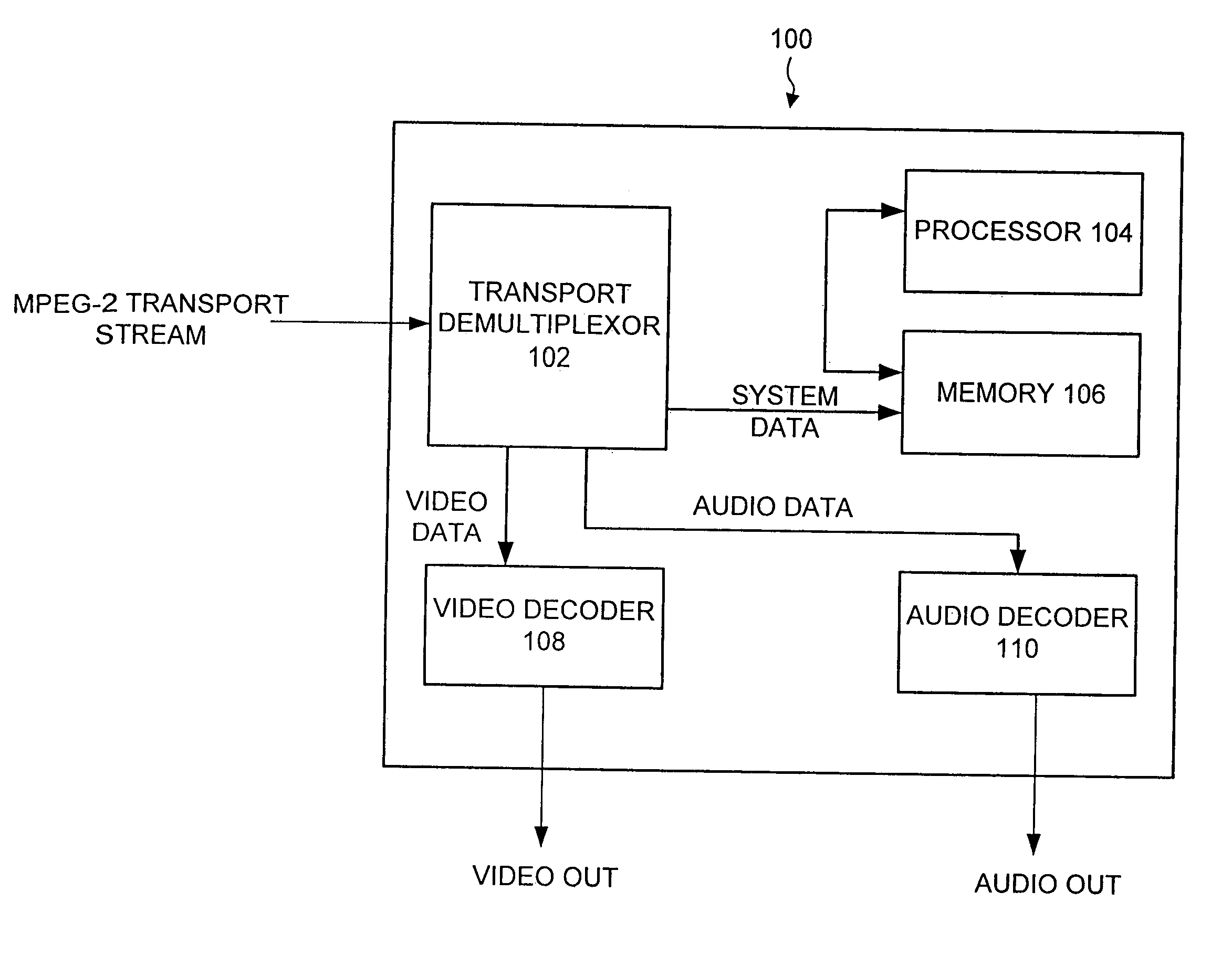
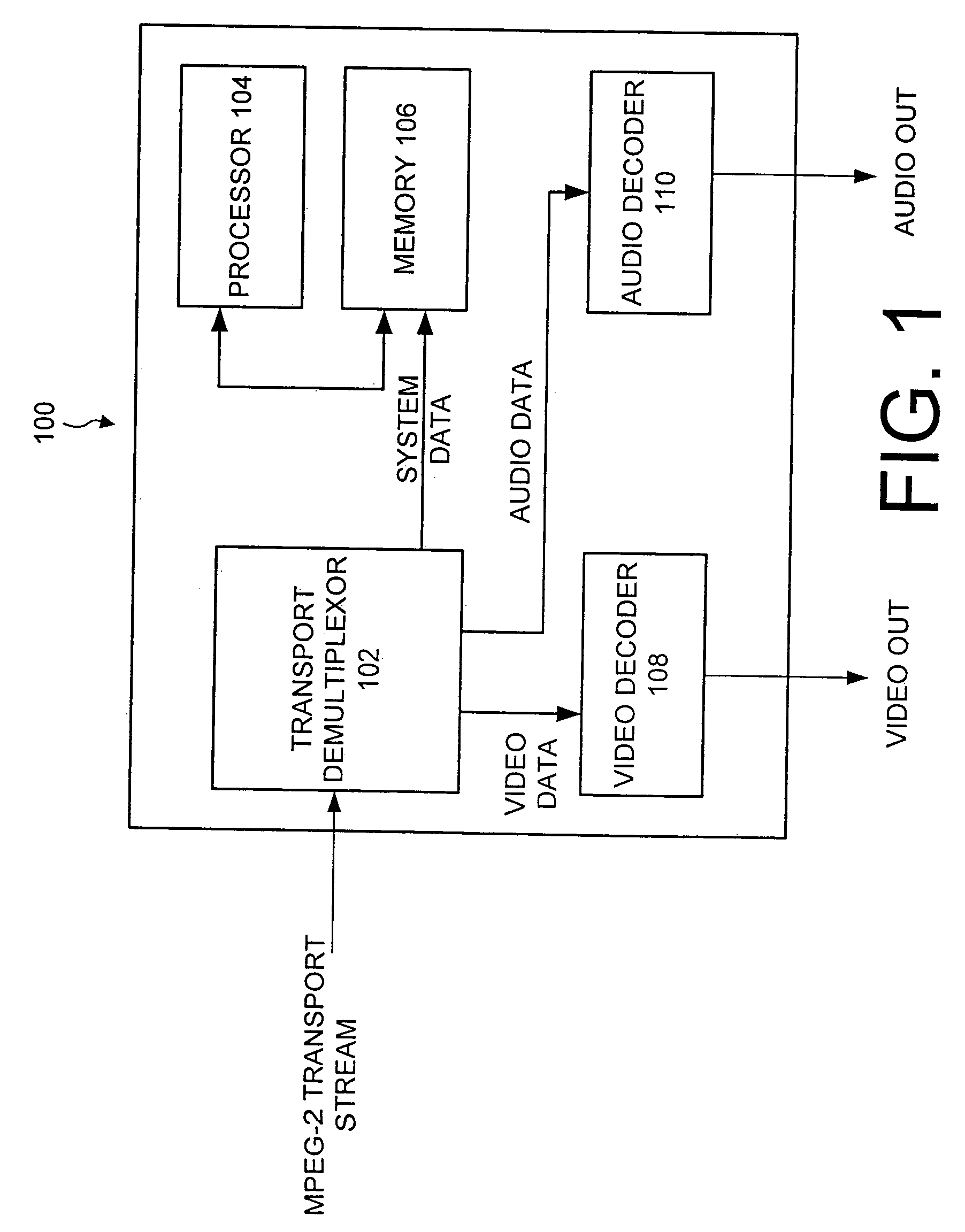
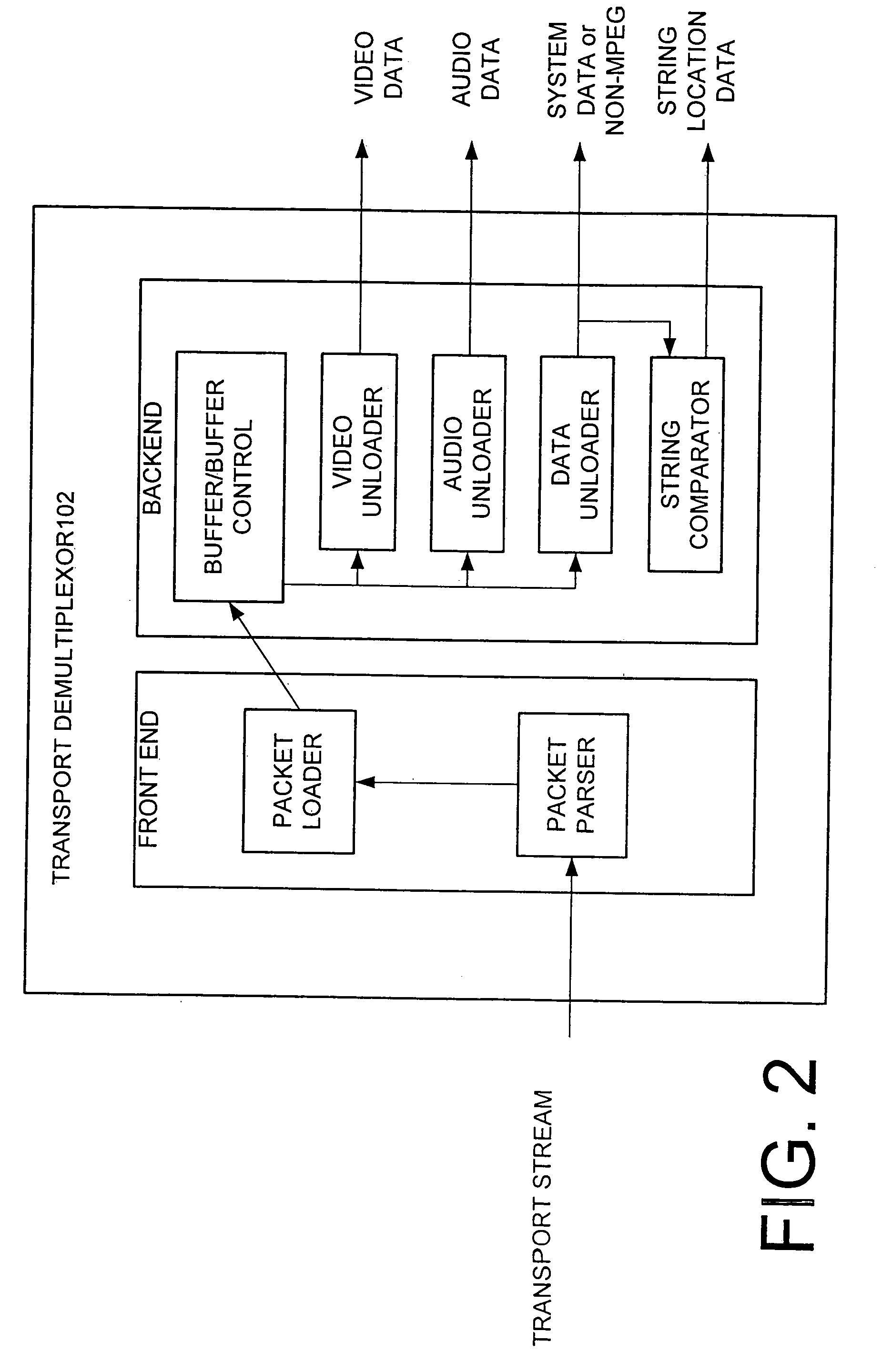
Transport demultiplexor with bit maskable filter
InactiveUS7024685B1Facilitate real time filteringGood real timeGHz frequency transmissionTime-division multiplexData matchingFilter system
The preferred embodiment of the present invention provides an improved transport demultiplexor that can receive and filter different data types before sending the data to system memory. The preferred embodiment provides a string comparator to facilitate real time filtering of continuous incoming data before loading the data into system memory. The string comparator preferably uses a bit-maskable matching filter that filters system data in real time as the data is being delivered to system memory. When data matching the filter is located, the destination address of that data is determined and delivered to the processor. This allows the processor to quickly locate the desired data and thus facilitates the real time processing of that data.
Owner:IBM CORP
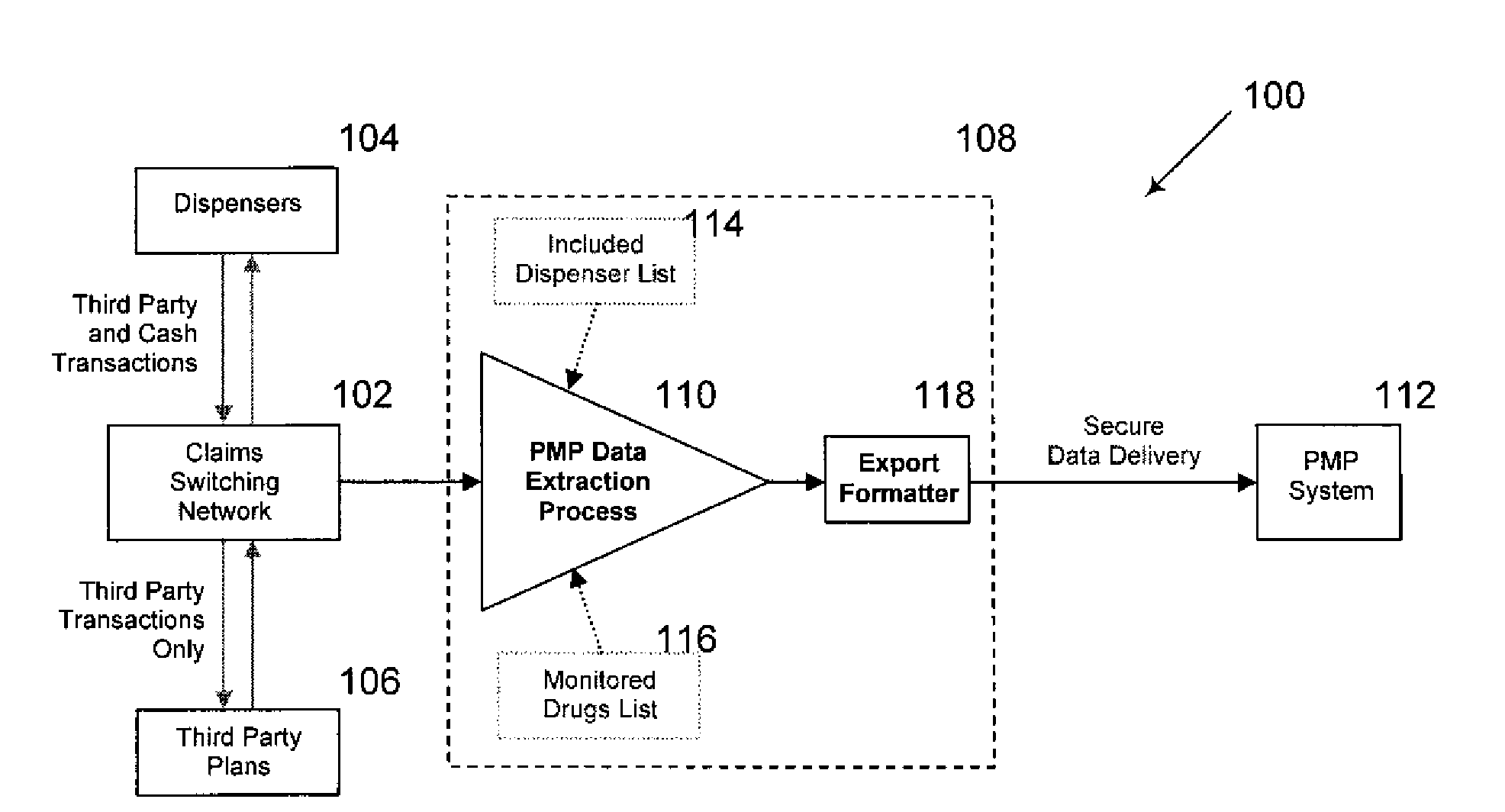
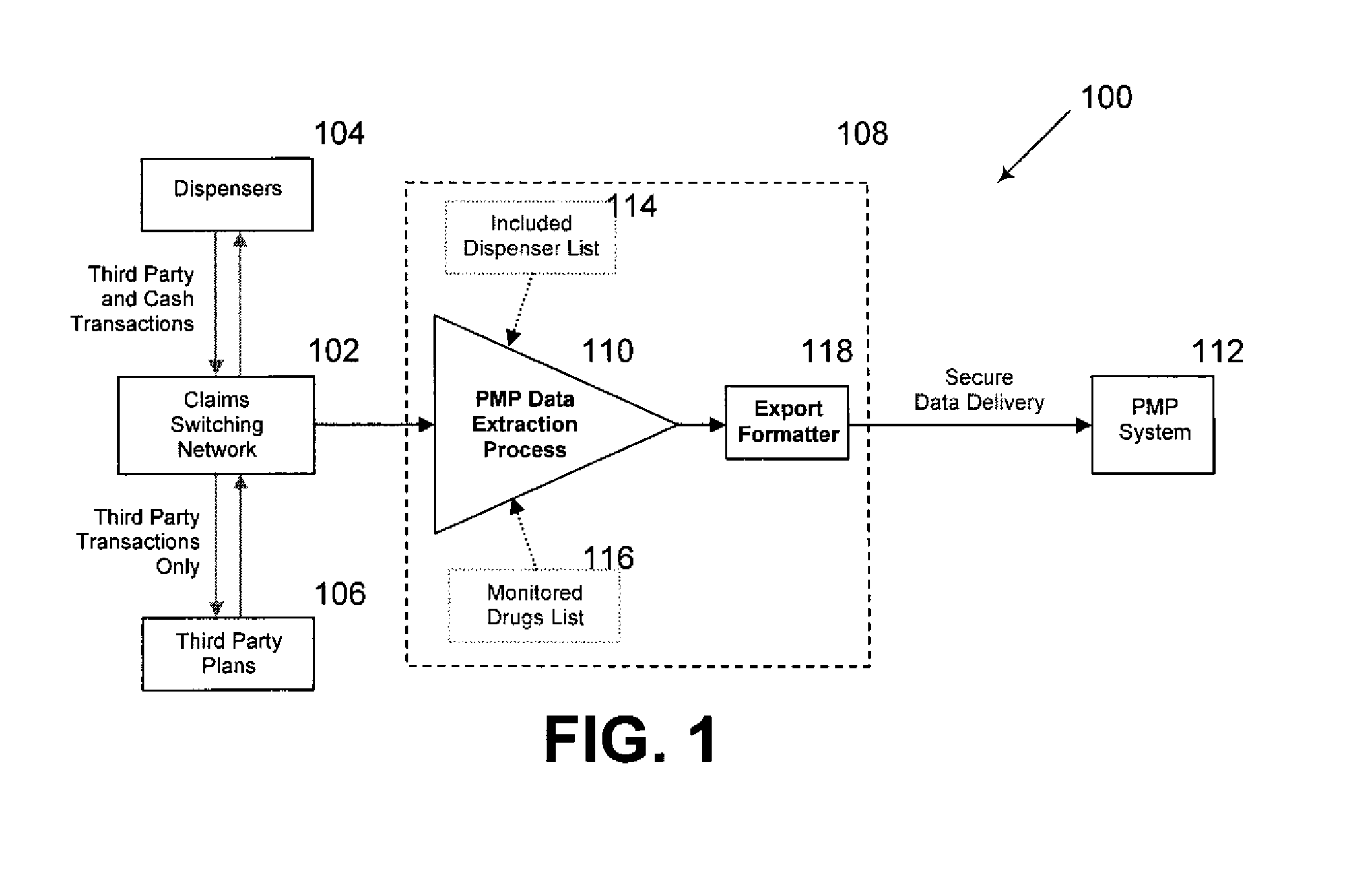
Systems and Methods for Controlled Substance Prescription Monitoring Via Real Time Claims Network
InactiveUS20090164376A1Easy to process in real timeEasy to processFinanceDrug and medicationsPrescription monitoringData mining
Embodiments of the invention can provide systems and methods for controlled substance prescription monitoring via a real time claims network. In one embodiment, a method for facilitating real-time processing of claims associated with one or more controlled substances can be provided. The method can include receiving a plurality of claims from a claims transaction switch, wherein each of the claims relates to both at least one predefined provider and at least one monitored controlled substance. In addition, the method can include validating some or all of the plurality of claims. Furthermore, the method can include formatting and transmitting data from validated claims to a prescription monitoring program system.
Owner:MCKESSON FINANCIAL HLDG
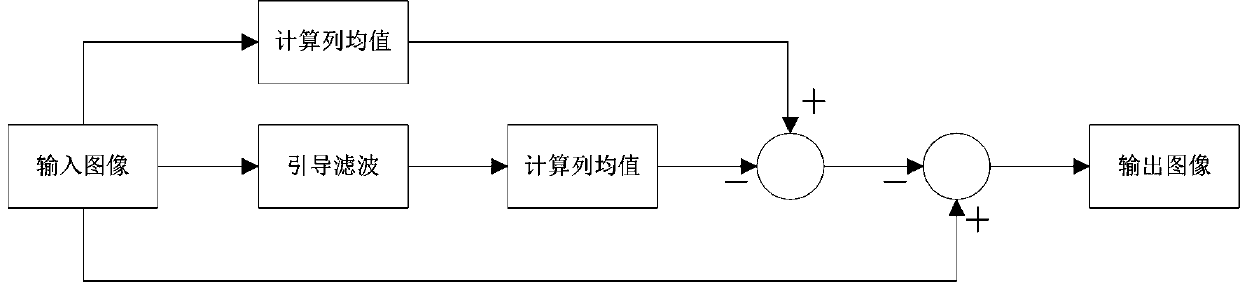
Infrared image stripe noise filtering method
InactiveCN107767346ACancel noiseImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage analysisComputation complexityImaging quality
The invention discloses an infrared image stripe noise filtering method, which comprises the following steps: 1) receiving image data obtained after preprocessing and output by an infrared focal planedetector; 2) carrying out guide filtering processing on the input image to obtain a base graph of the input image; 3) subtracting the mean value of each row or / and each column of pixels of the inputimage by the mean value of each row or / and each column of pixels of the base graph image to obtain stripe noise superposition amount of each row or / and each column of pixels of the input image; and 4)subtracting the pixel value of the input image by the stripe noise superposition amount of the row or / and the column of the pixels to obtain an output image of the infrared image after stripe noise removal processing. The method can effectively remove horizontal and vertical stripe noise of infrared focal plane imaging, improves image quality, is low in computation complexity and is convenient for realizing real-time processing.
Owner:HUBEI JIUZHIYANG INFRARED SYST CO LTD
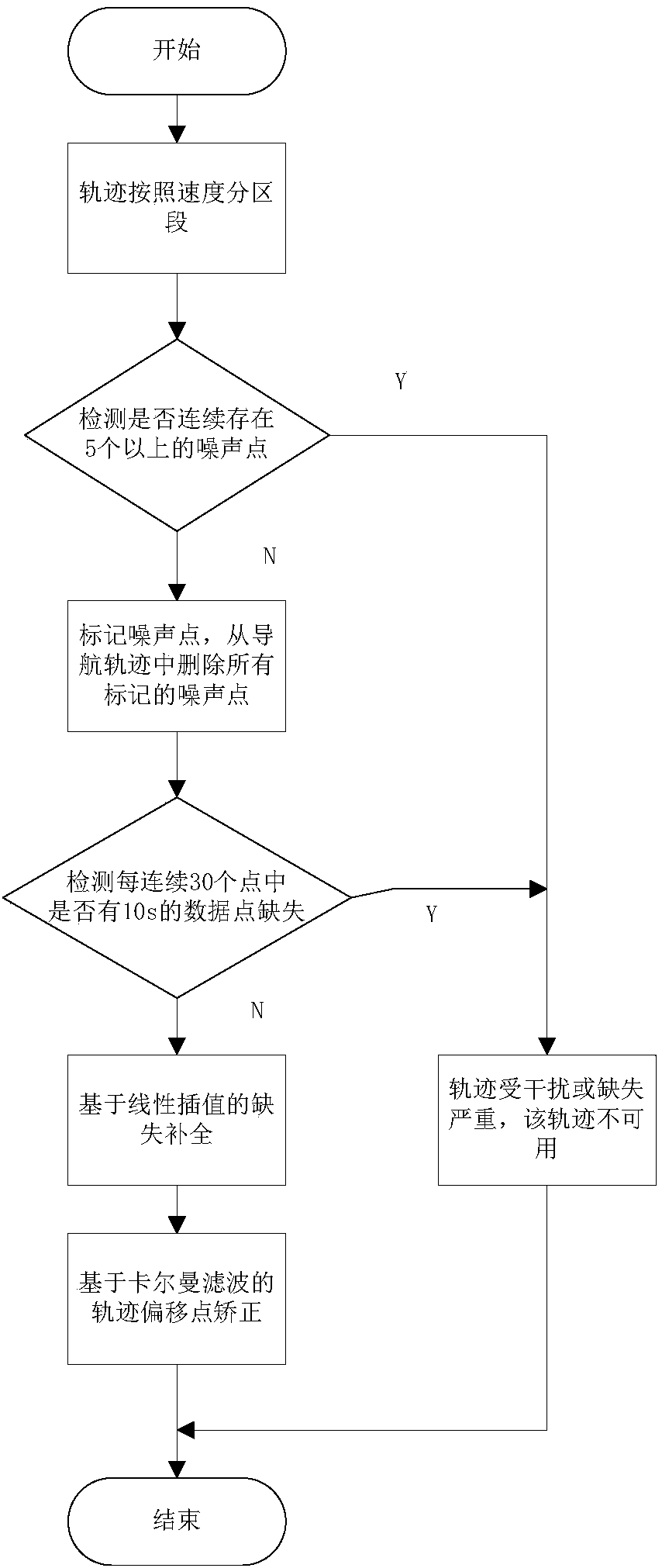
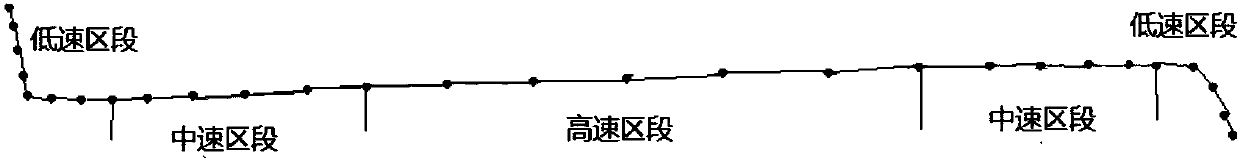
Vehicle navigation trail point offset correction method based on Kalman filtering
InactiveCN110031876AImprove usabilityEasy to process in real timeSatellite radio beaconingUsabilityCorrection method
The invention discloses a vehicle navigation trail point offset correction method based on Kalman filtering. The method comprises the following steps of step 1: de-noising the trail points in the navigation trail; step 2: complementing the missing points in the navigation trail; and step 3: performing offset correction on the de-noised and complemented navigation trail points by Kalman filtering.The offset points obeying Gaussian distribution are well corrected within a reasonable range by using the Kalman filter algorithm, and the navigation trail returned by the user positioning equipment is closer to the real driving trail by correcting the offset points of the historical navigation trail, thereby improving the usability of the historical navigation trail.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Optimal active time-reversal focusing method based on iterative least square/pre-filtering
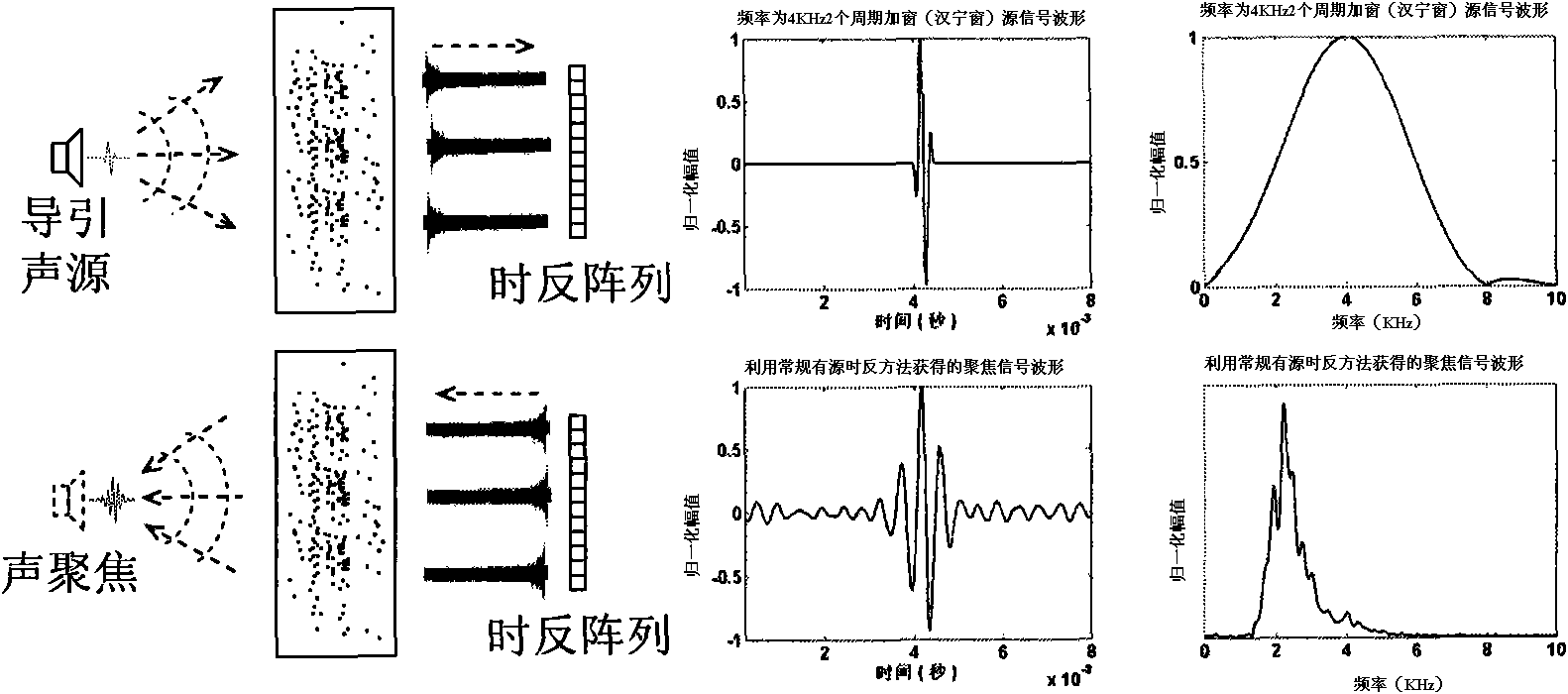
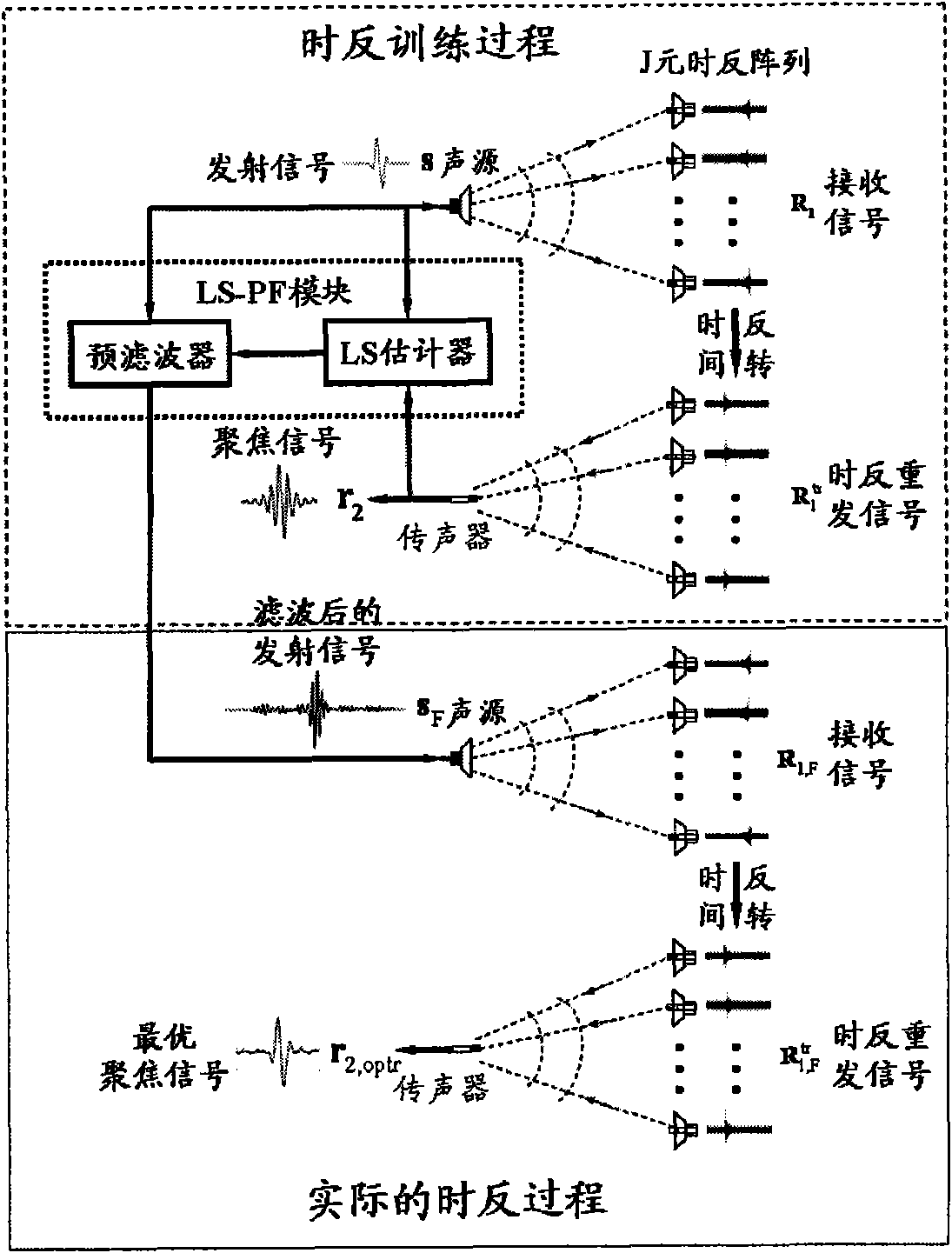
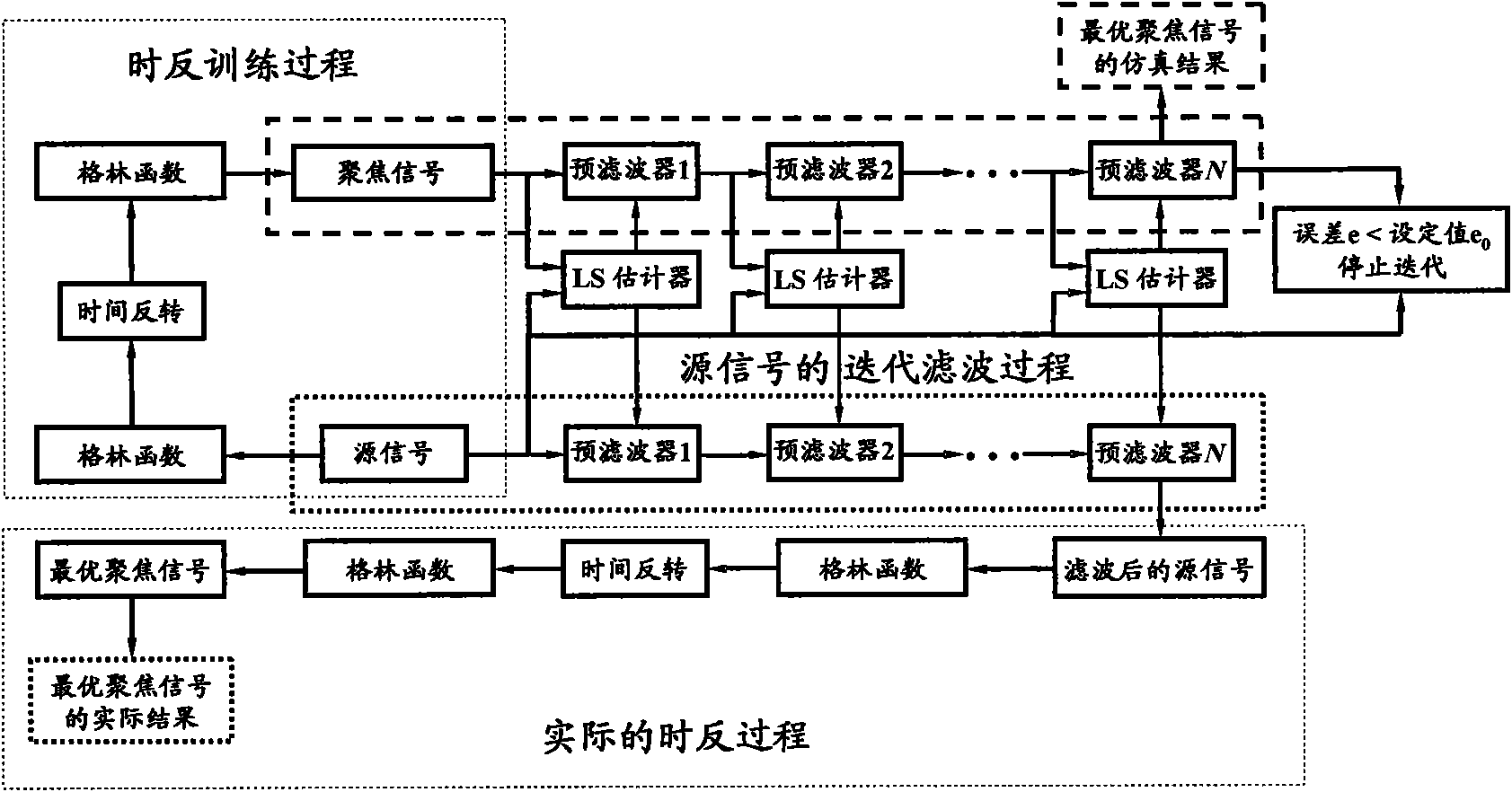
ActiveCN101645264ARealize inverse filter focusing in time domainEliminate focus blurAdaptive networkSound producing devicesSound sourcesSonification
The invention relates to an optimal active time-reversal focusing method based on iterative least square / pre-filtering. The method comprises the following steps: 1) sending source signals by a guide sound source, and conducting the operations of receiving, time-reversal and re-sending by a time-reversal array according to the conventional active time-reversal process, so as to acquire focusing signals at the location point of the sound source, wherein the source signals are wideband pulse signals with the bandwidth being 20Hz to 200kHz and the frequency range being within an audible sound or ultrasound frequency band range; 2) estimating a plurality of cascaded pre-filter time-domain responses used for carrying out the filtration treatment on the source signals on the basis of the iterative least square rule by combining the source signals and the focusing signals; and 3) re-sending the pre-filtered source signals by the guide sound source, and carrying out the operations of receiving,time-reversal and re-sending by the time-reversal array according to the conventional time-reversal process, so as to acquire the optimal focusing signal waveform at the location of the sound source.The invention can achieve the inverse-filtering and focusing effects within the time domains and recover the waveform of the source signals within the focusing region; the invention allows the randomdistribution of array elements and the difference in the frequency response among the array elements; and the invention has high spatial resolution.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Steel plate surface defect image extraction method
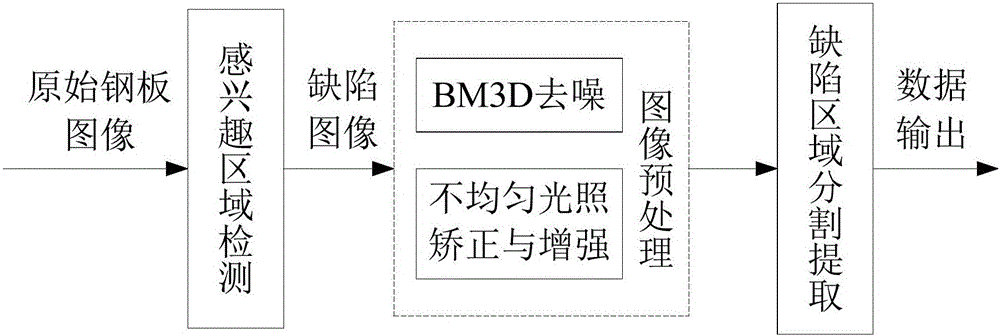
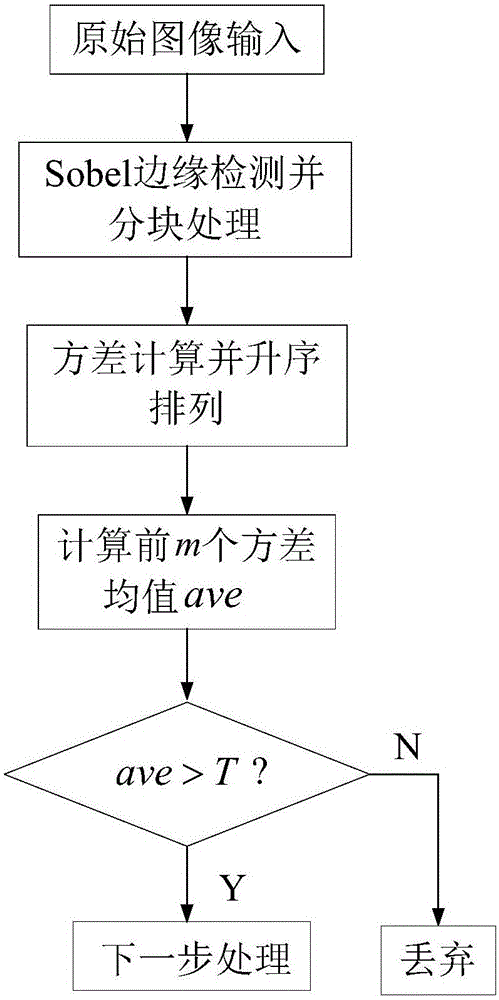
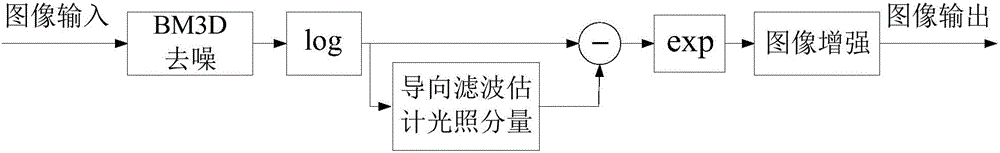
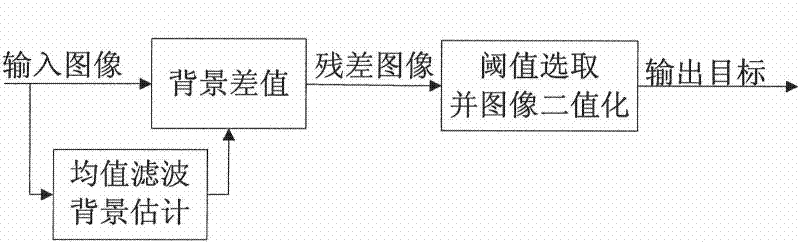
InactiveCN106780486AImprove efficiencyEasy to process in real timeImage enhancementImage analysisImage extractionPre treatment
The invention provides a steel plate surface defect image extraction method. The method is characterized by including the following steps that steel plate surface images are subjected to ROI detection, and non-defect images are removed; defect images are sequentially read, the images are preprocessed, the influences of noise and non-uniform illumination on the defect segmentation effect are removed, and the foreground and background contrast ratio is increased; the preprocessed steel plate defect images are subjected to defect region segmentation extraction through Center-Surround Difference, and finally data is output. The efficiency of an image extraction algorithm is improved, it is not needed to occupy large memory space, real-time processing is convenient, the influence of the noise is effectively weakened, wrong extraction, caused by illumination and brightness unevenness, of the images is avoided, the contrast ratio is increased, the defect extraction effect is more excellent, and details are complete.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Single-frame infrared image based real-time detection method of point target
InactiveCN102346910AEasy to realize real-time detectionEasy to process in real timeImage analysisPoint targetInfrared image
The invention relates to a single-frame infrared image based real-time detection method of a point target, which handles each pixel through the steps that: (1) whether a pixel is the maximum point in an adjacent area or not is judged by comparing the gray between the pixel and other pixels in the 3*3 adjacent area; (2) the average gray value of a 3*3 adjacent area which takes the pixel as the central pixel is calculated; the proportion of the difference between the gray value of the central pixel and the average gray value, in the average gray value filter of the sum of the differences between the all pixels with the gray values being more than the average gray value and the average gray value, is calculated, the determination result of the point is set to be 1, and otherwise, the determination result of the point is set to be 0; (3) the proportion of the pixel in four directions is respectively calculated; if the proportion in each direction is more than a set edge detection proportion threshold, the determination result of the point is set to be 1, and otherwise, the determination result of the point is set to be 0; and (4) the determination results of Step (2) and Step (3) are summated as the value of the point in a final binarization value.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
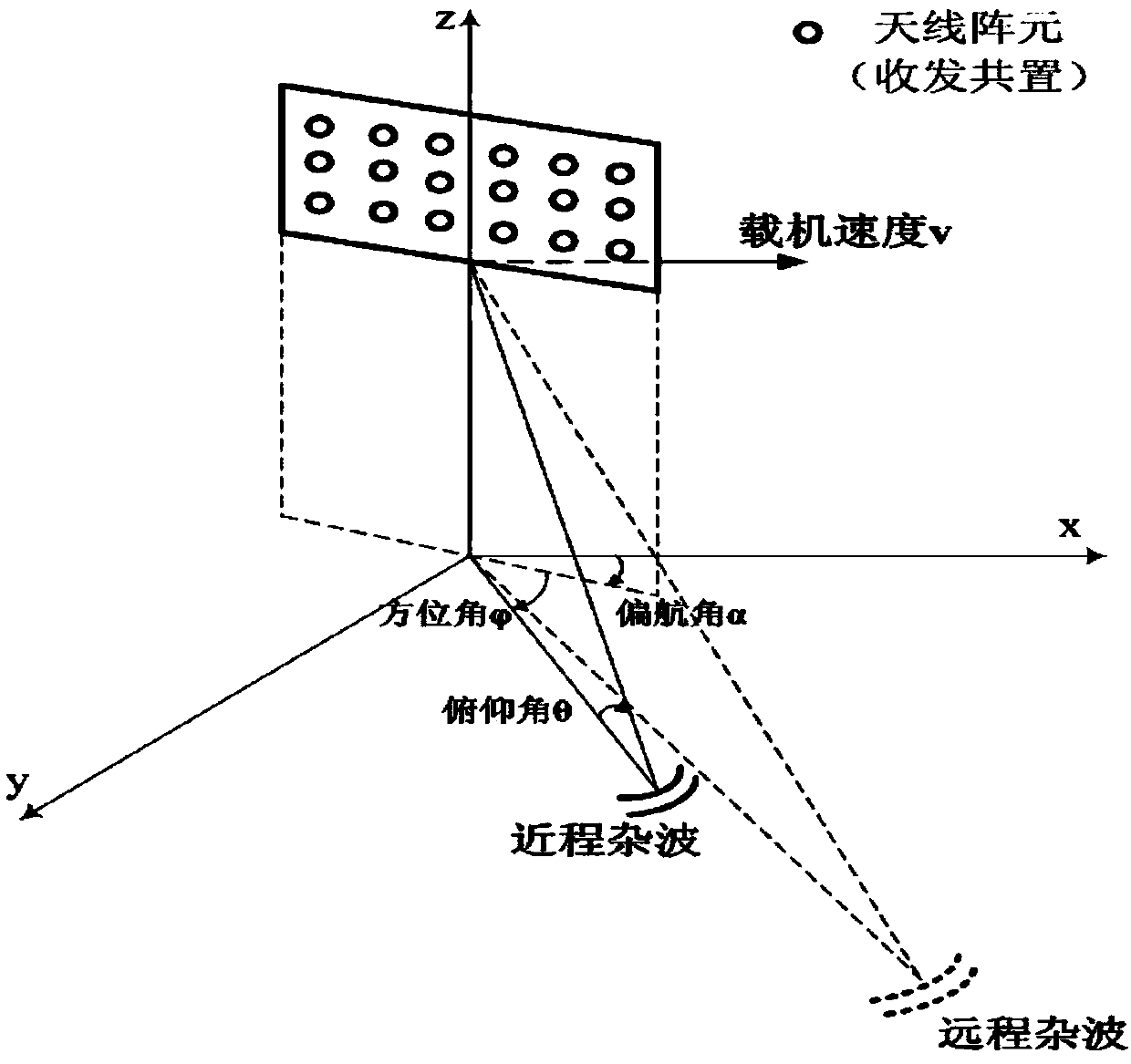
Non-adaptive airborne non-side-looking radar short-range clutter suppression method
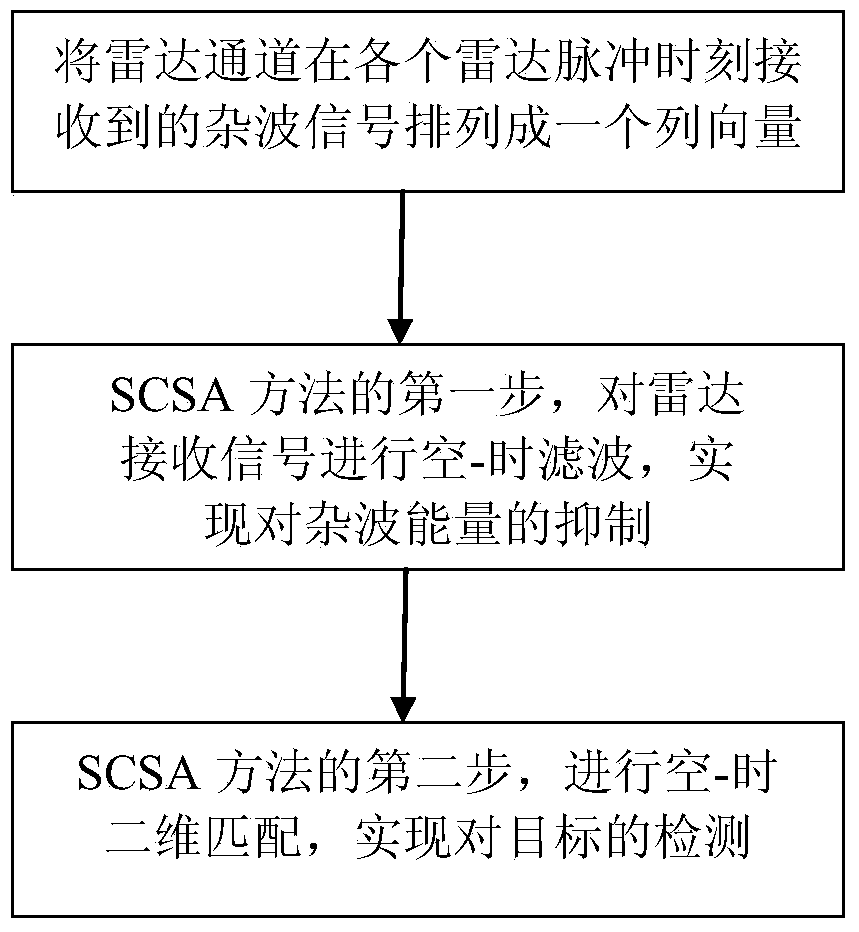
InactiveCN103744067ACan not meet the requirements of real-time processingMeet the requirements of real-time processingWave based measurement systemsComputation complexityRadar
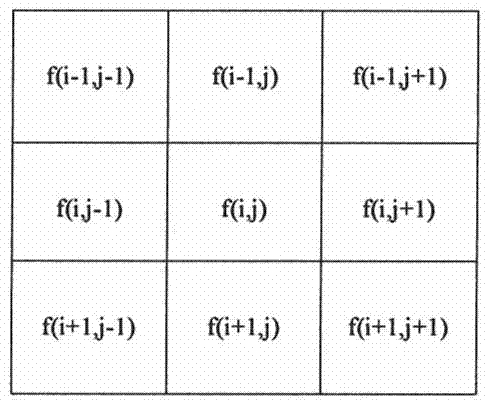
The invention discloses a non-adaptive airborne non-side-looking radar short-range clutter suppression method. A non-adaptive short-range clutter suppression method formed by space-time filtering and space-time matching is used for suppressing airborne radar short-range clutter. The method comprises the steps of firstly arranging received signals of all channels of radar into a column vector, then performing space-time filtering to the received signals to suppress clutter energy, and finally performing space-time two-dimensional matching to realize the detection of a target. The non-adaptive airborne non-side-looking radar short-range clutter suppression method overcomes the defects that a great number of training samples which satisfy independent and identical distribution conditions are needed when the traditional adaptive clutter suppression method is applied to airborne radar, the calculation amount is great and the performance during short-range clutter suppression is seriously decreased. Compared with the traditional adaptive clutter suppression method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that since the method is a non-adaptive method, the method is not influenced by non-uniform samples, the calculation complexity is low, the clutter suppression can be conveniently and quickly realized and the detection of the target is more greatly facilitated.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Linear array CCD spatial target posture based measuring systems and its measurement method
InactiveCN101216289AOvercome precisionHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansPhysicsImage sensor
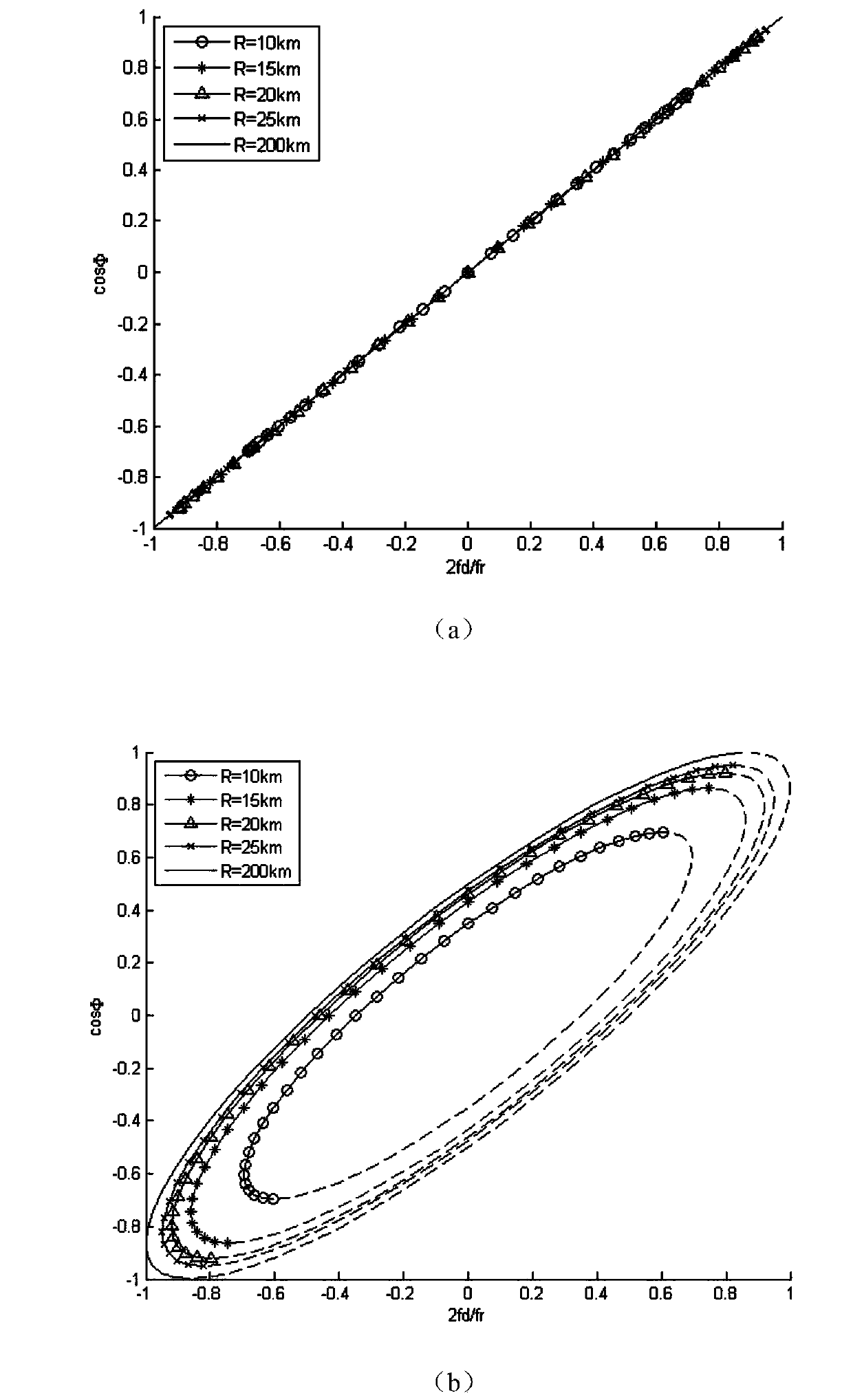
The invention provides an aerial target attitude measurement system based on linear CCD and a method thereof. The three-dimensional coordinates of three point cooperative targets arranged on a measured object in conformity to certain rules, carrying the attitude information thereof and corresponding to the wavelength range of optical filters arranged on reconstruction subsystems are respectively reconstructed by three three-dimensional coordinate reconstruction subsystems composed of nine selective one-dimension imaging units arranged with the optical filters, and the attitude angle of the measured target can be determined by spatial resolution. The invention also provides a special embedded system in pipeline system and with multiple parallel CPUs, and composed of the combined device, control panels of one-dimension imaging units, a main control panel, an extended LCD and a keyboard. The invention overcomes the contradiction of speed and precision when measuring the aerial target attitude with planar array image sensor as information input equipment, is easy to fulfill the real-time requirement of aerial target attitude measurement, and can be conveniently used.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Transport demultiplexor with bit maskable filter
InactiveUS20060080110A1Facilitate real time filteringGood real timeMultiplex communicationSpeech analysisData matchingFilter system
The preferred embodiment of the present invention provides an improved transport demultiplexor that can receive and filter different data types before sending the data to system memory. The preferred embodiment provides a string comparator to facilitate real time filtering of continuous incoming data before loading the data into system memory. The string comparator preferably uses a bit-maskable matching filter that filters system data in real time as the data is being delivered to system memory. When data matching the filter is located, the destination address of that data is determined and delivered to the processor. This allows the processor to quickly locate the desired data and thus facilitates the real time processing of that data.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Integrated method suitable for real-time processing of BM3D
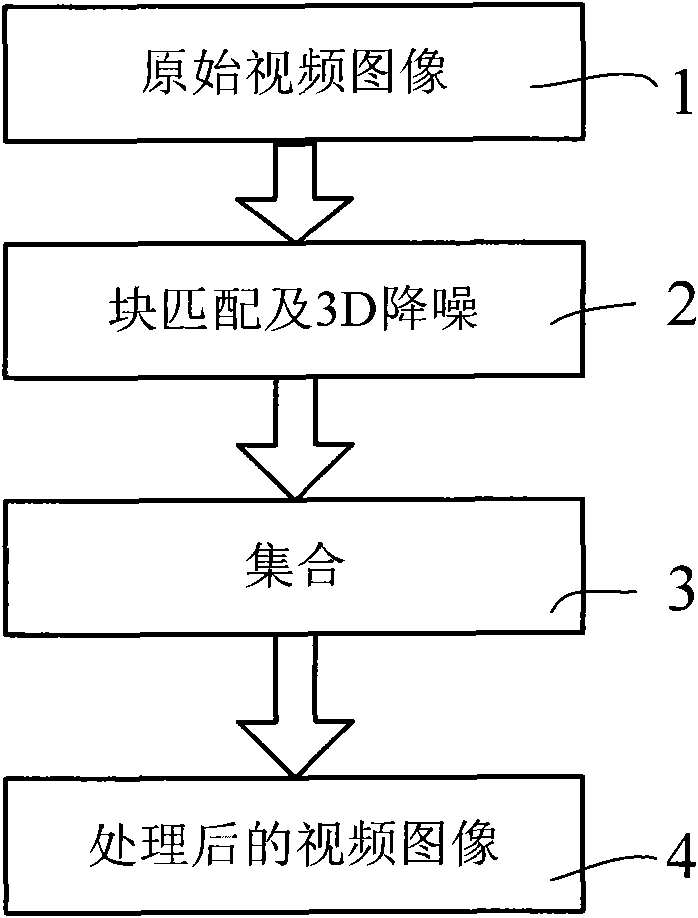
ActiveCN101895676AEliminate duplicate visitsSave bandwidthTelevision system detailsColor television detailsControl flowImaging processing
The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide a BM3D integration method. The method comprises the following steps: a, after 3D denoising processing, storing image processing information according to a line index or a column index; and b, reading the image processing information of a specific frame at a storing position from the storing position, reconstructing the image processing information of the specific frame and completing image reconstruction. The method realizes BM3D real-time integration processing by optimizing a BM3D integration process. In the method, the data structure and control flow are simple enough to be realized by software easily, and multiprocessor can be used for parallel processing. In addition, the method also makes the chip realization easy, is favorable for satisfying the high throughout needs for high-definition and multipath processing and realizes the video image BM3D real-time processing.
Owner:SHANGHAI FULLHAN MICROELECTRONICS
Method for tracking depth of sound source autonomously in real time at deep sea under lower signal-to-noise ratio condition
ActiveCN108562891ANo human intervention requiredReduce storageUsing reradiationSound sourcesSignal on
The invention relates to a method for tracking the depth of a sound source autonomously in real time at deep sea under a lower signal-to-noise ratio condition. According to the method of the invention, piecewise linear approximation processing is performed on a sound velocity profile, so that the direction of arrival information of signals on a vertical array is obtained; the information is utilized to obtain the autocorrelation function of the signals, and the autocorrelation function of the signals contains sound source depth information; a plurality of equations with low computational quantities are adopted to obtain sound source depths corresponding to each time delay coordinate of the autocorrelation function; the autocorrelation function is transformed into a function which adopts ahypothetical sound source depth as an independent variable, and the function is called a depth correlation function; and a smoothing filter is applied to the time sequence of the depth correlation function so as to weaken background noises, extract the correlation peaks of the signals and track a sound source depth. Compared with the calculation amount of a traditional ray model-based sound sourcedepth estimation method, the calculation amount of the method of the invention is greatly reduced; and time accumulation gain is obtained with a small calculation amount and low storage cost, and therobustness of the method of the present invention under the low signal to noise ratio condition is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Multi-input and multi-output fast estimation method for radar receiving and transmitting angles under color-noise environment
InactiveCN103217671AImprove estimation performanceSuppresses the effect of Gaussian color noiseWave based measurement systemsMulti inputComputation complexity
The invention provides a multi-input and multi-output fast estimation method for radar receiving and transmitting angles under color-noise environment. The multi-input and multi-output fast estimation method comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out matching and filtering on echo signals of all receiving array elements acquired by an A / D sampling module and obtaining received data of a virtual array; (2) carrying out rearrangement on the received data of the virtual array; (3) respectively carrying out subarray division on the received data and a rearranged matrix and meeting the characteristic of constant rotation of a transmitting end and a receiving end; (4) constructing two four-order cumulant matrix pairs; (5) obtaining signal subspaces including the characteristic of constant rotation in transmitting and receiving respectively by characteristic values; (6) estimating the receiving and transmitting angles of a target by utilizing an ESPRIT algorithm; and (7) realizing correct pairing of the receiving and transmitting angles by utilizing a maximum likelihood estimation method. The multi-input and multi-output fast estimation method provided by the invention has the advantages that the influence of Gaussian color noise can be effective inhibited, no special requirement exists for the quantity of transmitted / received array elements, the estimation accuracy is high, and the computation complexity is low, so that the multi-input and multi-output fast estimation method can be used for positioning targets on sea or at low altitude in tracking and guidance.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Defect detection system
InactiveUS20050018181A1Easy to detectReduce crosstalkPolarisation-affecting propertiesOptically investigating flaws/contaminationForward scatterScanning probe microscopy
Scattered radiation from a sample surface is collected by means of a collector that collects radiation substantially symmetrically about a line normal to the surface. The collected radiation is directed to channels at different azimuthal angles so- that information related to relative azimuthal positions of the collected scattered radiation about the line is preserved. The collected radiation is converted into respective signals representative of radiation scattered at different azimuthal angles about the line. The presence and / or characteristics of anomalies are determined from the signals. Alternatively, the radiation collected by the collector may be filtered by means of a spatial filter having an annular gap of an angle related to the angular separation of expected pattern scattering. Signals obtained from the narrow and wide collection channels may be compared to distinguish between micro-scratches and particles. Forward scattered radiation may be collected from other radiation and compared to distinguish between micro-scratches and particles. Intensity of scattering is measured when the surface is illuminated sequentially by S- and P-polarized radiation and compared to distinguish between micro-scratches and particles. Representative films may be measured using profilometers or scanning probe microscopes to determine their roughness and by the above-described instruments to determine haze in order to build a database. Surface roughness of unknown films may then be determined by measuring haze values and from the database.
Owner:VAEZ IRAVANI MEHDI +4
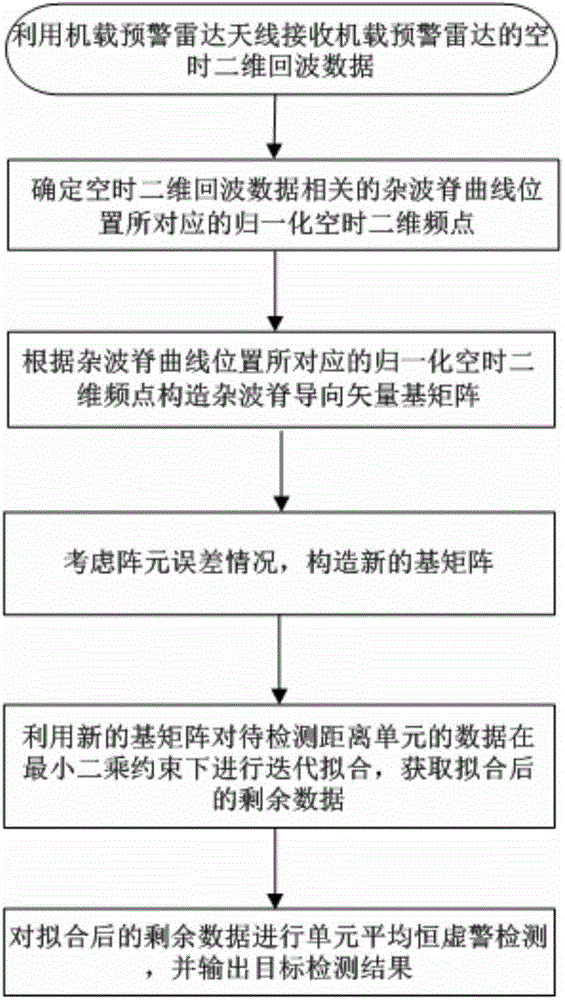
Target detection method by use of airborne early warning radar
InactiveCN104535973AWell fittedEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsAirborne early warningConstant false alarm rate
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar clutter inhibition and in particular relates to a target detection method by use of airborne early warning radar. The target detection method comprises the following specific steps: receiving space-time two-dimensional echo data by use of airborne early warning radar; determining normalized space-time two-dimensional frequency points corresponding to the positions of a clutter ridge curve related to the space-time two-dimensional echo data; constructing a clutter ridge steering vector basis matrix Psi according to the normalized space-time two-dimensional frequency points corresponding to the positions of the clutter ridge curve; constructing a matrix element error vector Es and a new clutter ridge steering vector basis matrix Psi', and performing iterative fitting on the data of the first unit to be tested in distance under the least square constraint by use of the new clutter ridge steering vector basis matrix Psi', thereby obtaining the fitted residual data of the first unit to be tested in distance; performing unit average constant false alarm rate detection on the fitted residual data of the first unit to be tested in distance, thereby obtaining a target detection result.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com