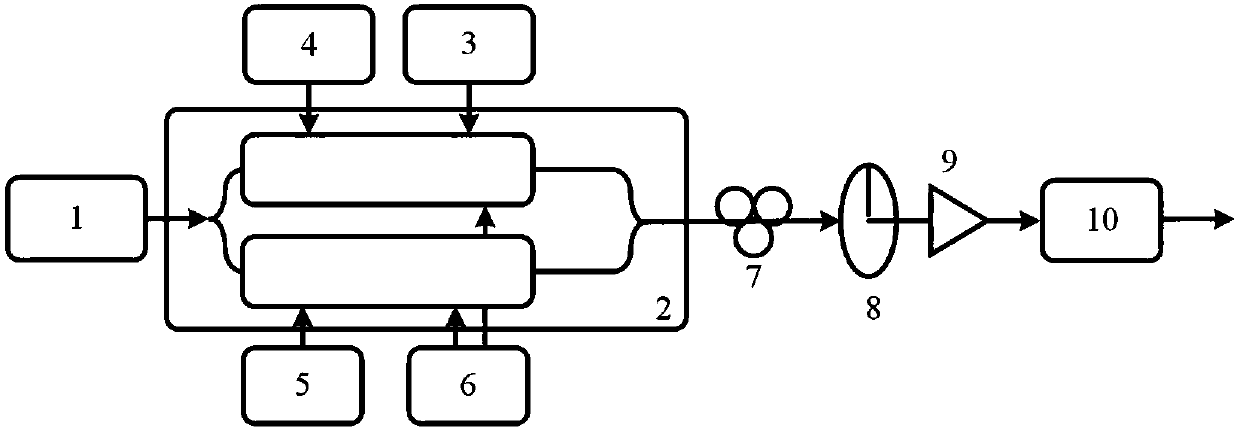
Microwave same-frequency signal interference suppression and down-conversion receiving device and method
A technology for interference suppression and co-frequency signals, which is applied in the phase modulation carrier system, electromagnetic wave transmission system, distortion/dispersion elimination, etc., can solve the problems of periodic fading of useful signals, affecting the suppression level of interference signals, etc., and achieve the effect of periodic fading The effect of reducing, realizing optical down-conversion, and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
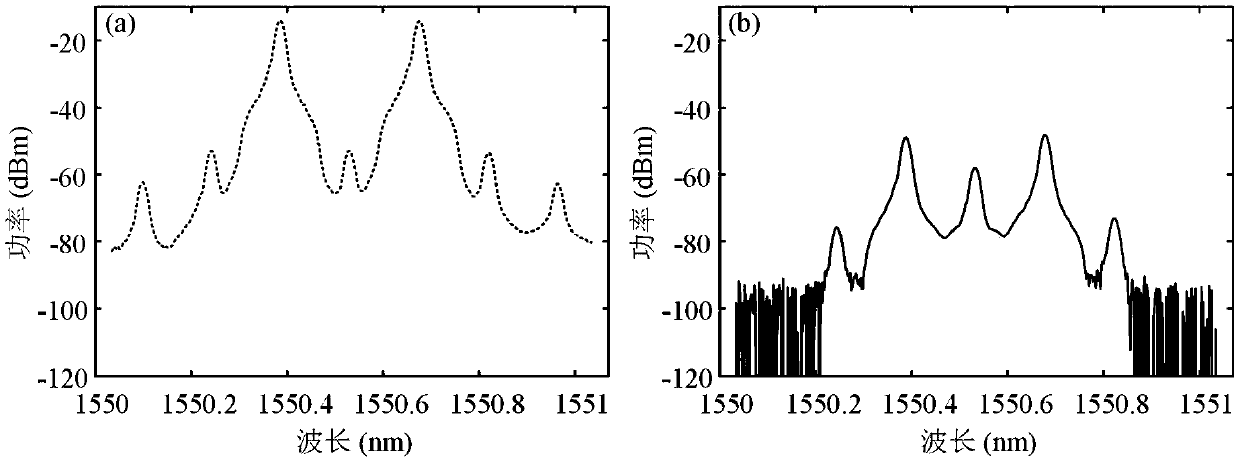
[0057] In this embodiment, the wavelength of the optical signal output by the laser is 1550.55 nm. Adjust the DC bias voltage so that the two sub-MZMs of the sub-DP-MZM that input the receiving signal and interference signal at the RF input port are biased at the minimum transmission point, and the main MZM is biased at the minimum transmission point; make the RF input port input the local oscillator signal The two sub-MZMs of the sub-DP-MZM are biased at the minimum transmission point, and the main MZM is biased at the maximum transmission point. In this embodiment, the suppression performance of single-frequency and co-channel interference signals is mainly studied. At this time, the useful signal in the received signal is set to 0, that is, the received signal only contains the interference signal. figure 2 When the frequency of the input signal is 18 GHz, the spectrogram (a) of the output optical signal of the sub-DP-MZM of the input receiving signal and interference sign...
Embodiment 2
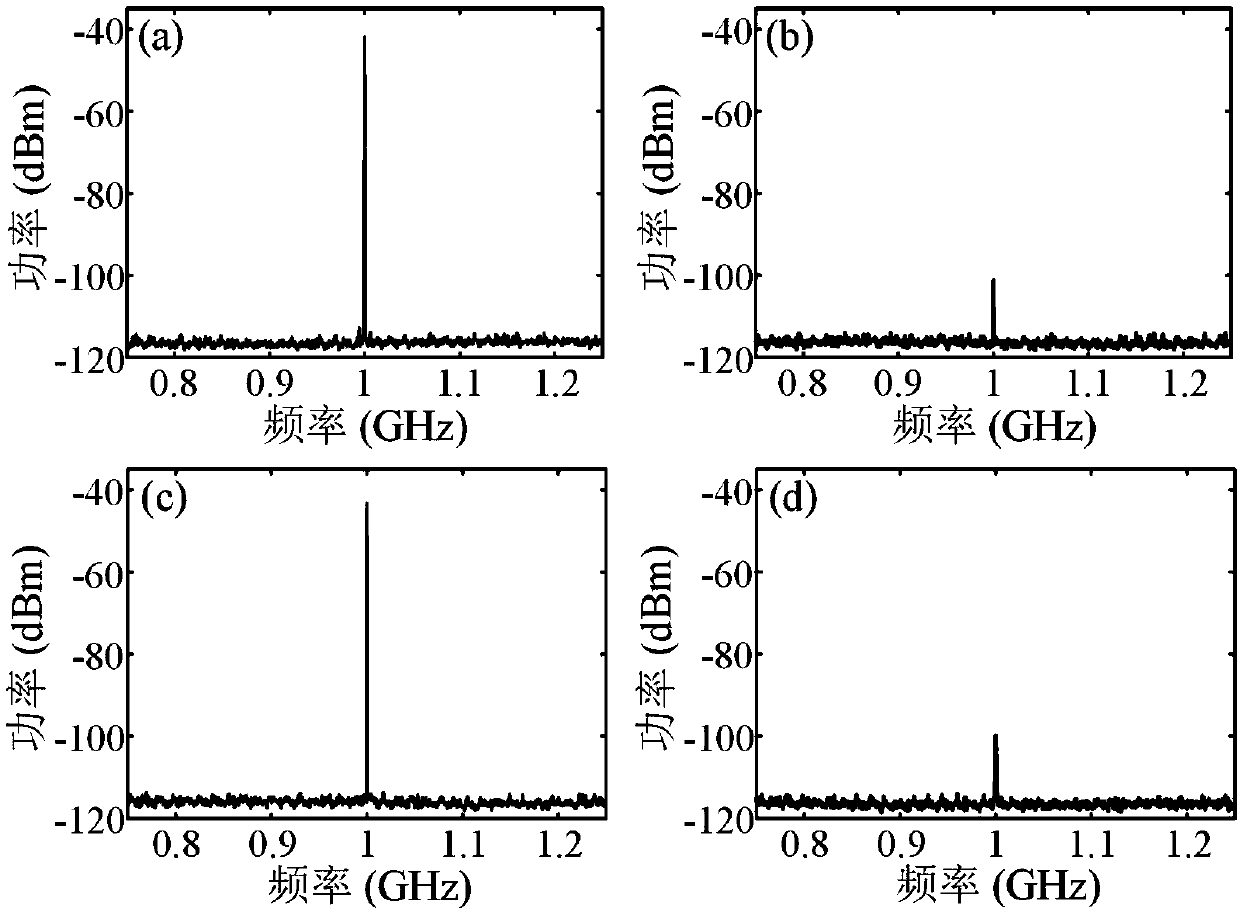
[0059] In this embodiment, the wavelength of the optical signal output by the laser is 1550.55 nm. Adjust the DC bias voltage so that the two sub-MZMs of the sub-DP-MZM that input the receiving signal and interference signal at the RF input port are biased at the minimum transmission point, and the main MZM is biased at the minimum transmission point; make the RF input port input the local oscillator signal The two sub-MZMs of the sub-DP-MZM are biased at the minimum transmission point, and the main MZM is biased at the maximum transmission point. In this embodiment, the suppression performance of broadband co-frequency interference signal is mainly studied. At this time, the interference signal in the received signal is set as a broadband QPSK modulation signal with a symbol rate of 200 Mbps, and the useful signal is a pure microwave signal of the same frequency. Figure 4 IF signal spectrogram generated for broadband co-channel interference suppression, Figure 4 (a)(b) are...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com