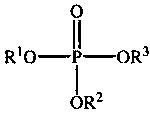
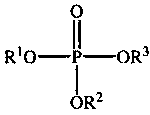
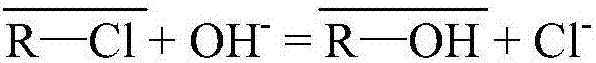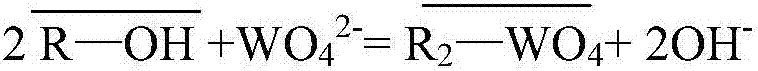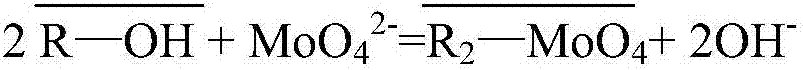Patents
Literature
95 results about "MOLYBDATE ION" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
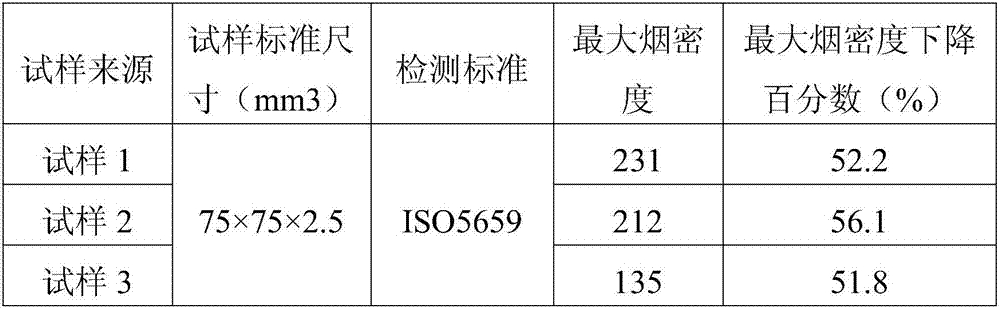
Ion-exchange separation method for tungsten and molybdenum in tungstate and molybdate mixed solution
InactiveCN102162030AEasy to parsePromote regenerationMolybdeum compoundsProcess efficiency improvementTungstate ionMOLYBDATE ION
The invention discloses an ion-exchange separation method for tungsten and molybdenum in a tungstate and molybdate mixed solution, technically characterized by comprising the following steps of: adjusting the pH of the tungstate and molybdate mixed solution by mineral acid to be appropriate, so that the tungstate ions in the solution are polymerized into paratungstate ions, while molybdenum still exists in the form of tungstate ions; adjusting the concentration of Cl<-> in the solution to be appropriate, enabling the solution to flow through ion exchange columns loaded with macroporous strong base anion exchange resin, so that the tungsten in the solution is absorbed firstly, thereby separating the tungsten from the molybdenum; rinsing a small amount of MoO4<2-> ions absorbed by the resin in the ion exchange columns by a solution with an appropriate concentration of Cl<->; and finally resolving the tungsten absorbed on the resin by using an alkali solution with an appropriate concentration of Cl<-> as a resolving agent to regenerate the resin.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
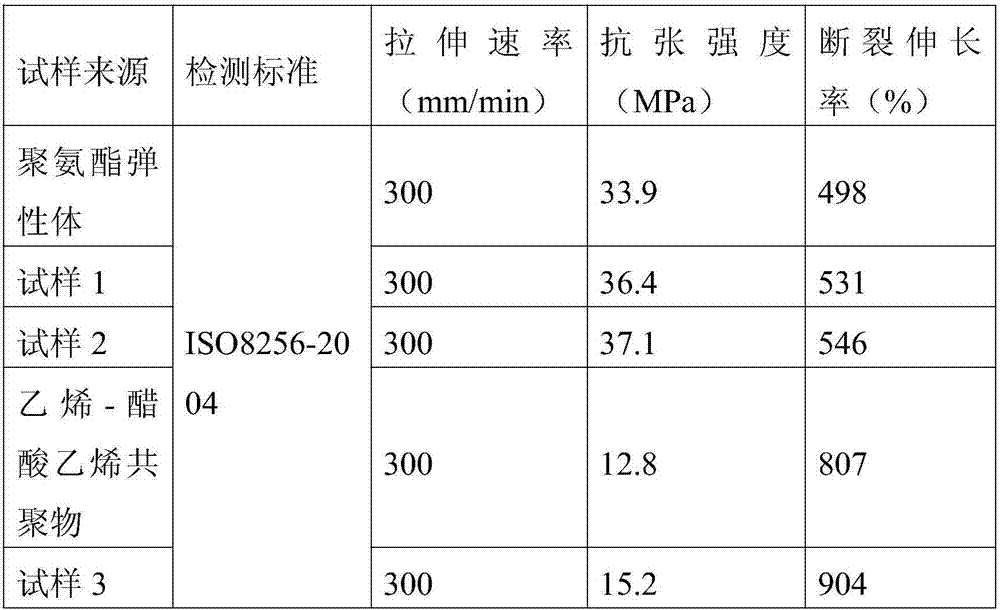
Intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor and a preparation method thereof. The smoke inhibitor is a layered structural material formed by assembling a laminated sheet consisting of metal cations and interlayer anions, wherein a specific composition general formula of the smoke inhibitor is M<2+>1-xM<3+>x(OH)2(A<n->)n / 2.mH2O. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor is prepared by adopting a one-step coprecipitation method or a clean hydrothermal reaction at one step; the preparation method is simple and practical; according to the obtained intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor, smoke inhibiting groups such as molybdate anions, an octamolybdate radical, a cuprate radical and a stannate radical are arranged at an interlayer, and smoke inhibiting elements such as iron and copper are introduced into the laminated sheet, so that a good carbon forming effect is realized, the smoke generating amount can be reduced, and the smoke inhibiting effect is synergically enhanced; meanwhile, a layered double hydroxide laminated sheet forms an alkaline porous substance at high temperature; the alkaline porous substance has greater specific surface area and can effectively adsorb smog; the prepared intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor is applied to an ordinary rubber-plastic product and a high-temperature rubber-plastic product; the maximum density (Ds, max) at low additive amount (1phr) can be reduced by 87.3 percent; the intercalated layered double hydroxide smoke inhibitor is remarkable in smoke inhibiting effect and is a smoke inhibitor material with excellent performance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
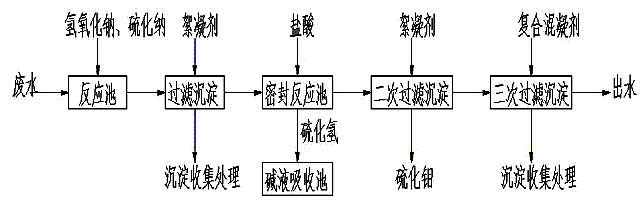
Method for purifying molybdenum sulfide in heavy metal waste water containing molybdenum, and the like
ActiveCN101973652AReduce purification costsReduce contentMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationAluminium chlorideMolybdic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of water treatment, in particular to a method for purifying molybdenum sulfide in heavy metal waste water containing molybdenum, and the like. The method comprises the following steps of: putting waste water containing the heavy metal molybdenum and other heavy metals to be purified in a reaction tank; regulating the waste water to alkalinity and adding sodium sulfide for reacting; filtering the waste water and putting filtered water in a sealing device; regulating the pH value of the waste water to 1-3 and reacting at normal temperature to guarantee that molybdenum acid radical ions are all converted into molybdenum sulfide to precipitate; absorbing gas generated by using an absorption tower, wherein sodium hydroxide is used as absorption liquid; adding polyacrylamide used as a flocculating agent to an obtained solution and quickly stirring for reacting; standing still; after the precipitate subsides, draining the supernate, filtering through a filtering device, and treating the precipitate for recycling; regulating the pH of the obtained acid solution to neutrality, adding a coagulant compounded by polymeric aluminum and ferrous sulphate and quickly stirring to remove redundant sulfur ions and further improve the quality of yield water; standing still; and after the precipitate subsides, filtering. The invention has the advantages of good treatment effect, simple and convenient treatment equipment, low treatment cost, higher purity of recovered molybdenum sulfide, and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Composite water treating agent for central air conditioner cooling water
ActiveCN1880244AGood synergyGood scale inhibitionTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsRare-earth elementSuccinic acid
The invention discloses a treating agent of cooling water and composite water in central air-conditioning, including the weight or portioning components listed as following: one to ten portion of epoxy succinic acid; one to ten portion of phosphonate; one to ten portion of molybdate calculated according to molybdic acid ion; 0.1 to ten portion of rare-earth element salts; one to five portion of copper inhibitor; zero to three portion of zinc calculated according to zinc ion. This invention is low-phosphorus and environment-friendly type, good quality in antisludging and corrosion inhibit, easy to obtain material, explore the application area of using rare-earth element in water treatment, and have greatly active meaning in developing rare earth project of our country.
Owner:SHANGHAI EMPEROR OF CLEANING HI TECH
Composition and process for etching and desmutting aluminum and its alloys
InactiveUS20020162990A1Water softeningTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsSulfonateMOLYBDATE ION
Owner:HENKEL CORP
Treatment Solution for Coating Metal Surface
ActiveUS20110132497A1Small volumeReduce weightSolid state diffusion coatingChromium freeMOLYBDATE ION
A chromium-free aqueous treatment solution for coating metal surfaces is described. The treatment solution contains fluorocomplex ions of titanium and / or zirconium and molybdate ions, vanadium ions and one or more aromatic carboxylic acids with at least one carboxyl groups and at least two further functional groups, wherein the two further functional groups are selected from the group comprising carboxyl groups, hydroxyl groups, amino groups and nitro groups.
Owner:BULK CHEM
Culture medium for spore germination and seedling culturing of pteridophyte
InactiveCN101911914AImprove germination rateHigh induction rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSpore germinationPteridophyte
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, and relates to a culture medium for the spore germination and seedling culturing of pteridophyte, which is characterized by consisting of the following nutritional components: 2 to 60 mmol.L<-1> nitrate ions, 1 to 30 mmol.L<-1> ammonium ions, 0.3 to 8 mmol.L<-1> phosphate radical ions, 2.7 to 66 mmol.L<-1> potassium ions, 0.37 to 12.0 mmol.L<-1> calcium ions, 0.18 to 1.8 mmol.L<-1> magnesium ions, 0.173 to 1.73 mmol.L<-1> sulfate ions, 10 to 100 mumol.L<-1> chelated ferric salt or chelated ferrous salt, 10 to 200 mumol.L<-1> boric acid, 10 to 100 mumol.L<-1> divalent manganese ions, 3 to 30 mumol.L<-1> zinc ions, 0.5 to 8 mumol.L<-1> divalent copper ions or complexes thereof, 0.1 to 1 mumol.L<-1> molybdate ions, 0.01 to 0.1 mumol.L<-1> divalent cobalt ions, 0.05 to 12 mumol.L<-1> chloride ions, 0.3 to 30 mumol.L<-1> thiamine hydrochloride and the balance of water, wherein the pH value of the culture medium is between 4.0 and 9.0. The culture medium can improve the germination rate of spores.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Composite water treating agent for industrial circulation cooling water
ActiveCN1880246ALow in phosphorusImprove stabilityTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsRare-earth elementMOLYBDATE ION
The invention discloses a treating agent of cooling water and composite water in industrial cycle, including the weight or portioning components listed as following: one to ten portion of phosphoric carboxylate copolymerisate; one to ten portion of molybdate calculated according to molybdic acid ion; 0.1 to ten portion of rare-earth element salts; one to five portion of copper inhibitor; zero to five portion of zinc calculated according to zinc ion. This invention is low-phosphorus and environment-friendly type, good quality in antisludging and corrosion inhibit, especially suitable for the harsh water quality of large hard value, large basic value, large PH value, large suspended matter value, and easy to obtain material, explore the application area of using rare-earth element in water treatment, and have greatly active meaning in developing rare earth project of our country.
Owner:SHANGHAI EMPEROR OF CLEANING HI TECH
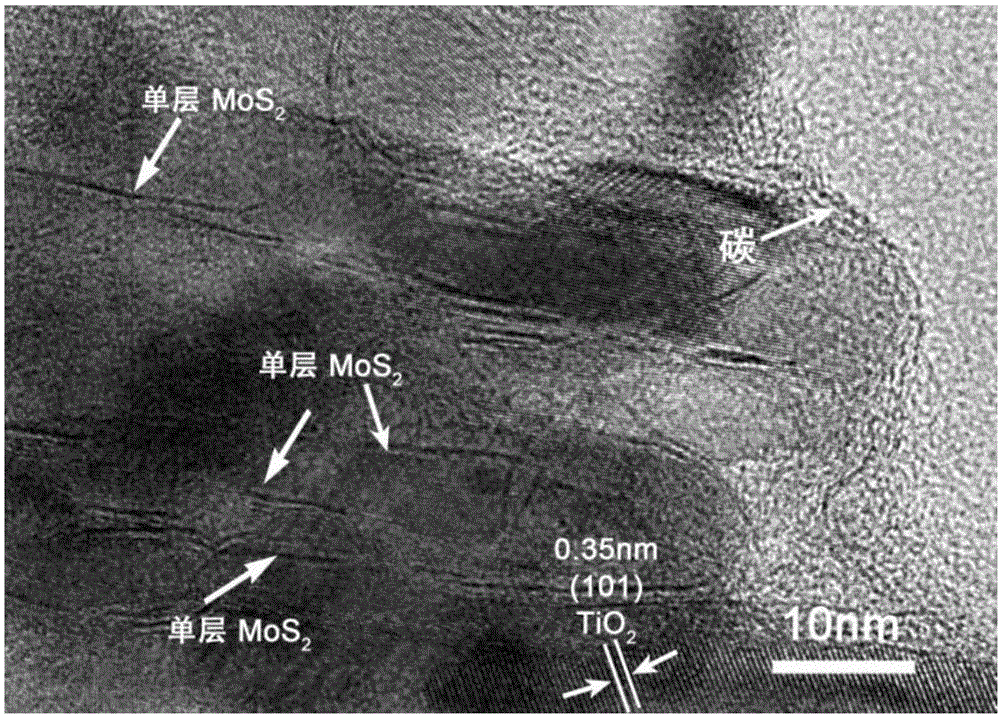
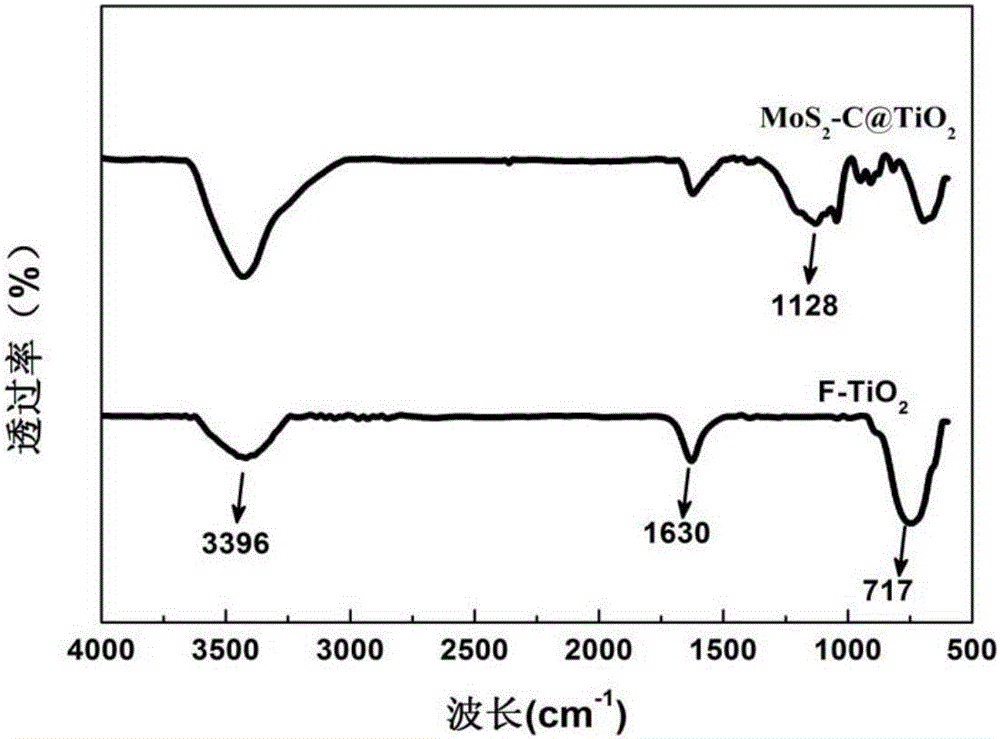
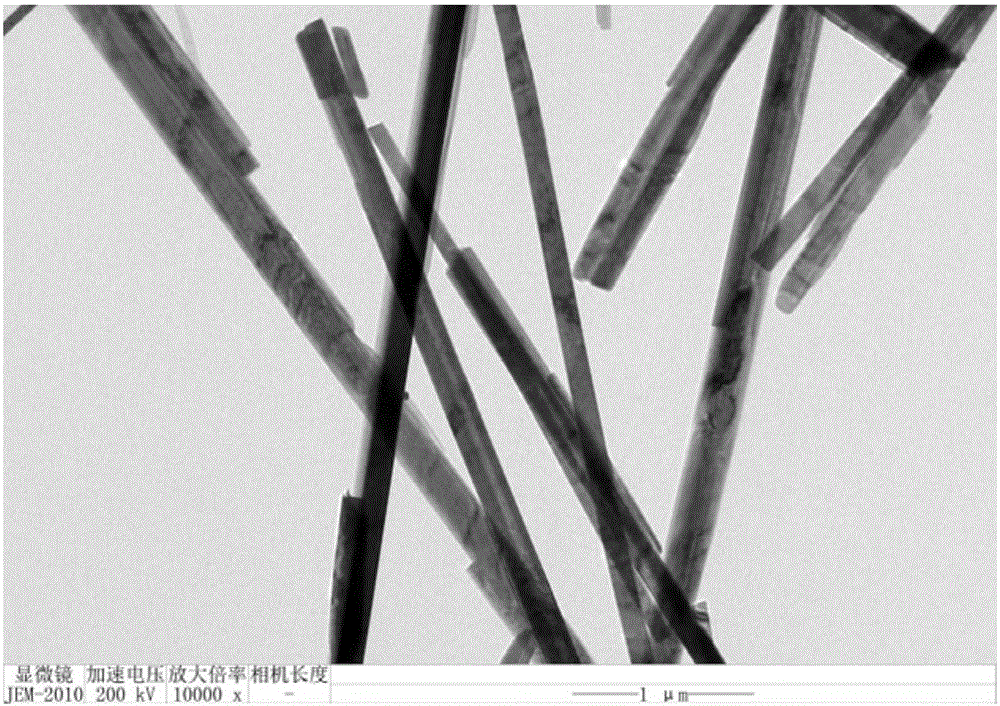
Method for modifying titanium-dioxide lithium-ion battery negative pole material simultaneously by using carbon and monolayer molybdenum disulfide
InactiveCN106058200AInhibition of agglomerationCoated evenlyCell electrodesSecondary cellsThioureaDecomposition
The invention relates to a method for modifying a titanium-dioxide lithium-ion battery negative pole material simultaneously by using carbon and monolayer molybdenum disulfide. According to the method, a composite material adopts TiO2 as a skeleton, fluoride ions of the surface of the composite material adsorb glucose molecules in a suspension firstly, functional groups in the glucose molecules adsorb molybdate ions and thiourea molecules, an outer layer of each titanium dioxide nanosheet is coated with a glucose membrane and a sodium molybdate-thiourea membrane after freeze drying, glucose is carbonized into amorphous carbon after a chemical vapor deposition process, and meanwhile, thiourea is subjected to high-temperature decomposition so as to prepare hydrogen sulfide and reduce the molybdate ions into molybdenum disulfide, thereby obtaining TiO2 nanosheets which are simultaneously modified by carbon and monolayer molybdenum disulfide nanosheets. The prepared negative pole material has a uniformly-coated structure, all components are in close contact, and the agglomeration of MoS2 nanosheets is effectively inhibited; when the prepared negative pole material is applied to negative pole materials of lithium-ion batteries, the lithium-ion batteries have relatively high specific capacity and stable cycle performance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
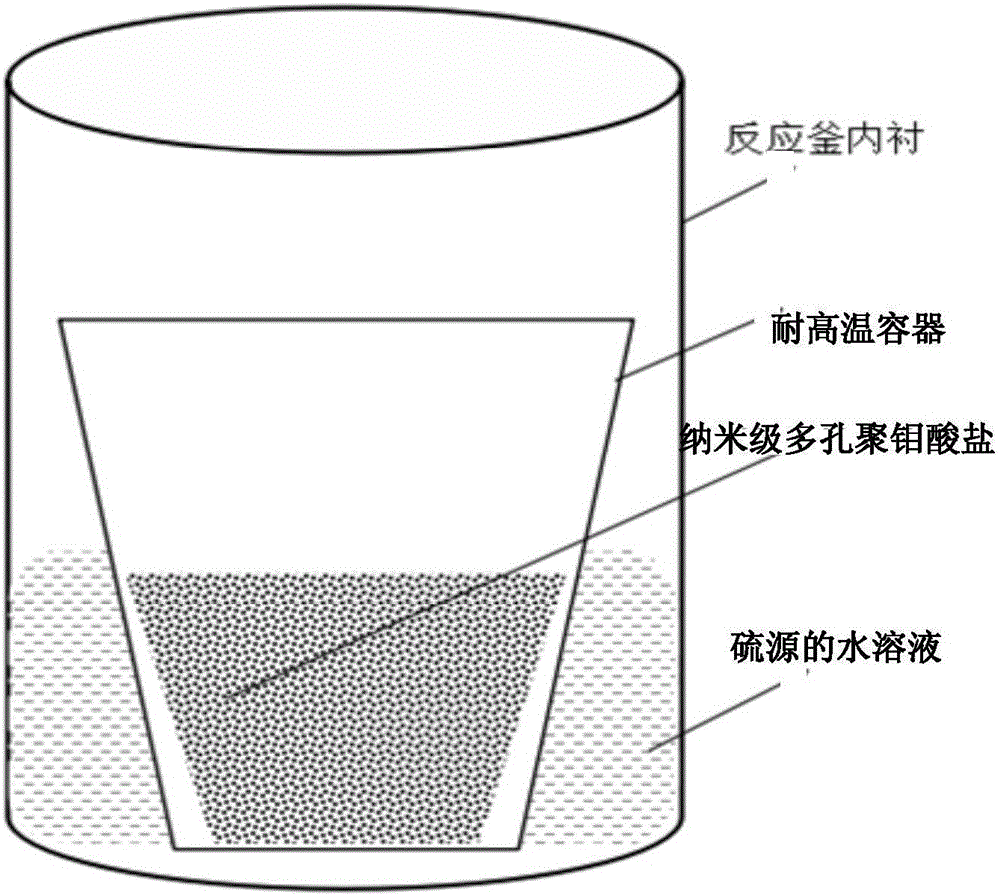
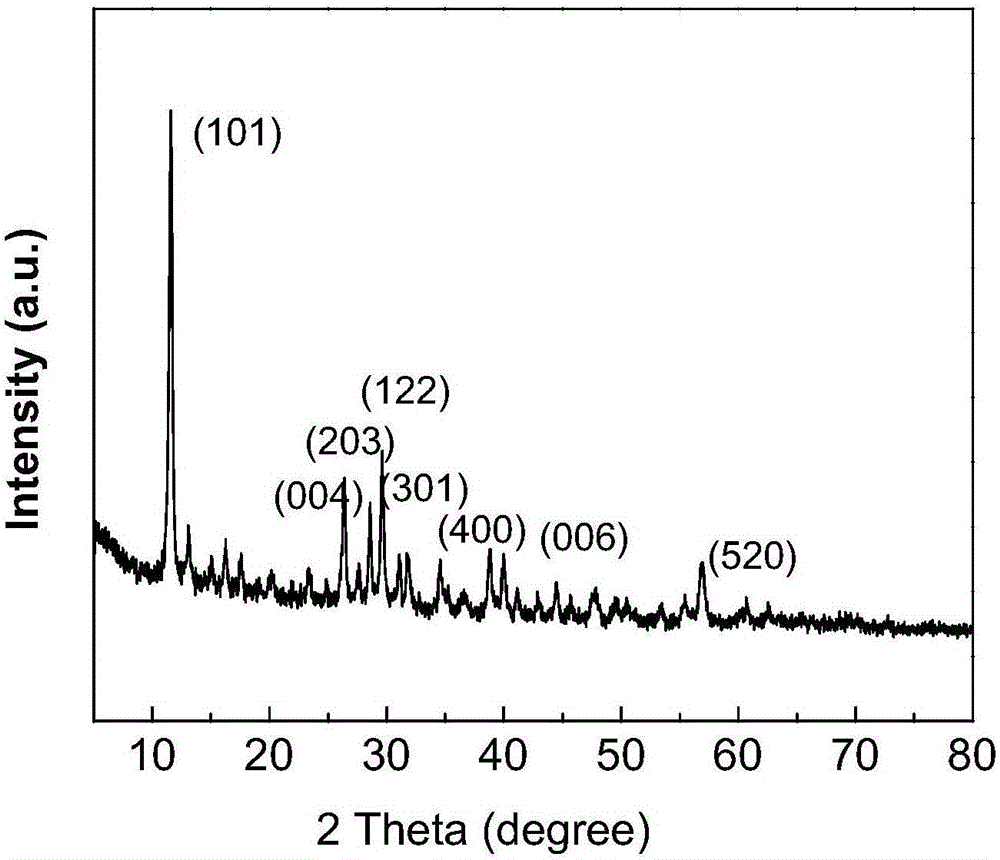
Method for preparing porous defect-enriched molybdenum disulfide
ActiveCN106186070AAvoid wastingAchieve in-situ vulcanizationPhysical/chemical process catalystsMolybdenum sulfidesMOLYBDATE IONVulcanization
The invention discloses a method for preparing a porous defect-enriched molybdenum disulfide, and is characterized in that the method comprises the steps: adding a soluble acid or a soluble salt in an aqueous solution of molybdate, then heating, and making molybdate ions subjected to stepwise polymerization into porous heterozygous ordered aggregates under induction of cation; and centrifuging, washing and drying the product, transferring the product to a reactor kettle, taking a compound containing negative bivalent sulfur elements as a sulfur source, and thus obtaining the porous defect-enriched molybdenum disulfide through a hydrothermal-gas phase in-situ vulcanization method. The method has the advantages of simple operation, and cheap and easily obtained raw materials, and the obtained product has the advantages of good morphology and large specific surface area, and can be used for large-scale synthesis.
Owner:合肥庐阳科技创新集团有限公司
Method for improving concentration of alcohol substances in fermented product of anaerobic gas-feeding microbes
InactiveCN105039423AIncrease concentrationIncrease valueBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The inventions aims to provide a cultivation system for improving concentration of alcohol substances in a fermented product of anaerobic gas-feeding microbes, specifically for improving the concentration of the alcohol substances in the fermented product of the anaerobic gas-feeding microbes in a shaking cultivation or continuous air agitation cultivation system by optimizing components in a cultivation medium. A method for improving the fermentation efficiency of the anaerobic gas-feeding microbes is characterized in that the final concentration of molybdate ions in the cultivation medium for fermentation is not higher than 0.1mg / L. By the method, the concentration of alcohols in the fermented product of gas biotransformation can be improved and the value of the bio-fermentation production of gas can be improved effectively.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for separating tungsten and molybdenum from tungsten and molybdenum acid salt solution
The invention discloses a method for separating tungsten and molybdenum from a tungsten and molybdenum acid salt solution. The method comprises the steps that quaternary ammonium salt is added in thetungsten and molybdenum acid salt solution to serve as a stabilizer, the pH value is adjusted to be 8-11, then, divalent manganese salt is added to serve as a precipitator, and solid-liquid separationis conducted after the reaction. Through introduction of the stabilizer, the function of stabilizing molybdenum acid radical ions in the tungsten and molybdenum acid salt solution can be achieved, the efficiency of the precipitator is improved, and then the tungsten and molybdenum separation efficiency is improved; in the process of selective separation of tungsten through introduction of the stabilizer and the precipitator, toxic and harmful gas generation is avoided, the raw material cost is low, the operation environment is good, the equipment requirement is low, and industrial achieving is easy; and the conditions of the tungsten and molybdenum separating process are moderate, usage of strong acid, strong base, high temperature and high pressure is avoided, and compared with a traditional method, the reaction time is shortened, energy consumption is reduced, economic benefits are high, and the actual application prospects are good.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for deeply purifying ammonium tungstate solution
PendingCN110563041AReduce consumption costReduce manufacturing costTungsten compoundsVulcanizationSlag
The invention discloses a method for deeply purifying ammonium tungstate solution. The method comprises the following steps: adding excessive (NH4)2S into a coarsely treated ammonium tungstate solution under a stirring condition until S2<-> reaches a set concentration, and then carrying out vulcanization reaction at a set temperature, so that molybdenum in the ammonium tungstate solution is converted into thiomolybdate ions (MoS42 <->) to obtain a vulcanized ammonium tungstate solution; adding a calcium agent into the vulcanized ammonium tungstate solution under a stirring condition, and thencarrying out stirring reaction under a set condition, so as to obtain calcium tungstate precipitate and a mother liquor containing ammonia water after the reaction is finished; adding the calcium tungstate precipitate into a hydrochloric acid solution at a set temperature under a stirring condition, carrying out heat preservation and stirring reaction, and filtering after the reaction is finished,so as to obtain refined tungstic acid and an acid decomposition mother liquor; cleaning the refined tungstic acid, putting the cleaned tungstic acid into ammonia water for ammonia dissolution, and filtering to obtain ammonia dissolution slag and an ammonium tungstate deep purification liquid.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Layered double hydroxide-molybdate ion modified graphene flame-retarding and smoke-inhibiting agent and preparation method of same
ActiveCN107163289AImprove flame retardant and smoke suppression performanceImprove mechanical propertiesMOLYBDATE IONCvd graphene
The invention belongs to the technical field of flame-retarding and smoke-inhibiting agents and particularly relates to a layered double hydroxide-molybdate ion modified graphene flame-retarding and smoke-inhibiting agent and a preparation method of same. The preparation method includes the steps of supporting LDH onto surface of graphene and intercalating molybdate ions between layers of the LDH. The flame-retarding and smoke-inhibiting agent not only improves the flame-retarding and smoke-inhibiting performances of a polymer but also improves physical and mechanical performances of the polymer.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE
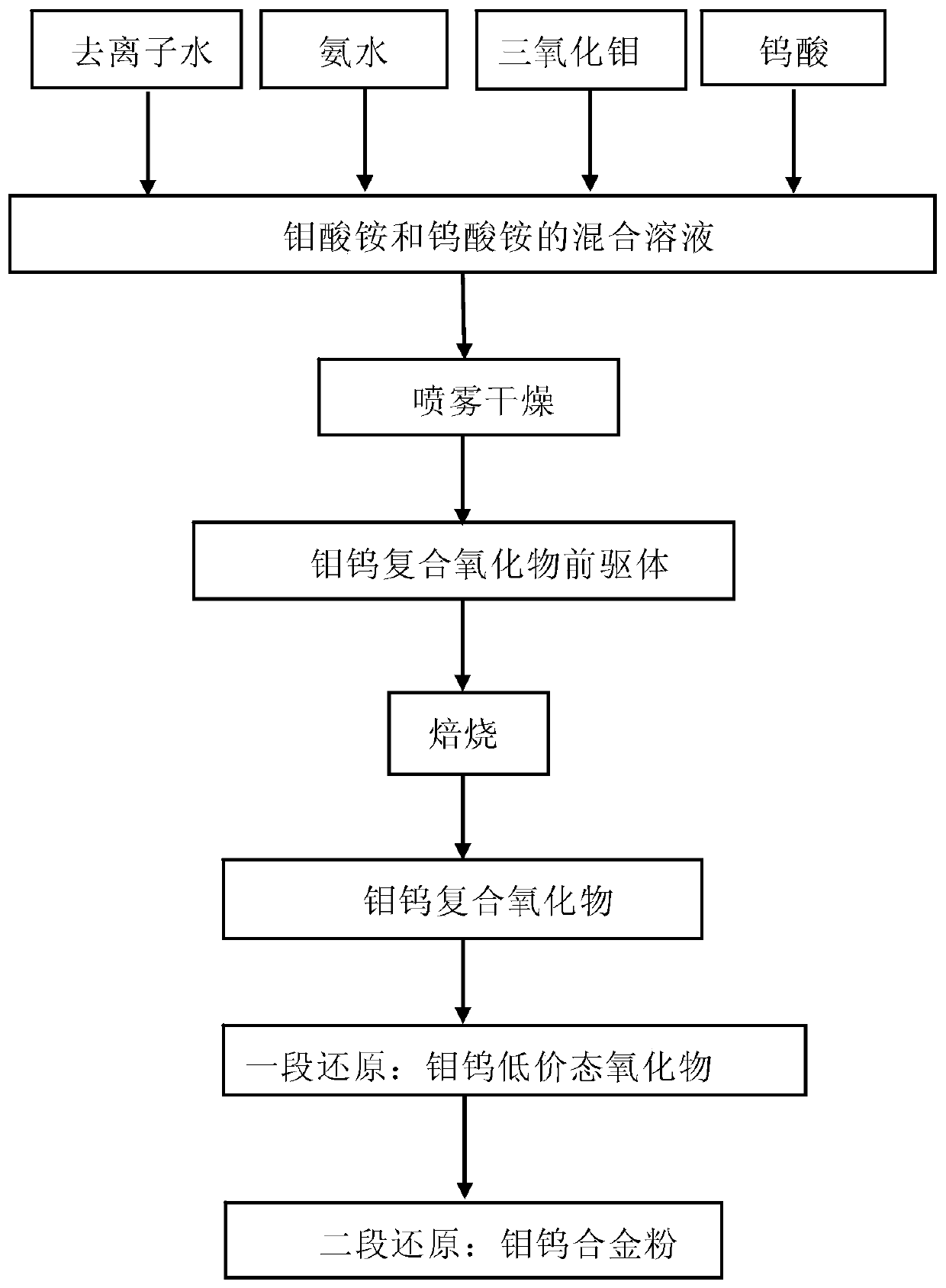
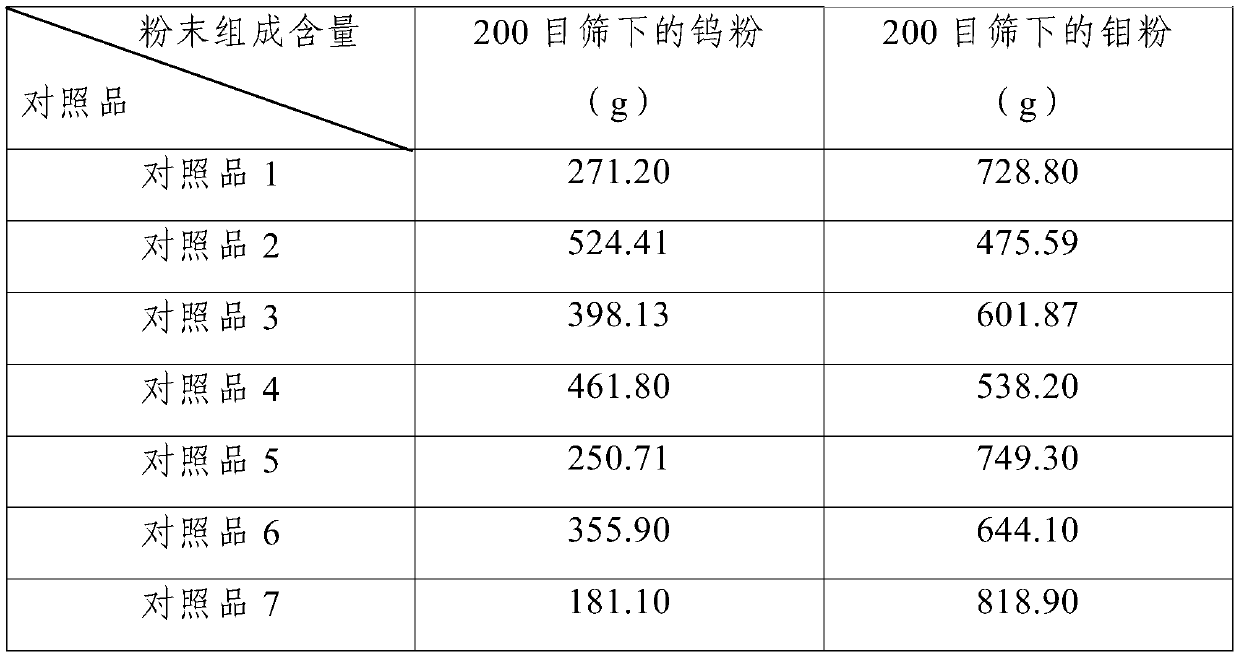
Preparation method of molybdenum-tungsten alloy powder
The invention discloses a preparation method of molybdenum-tungsten alloy powder. The method comprises the steps that firstly, molybdenum trioxide and tungstic acid are added into diluted ammonia water to be dissolved to obtain an ammonium molybdate and ammonium tungstate mixed solution; secondly, the ammonium molybdate and ammonium tungstate mixed solution is sprayed and dried to obtain a molybdenum-tungsten composite oxide precursor; thirdly, the molybdenum-tungsten composite oxide precursor is subjected to roasting decomposition under the temperature gradient condition to obtain a molybdenum-tungsten composite oxide; fourthly, the molybdenum-tungsten composite oxide is subjected to first-stage reduction under the hydrogen condition to obtain a molybdenum-tungsten low-valence oxide; andfifthly, the molybdenum-tungsten low-valence oxide is subjected to second-stage reduction under the hydrogen condition to obtain the molybdenum-tungsten alloy powder. The molybdenum-tungsten alloy powder is prepared by fully mixing molybdate ions and tungstate ions and conducting roasting and reduction, so that size and mass differences of molybdenum particles and tungsten particles are small, hybrid power is high, the uniformity of the molybdenum-tungsten alloy powder is improved, and the problem of insufficient uniformity caused by mechanical mixing of molybdenum powder and tungsten powder is eliminated.
Owner:JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO LTD
All-vanadium-redox-flow-battery electrode material and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN106410219AImprove efficiencyImprove energy efficiencyCell electrodesRegenerative fuel cellsVanadium redox batteryMolybdenum trioxide
The invention provides a method for preparing an all-vanadium-redox-flow-battery electrode material. The method includes the following steps that a carbon base material is soaked into an acid solution containing molybdate anions and fully dispersed; heating is carried out; the carbon base material is taken out and dried in the vacuum or inert atmosphere; the dried carbon base material is put in the inert atmosphere and subjected to an isothermal reaction, and the all-vanadium-redox-flow-battery electrode material with the surface modified with molybdenum trioxide is obtained. The all-vanadium-redox-flow-battery electrode material comprises the carbon base material and an electrocatalyst which is combined on the surface of the carbon base material and contains the molybdenum trioxide. According to method, as the electrocatalyst containing the molybdenum trioxide is arranged on the surface of the carbon base material for modification, the carbon base material has the high catalytic activity, the electro-catalysis activity of the electrode material is improved, electrochemical polarization is reduced, and the voltage efficiency and the energy efficiency of a vanadium battery are improved; the method is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Molybdate radical ion and nitrite radical ion concentration test card and its preparing method
InactiveCN1648642ASimple processLow costMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical methods analysisNitrite ionGallic acid ester
The present invention relates to a kind of molybdate radical ion and nitrite radical ion concentration test card and its preparation process. The test card includes test paper and standard color check card, and the test paper has molybdate radical ion indicating color developing paper sheet and nitrite radical ion indicating color developing paper sheet fixed on the base sheet. The molybdate radical ion indicating color developing paper sheet is prepared through soaking filter paper in mixed solution of gallic acid and hydroxylamine sulfate, drying and photophobic keeping; and the nitrite radical ion indicating color developing paper sheet is prepared through soaking filter paper in mixed solution ofaminobenzene sulfonic acid, dihydrochloride-1-naphthyl ethylene diamine and tartaric acid, drying and photophobic keeping. The present invention may be used in testing the concentration of molybdate radical ion and nitrite radical ion simultaneously.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
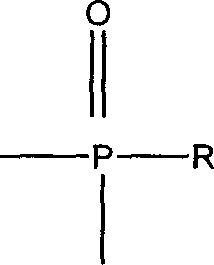
Method for adsorption and separation of molybdenum from aqueous phase
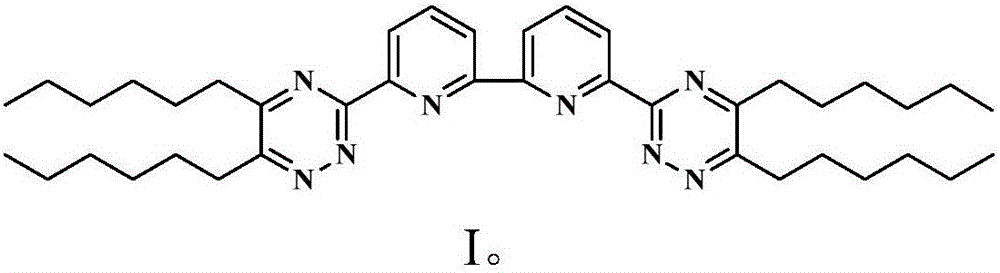
The invention discloses a method for adsorption and separation of molybdenum from an aqueous phase. The method comprises the following steps: an adsorbent is mixed with a nitric acid aqueous solution containing a variety of metal ions, molybdate ions in the nitric acid aqueous solution are adsorbed by the adsorbent to be separated, and the adsorbent is prepared by compounding a compound as shown in formula I and a carrier. Each gram of the adsorbent is mixed with 15 to 25 milliliters of the nitric acid aqueous solution. The carrier is macroporous SiO2 of which the surface is coated with a polymer, and the concentration of nitric acid in the nitric acid aqueous solution is 0.4 to 6.0 mol / L. According to the invention, a diluent with special performance is not required to dilute or dissolve in the adsorption process, and the method is good selectivity, fast in separation speed, simple to operate and easy to popularize.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of biomass Fe-based porous carbon composite adsorption material
ActiveCN107715836AExtended pH rangeLarge adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsAir atmosphereMOLYBDATE ION
The invention relates to a preparation method of biomass Fe-based porous carbon composite adsorption material. Palm fibers are used as raw materials, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, palm fibers are washed, and dried at 50-80 DEG C and cut up; 2. palm fibers are placed in a sodium hydroxide solution, stirring and filtering are carried out, washing is carried out till pH value is neutral, and then drying is carried out; 3. preoxidation treatment of the palm fibers are carried out 200-400 DEG C under air atmosphere for 1-5 hours, cooling is carried out till the temperature is ata room temperature, heating rate is 1-5 DEG C / min, heating is carried out till the temperature is at 600-1200 DEG C, constant temperature treatment is carried out at 60-240 minutes, finally cooling rate is controlled at 2-10 DEG C / min and the materials are cooled to a room temperature and taken out, and the materials are immersed in a solution of ferric salt; after the immersion ends, filtering iscarried out, and then under protection of nitrogen, heating rate is 1-5 DEG C / min, heating is carried out till the temperature is at 500-800 DEG C, constant temperature treatment is carried out at 30-240 minutes, and finally the cooling rate is controlled at 2-10 DEG C / min, cooling is carried out till the temperature is at room temperature, and the composite adsorption material is obtained. The removal rate of adsorption materials for molybdate ions reaches 95% or above in a wider pH value range.
Owner:洛阳巴库生物科技有限公司
Method for removing arsenic from nickel sulfate solution
ActiveCN107090546AReduce dosageIncrease conversion rateProcess efficiency improvementMOLYBDATE IONDesorption
The invention relates to a method for removing arsenic from a nickel sulfate solution, in particular to a method for removing arsenic in an industrial nickel sulfate solution by means of modified large-aperture anion resin. The method comprises the following steps that Cl<-> type large-aperture anion resin is converted into OH<-> type large-aperture anion resin, and then OH<-> type large-aperture anion resin is converted into WO4<2-> type or MoO4<2-> type large-aperture anion resin; the nickel sulfate solution passes through a WO4<2-> type or MoO4<2-> type resin column, and the purpose of removing arsenic is achieved by utilizing functional groups (WO4<2-> or MoO4<2->) on the resin and pentavalent arsenic in the solution to form heteropolyacid; according to the resin achieving adsorption, adsorbed arsenic is washed with dilute sulfuric acid, the resin is washed to be neutral with distilled water, desorption is conducted with a low-concentration mixed solution of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide, the resin is washed to be neutral, and then resin regeneration is achieved. According to the method for removing arsenic from the nickel sulfate solution, raw materials used in the whole process can be recycled, losses of tungstate and molybdate ions do not exist, and the arsenic content of the finally obtained exchanged solution is below 0.5 ppm and completely meets the industrial production requirement.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for doping rare earth lanthanum in nano molybdenum powder
The invention provides a method for doping rare earth lanthanum in nano molybdenum powder, and belongs to the field of rare earth materials. The method includes the following steps that (1) ammonium paramolybdate, rare earth lanthanum nitrate and complexing agent citric acid are doped in a solution mode, the pH value of the solution is adjusted through HNO3 and NH3 water to be 1-3, complexing is performed on citrate ions, molybdate ions and rare earth ions to obtain a stable compound, water bath is performed on the solution at the temperature of 70-90 DEG C to obtain transparent faint yellow sol, and the transparent faint yellow sol is dried at the temperature of 100-120 DEG C to obtain xerogel; (2) the xerogel is sintered for 6 hours at the temperature of 560 DEG C, then in a four-tube sintering reduction furnace, two-step reduction is performed with hydrogen as a reducing agent to obtain doped MoO3 powder and doped Mo powder respectively, the reduction temperatures of the two-step reduction are 540 DEG C and 980 DEG C respectively, the doped nano rare earth molybdenum powder which is round and normal in particle and even in distribution is prepared, the size of doping phase is below 100nm, and the size of doped molybdenum powder particles is 300-500nm. According to the method, the nano molybdenum powder doped with the earth lanthanum evenly is prepared, and meanwhile chemical reaction sediments in the liquid-liquid doping process are eliminated.
Owner:刘成涛
An amorphous phase molybdenum trisulfide cathode material of a lithium sulfide battery and a preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109167037AGood effectReduce shuttleCell electrodesSecondary cellsArgon atmospherePorous carbon
The invention provides an amorphous phase molybdenum trisulfide cathode material of a lithium sulfide battery and a preparation method thereof. Ammonium tetrathiomolybdate is added into deionized aqueous solution, PH is adjusted to acidity, porous carbon spheres are used for adsorption and evaporation drying solvent, the adsorbed carbon spheres are calcined in hydrogen / argon atmosphere, and annealed after calcination to obtain carbon-coated amorphous molybdenum trisulfide cathode material. The invention adopts porous hollow carbon sphere to adsorb thiomolybdate ion and calcine at high temperature, the thiomolybdate salt inside is converted into amorphous phase molybdenum trisulfide, in the process of recombination with lithium ions, S-S bond of amorphous phase molybdenum trisulfider ruptures to form short chain low sulfide and lithium composite which is not easy to dissolve in the electrolyte, thus reducing the shuttle of sulfide and overcoming the problem of cycle performance degradation caused by the large shuttle effect of the existing cathode materials of lithium-sulfide batteries.
Owner:CHENDU NEW KELI CHEM SCI CO LTD
Method and apparatus for measuring trace ingredients in water
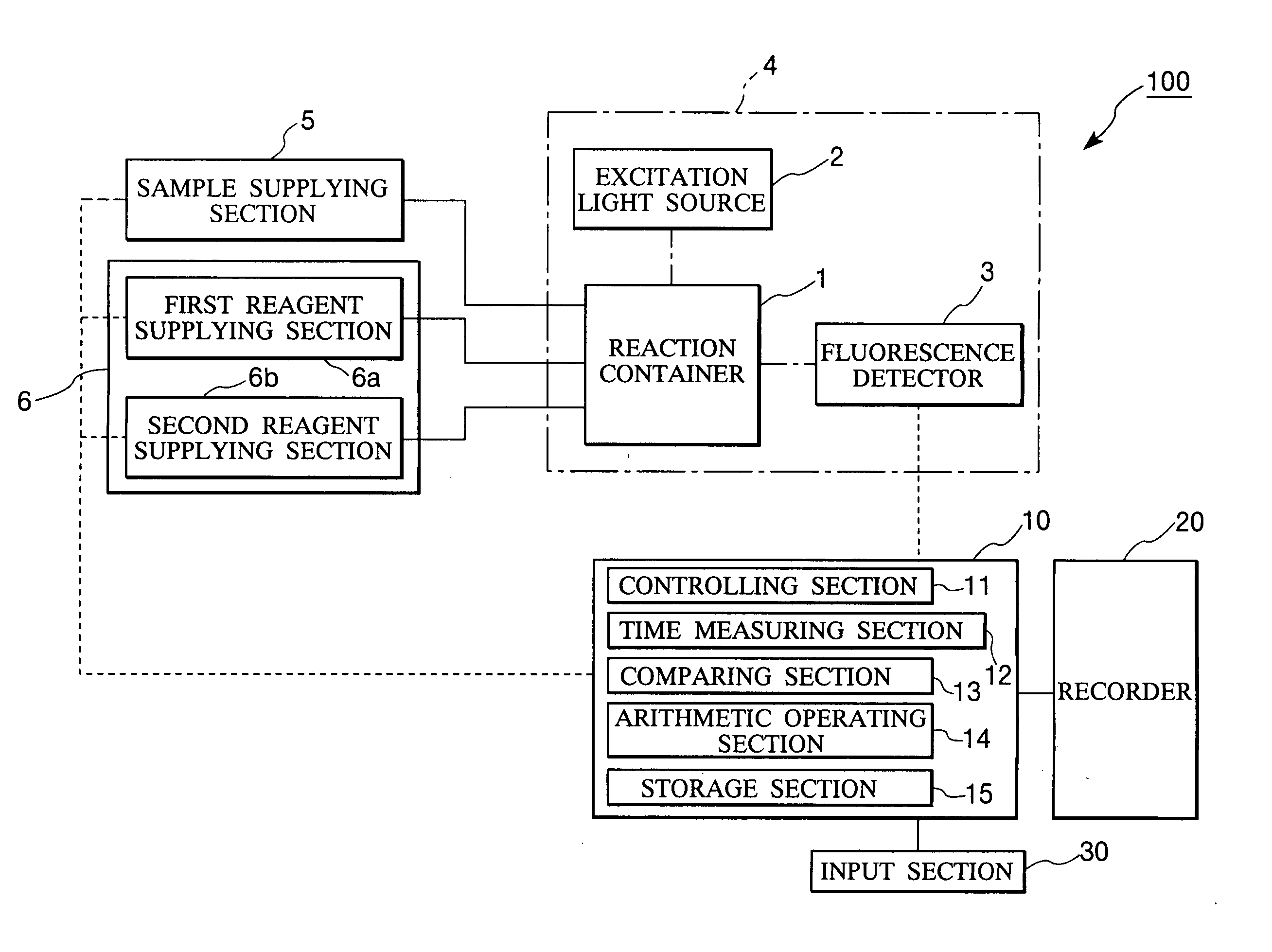
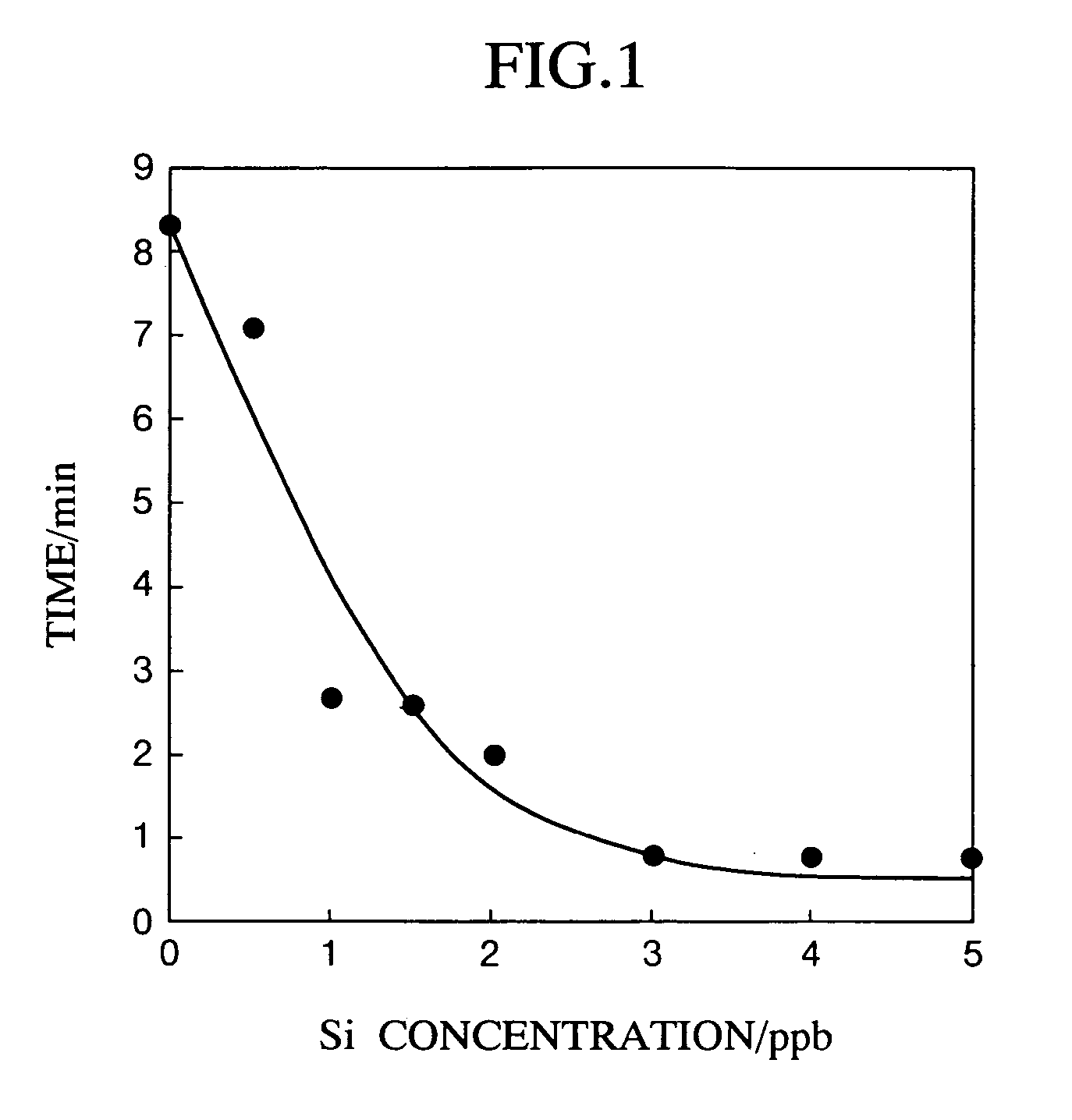
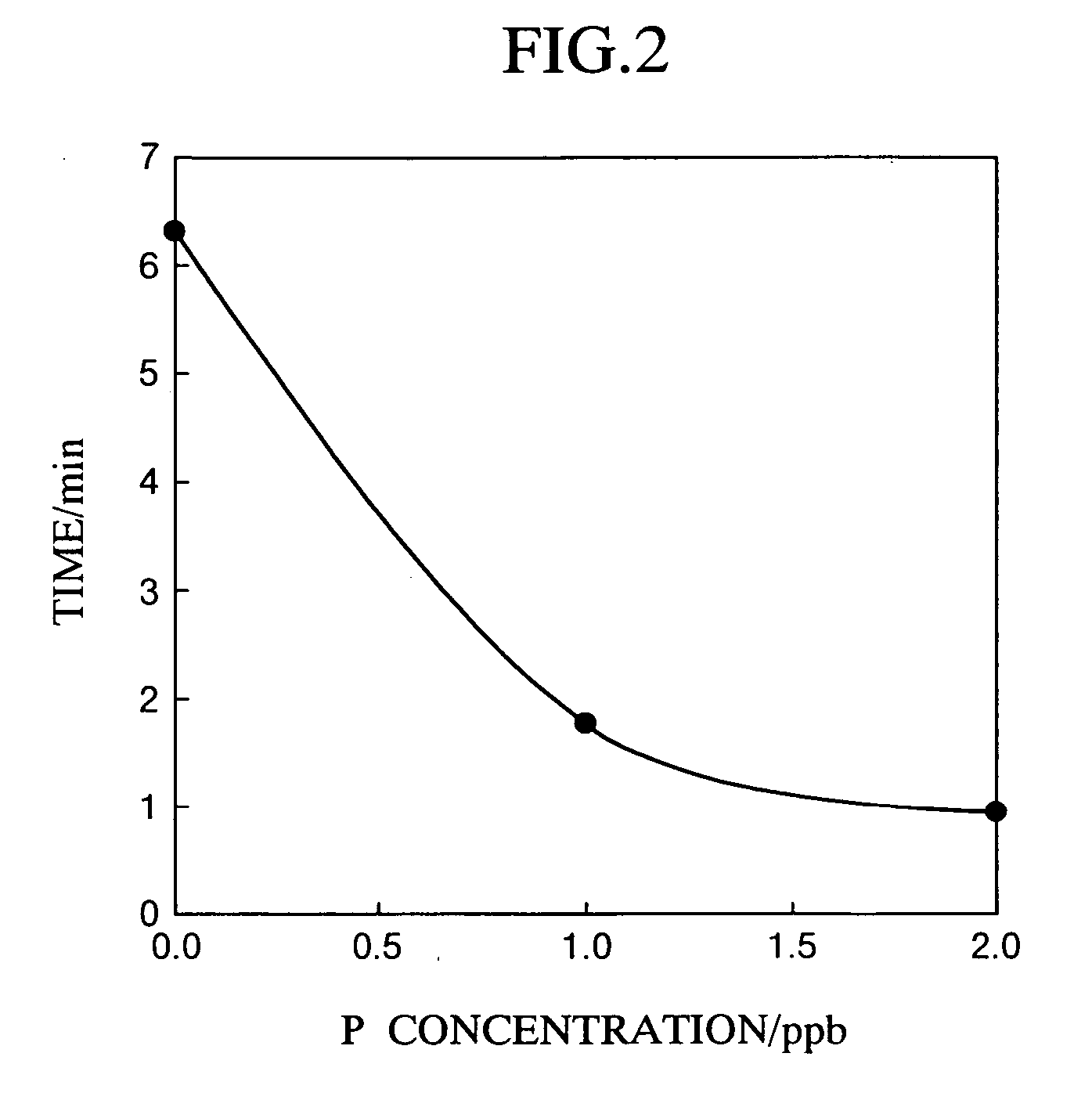
InactiveUS20050208669A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementMeasurement deviceAdditive ingredient
A method and an apparatus are provided for measuring trace ingredients in water, which make it possible to perform detection and quantitative determination of silica, phosphorus or arsenic in a sample solution. The method includes adding a molybdate ion to a sample solution under an acidic condition, then adding a fluorescent counter cationic pigment thereto, and measuring the time required for the fluorescence emitted by the resultant solution to be attenuated to a prescribed intensity. The measuring apparatus includes an excitation light source which irradiates excitation light to the above-modified solution; a fluorescence detector which detects the fluorescence emitted by the solution; means for measuring the time required for the fluorescence detected by the fluorescence detector to be attenuated to a prescribed intensity; and control means for determining the concentration of silica, phosphorus or arsenic in the sample solution from the time measurement.
Owner:TOHOKU TECHNO ARCH CO LTD +1
Fluorescence probe for recognizing molybdate and production method and recognition method thereof
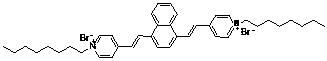
ActiveCN110128328AImprove anti-interference abilityHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceN dimethylformamideFluorescence
The invention discloses a fluorescence probe for recognizing molybdate and a production method and a recognition method thereof. The production method of the fluorescence probe comprises the steps of(1) adding 1,4-dibromonaphthalene, 4-vinyl pyridine, palladium dichloride, triphenylphosphine and potassium carbonate into triethylamine for mixing, sealing a mixture in a high-pressure reaction bottle in a N2 atmosphere, carrying out reaction at 110-120 DEG C for 24-36 h, extracting a product by using dichloromethane and a saturated salt solution, then conducting spin dry, conducting recrystallization by means of ethyl alcohol, and then conducting filtering and drying to obtain a product A; and (2) dissolving the product A in N,N-dimethylformamide, then adding 1-bromooctane, heating a mixtureto 80-90 DEG C, carrying out reaction for 20-24 h, then adding diethyl ether until a mixture completely participates, conducting suction filtering, washing a participate twice with diethyl ether, andconducting drying to obtain the probe. By means of the fluorescence probe for recognizing the molybdate and the production method and the recognition method thereof, the molybdate can be recognized,and the fluorescence probe for recognizing the molybdate and the production method and the recognition method thereof have the characters that the recognition cost is low, operation is simple, a result is visible, the sensibility is high, and the selectivity is good.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Heat transfer fluids and methods for preventing corrosion in heat transfer systems
Heat transfer fluid concentrates include: a freezing point depressant, water, or a combination thereof; an organophosphate; a carboxylic acid or a salt thereof; and a component selected from the groupconsisting of an alkaline earth metal ion, an alkali metal ion, a transition metal ion, an inorganic phosphate, molybdate ion, nitrate ion, nitrite ion, an azole compound, a copper and copper alloy corrosion inhibitor, a silicate, a silicate stabilizer, a water-soluble polymer, and combinations thereof. Ready-to-use heat transfer fluids and methods for preventing corrosion in heat transfer systems are described.
Owner:布拉斯通产品公司
Treatment solution for coating metal surface
ActiveUS8728251B2Excellent corrosion protectionImprove protectionSolid state diffusion coatingChromium freeMOLYBDATE ION
A chromium-free aqueous treatment solution for coating metal surfaces is described. The treatment solution contains fluorocomplex ions of titanium and / or zirconium and molybdate ions, vanadium ions and one or more aromatic carboxylic acids with at least one carboxyl groups and at least two further functional groups, wherein the two further functional groups are selected from the group comprising carboxyl groups, hydroxyl groups, amino groups and nitro groups.
Owner:BULK CHEM
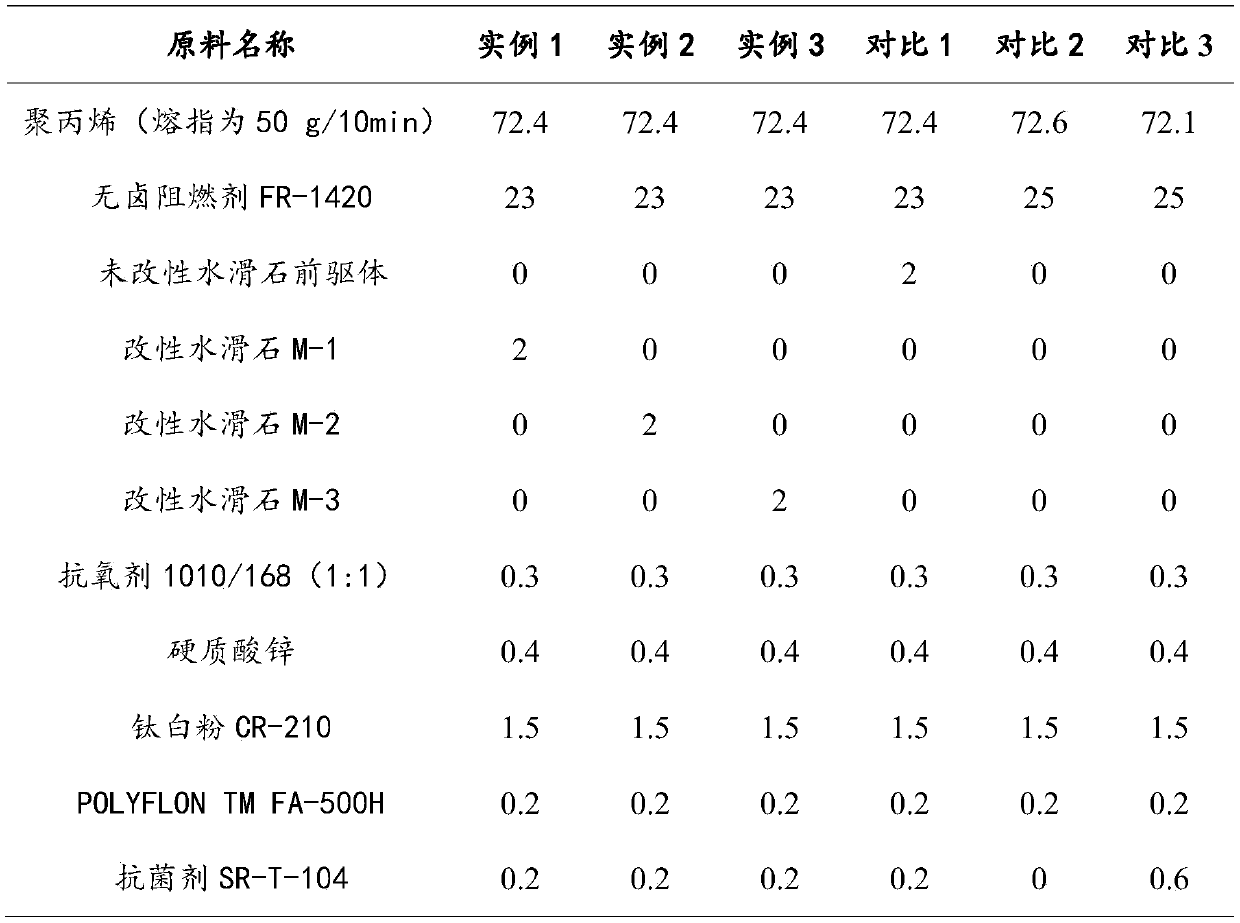
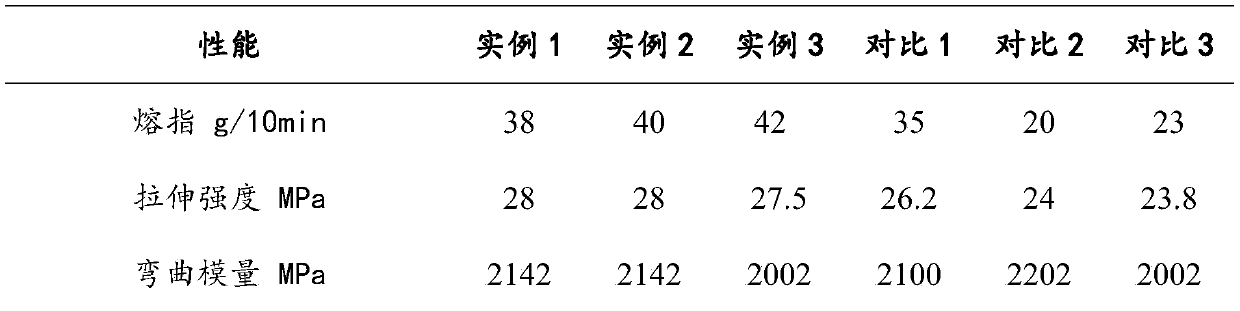
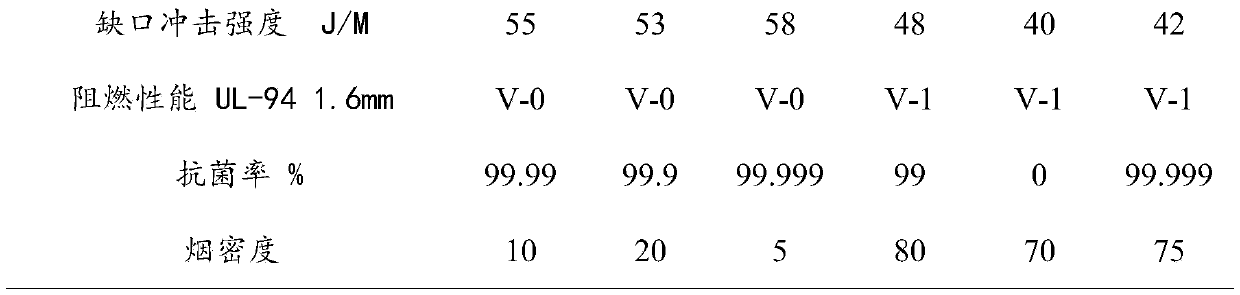
High-fluidity antibacterial halogen-free flame retardant composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-fluidity antibacterial halogen-free flame retardant composite material. The composite material comprises polypropylene, halogen-free flame retardants, modified hydrotalcite, antioxidants, lubricating agents, anti-dripping agents, titanium dioxide and antibacterial agents. The composite material has a higher melt flow index, a hydrotalcite precursor and silver nitrateare mixed and calcined, molybdate is added into mixture to prepare the modified hydrotalcite, the modified hydrotalcite is added, so that multiple performances are provided, flame-retardant efficiency can be improved, flame-retardant level reaches UL94 1.6 V-0, and high antibacterial action can be achieved under less antibacterial agents. Molybdic acid ions are introduced between hydrotalcite layers, so that the composite material has a smoke suppression function.
Owner:WANHUA CHEMICAL (NINGBO) CO LTD +1
Molybdenum-tonifying feed additive and its preparation method
InactiveCN101164432AEasy to implementSuitable for industrial productionAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsMOLYBDATE IONIon-exchange resin
The present invention discloses a molybdenum-supplementing feed additive and its preparation method. The described feed additive is an anion-exchange resin containing exchangeable molybdic acid radical, the molybdenum content in the anion-exchange resin is (by wt%) 1.0-8.5% Its preparation method is characterized by that it utilizes the feature of that the anion-exchange resin can produce exchange action with anion, so that it can make the molybdic acid radical ions be loaded in the anion-exchange resin. Because the anion-exchange resin is a controlled slowly-releasing carrier with excellent property, said anion-exchange resin possess the controllable slowly-releasing action for loaded molybdenum, so that the absorption utilization rate of molybdenum can be greatly raised. The molybdenum-supplencenting feed additive prepared by said invention has the characteristics of low-toxicity and high-efficiency, and is easily mixed with feed, can form uniform dispersion system, and is convenient for use.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Composite water treating agent for central air conditioner freezing water
ActiveCN1880245ANo pollution in the processLow costTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsRare-earth elementMOLYBDATE ION
The invention discloses a treating agent of cooling water and composite water in central air-conditioning, including the weight or portioning components listed as following: one to ten portion of organic phosphinic acid compounds; one to ten portion of molybdate calculated according to molybdic acid ion; 0.1 to ten portion of rare-earth element salts; one to five portion of copper inhibitor; zero to two portion of zinc calculated according to zinc ion. This invention is low-phosphorus and environment-friendly type, good quality in antisludging and corrosion inhibit, easy to obtain material, explore the application area of using rare-earth element in water treatment, and have greatly active meaning in developing rare earth project of our country.
Owner:SHANGHAI EMPEROR OF CLEANING HI TECH
Method of extractively separating molybdenum from tungstate solution
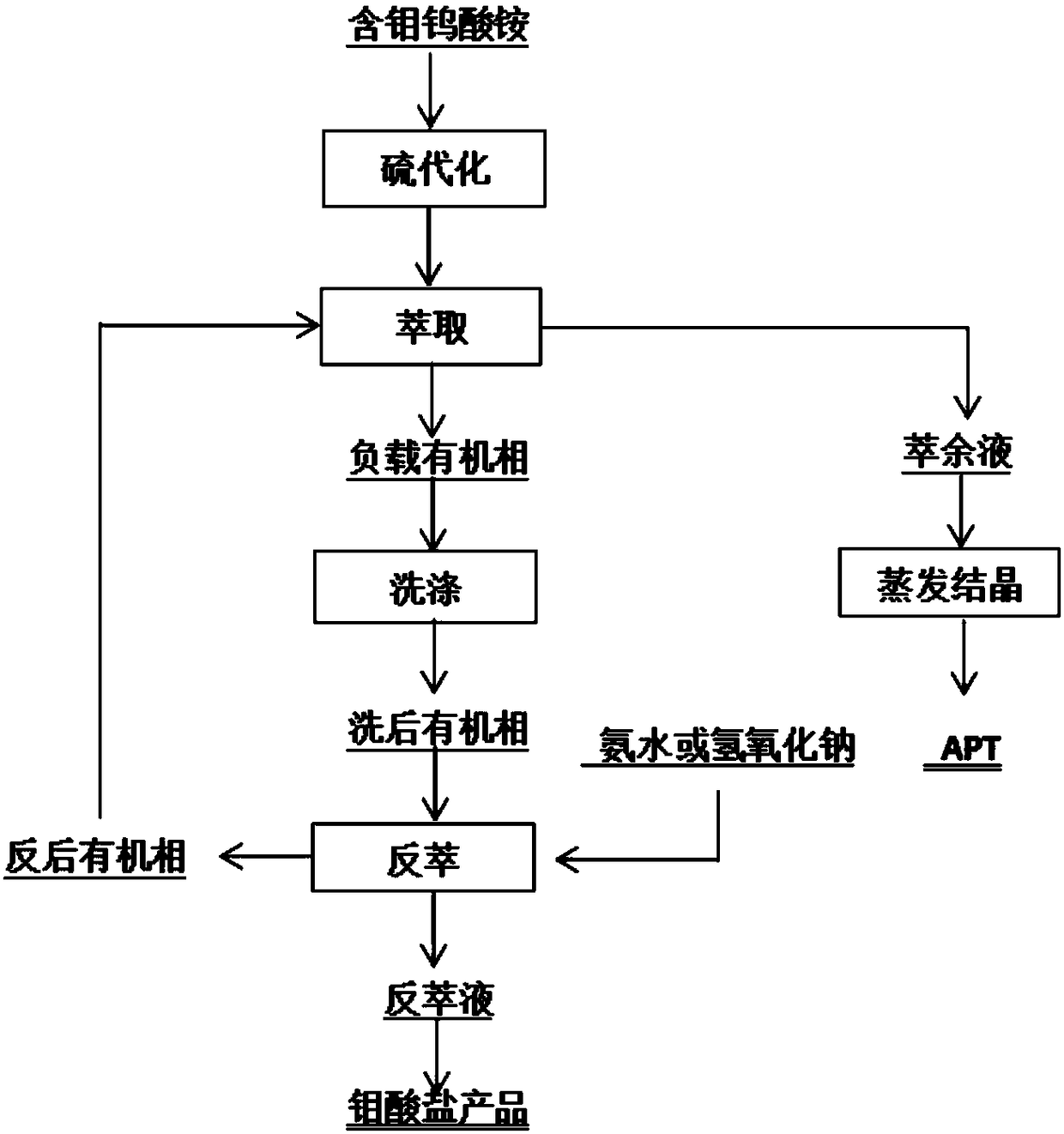
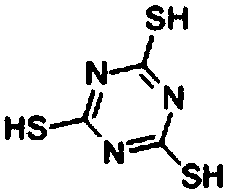
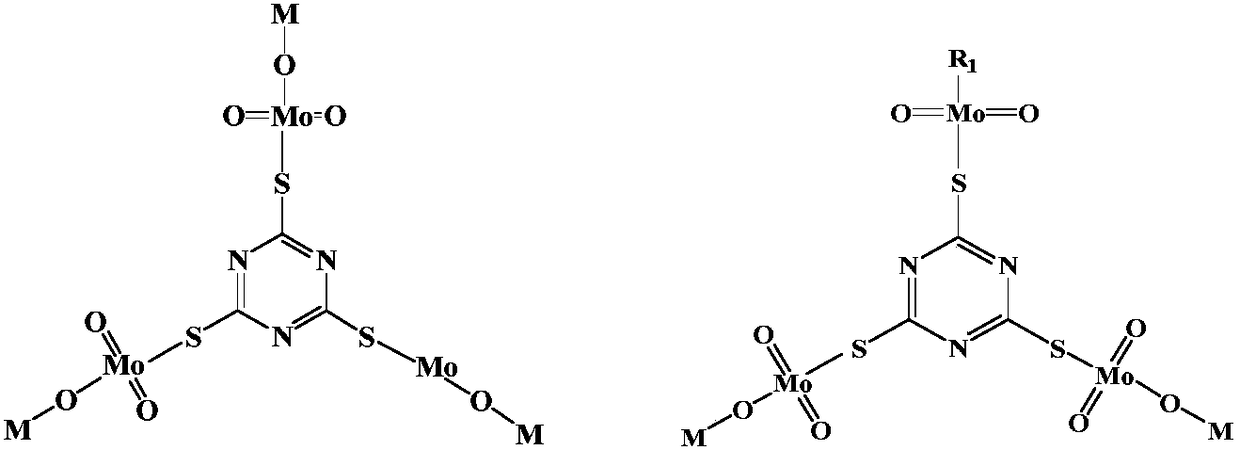
ActiveCN108588417ASolve the problem of difficult strippingEliminate generationProcess efficiency improvementMOLYBDATE IONTungstate
The invention discloses a method of extractively separating molybdenum from a tungstate solution. The method includes steps of: adding tripolythiocyanic acid (also called as 2,4,6-trithio-S-triazine,TTCA) to a molybdenum-containing tungstate solution to perform a sulfuration reaction to obtain a mixed solution; performing extraction separation to the mixed solution with an organic phase containing a primary amine extract agent; washing the organic phase supporting molybdenum, and performing reverse extraction separation with an alkaline solution to obtain the tungstate solution. The method can high-effectively separate the tungsten and molybdenum and directly prepare high-purity tungstate solution and molybdate solution; in addition, the sulfuration reaction is carried out with the tripolythiocyanic acid and is free of release of harmful gas, such as H2S, so that the method is safe and environment-friendly. The sulfuration product is easy to subject the extraction and reverse extraction. The reverse extraction separation is free of an oxidant, so that a problem that reverse extraction is difficult after extraction by quaternary ammonium salt is carried out to MoS2-4 generated by sulfurating the molybdate ions by a common sulfuration agent can be solved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com