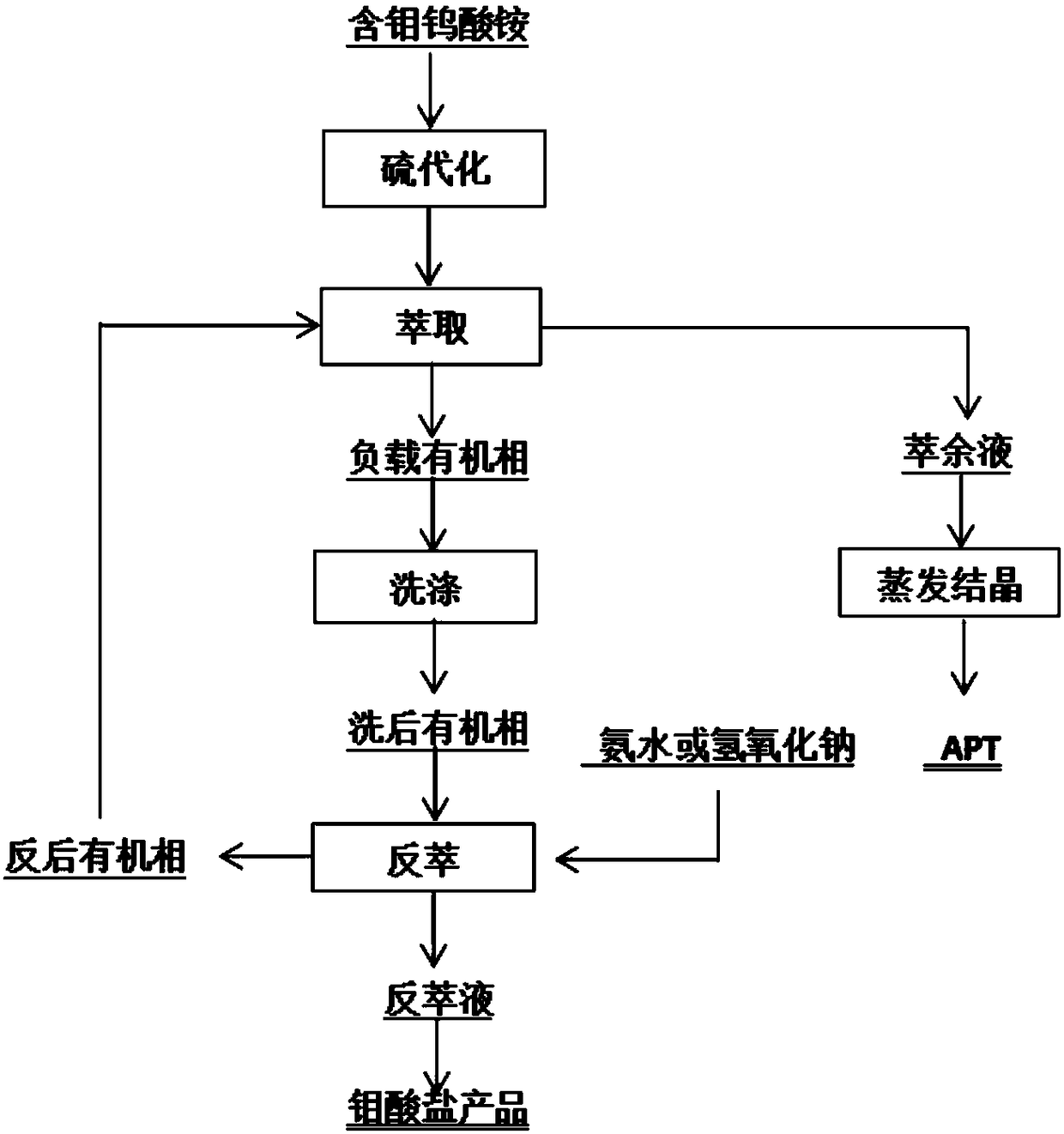
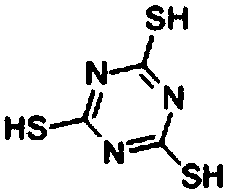
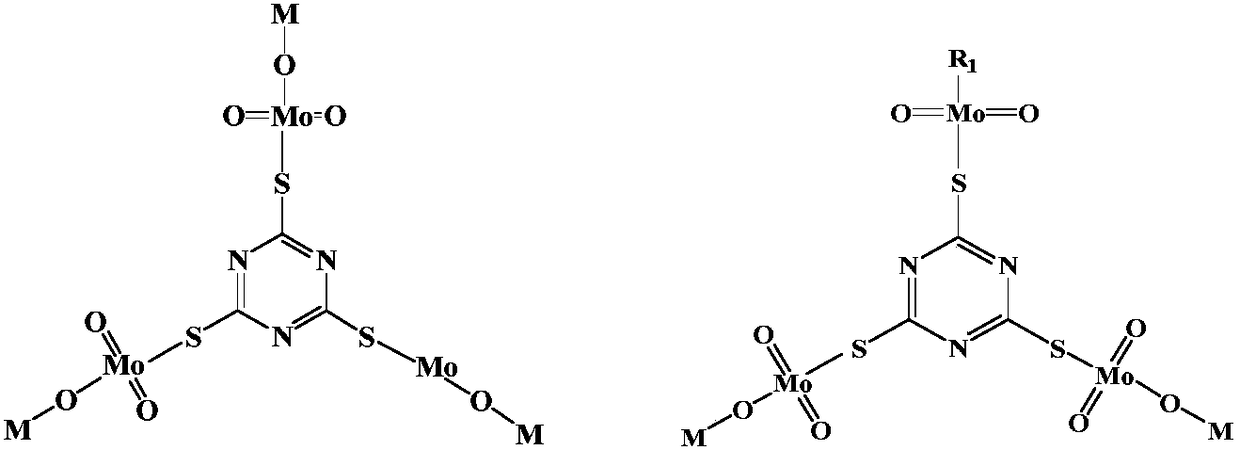
Method of extractively separating molybdenum from tungstate solution
A tungstate, molybdenum tungstate technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of complex tungsten metallurgical raw materials, increased production cost, difficult to control the amount of oxidant, etc., to improve the production environment, no harmful gas release, Eliminate the effect of H2S generation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The feed liquid is a molybdenum-containing ammonium tungstate solution prepared in the laboratory: the feed liquid contains Mo 1g / L, WO 3 100g / L. The original pH of the feed solution was 9.5. The amount of vulcanizing agent added is 1:4, 1:8, 1:10, 1:16, 1:20 according to the molar ratio of molybdenum and vulcanizing agent. Mix, stir, and heat to 70°C. Insulate the reaction for 12 hours, and adjust the end point pH to about 8.5 with ammonia water. By the detection method in embodiment 1, record each condition at the vulcanization rate of molybdenum as following table.
[0037] Table 1 The effect of the amount of vulcanizing agent added on the vulcanization effect of molybdenum
[0038]
[0039] It can be seen from Table 1 that when the temperature is constant, the degree of vulcanization of molybdenum increases significantly with the increase of the amount of vulcanizing agent within the same vulcanization time.
Embodiment 2
[0041] The feed liquid composition is exactly the same as that in Example 1, and the amount of adding vulcanizing agent is 5.91g (the molar ratio of molybdenum and vulcanizing agent is 1:16), but the temperature of reaction changes to some extent, and the control reaction temperature is respectively 40 ℃, 50 °C, 60 °C, 70 °C, heat preservation reaction for 12 hours, control the end point pH=8.5 or so. By the detection method in embodiment 1, record each condition at the vulcanization rate of molybdenum as following table.
[0042] Table 2 Influence of reaction temperature molybdenum vulcanization effect
[0043]
[0044] It can be seen from Table 2 that when the amount of vulcanizing agent is constant, as the reaction temperature increases, the vulcanization effect of molybdenum is significantly improved, so an appropriate increase in temperature is beneficial to the sulfidation of molybdenum. But too high temperature may lead to the decomposition of organic vulcanizing ag...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The feed liquid composition is exactly the same as in Example 1, the amount of adding vulcanizing agent is 5.91g (the molar ratio of molybdenum and vulcanizing agent is 1:16), only change the reaction time, the reaction time is respectively 4h, 6h, 8h, 10h, 12h. According to the detection method in Example 1, the vulcanization rate of molybdenum in each condition is recorded as Table 3.
[0047] Table 3 Effect of reaction time molybdenum vulcanization effect
[0048]
[0049] It can be seen from Table 3 that at a certain temperature and under the condition of controlling the amount of curing agent, prolonging the curing time can increase the curing rate of molybdenum, and the effect of curing time is not as significant as the amount of curing agent and reaction temperature.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com