Medical titanium material surface oxidization strengthening method
A surface oxidation and anodic oxidation technology, applied in the direction of surface reaction electrolytic coating, electrolytic coating, coating, etc., can solve the problems of easy peeling of nanotubes and poor mechanical stability, and achieve enhanced mechanical stability, improved corrosion resistance, Effect of improving corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1 Novel titanium (titanium alloy)-TiO 2 Preparation of nanotube materials
[0025] 1. Prepare ammonium fluoride electrolyte and phosphoric acid electrolyte: weigh 2.0 g ammonium fluoride and 400 mL ethylene glycol, put ammonium fluoride into ethylene glycol and stir to dissolve. Measure 12 mL phosphoric acid and 400 mL ethylene glycol, dissolve phosphoric acid in ethylene glycol and stir thoroughly.
[0026] 2. Put the Ti metal sheet or titanium alloy block in the ammonium fluoride electrolyte for anodic oxidation pretreatment, take it out after 30 minutes and place it in deionized water for ultrasonic cleaning, then put it back into the ammonium fluoride electrolyte for anodic oxidation for 1 hour, After immersing in the phosphoric acid electrolyte again for anodic oxidation for 3 minutes, a new type of titanium (titanium alloy)-TiO 2 nanotube material.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2 Material wear resistance test
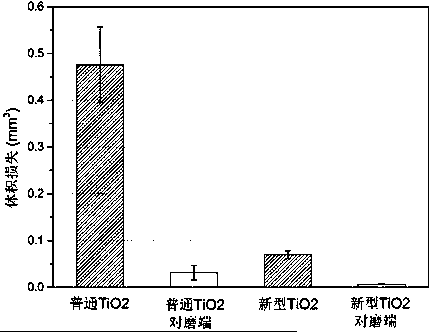
[0028] A model using six friction and wear testing machines working simultaneously ( figure 1 ), for the new type of titanium (titanium alloy)-TiO 2 The friction and wear properties of the nanotube material surface were measured and evaluated. The frictional couple is a curvature stainless steel Pin (R=60 mm), the friction mode is a reciprocating sliding mode, the sliding length is 10 mm, and the rotation angle of the stainless steel Pin is 5 o , the friction test cycle is 12000 cycles, ordinary titanium-TiO 2 Nanotube material as a comparison.
[0029] Such as figure 2 As shown, after the test, ordinary titanium-TiO 2 Nanotube materials have experienced severe wear, while the new titanium (titanium alloy)-TiO 2 The amount of wear of the nanotube material is extremely small. Further, we measured the wear volume of the material and the dual surface, as image 3 As shown, ordinary titanium-TiO 2 Nanotube materials and th...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Example 3 TiO 2 Interfacial peel strength test of nanotube layer
[0031] TiO2 is measured by national standard ASTM D4541 / D7234, ISO 4624 / 16276-1 2 Interfacial bonding strength of nanotube layer on substrate surface, ordinary titanium-TiO 2 nanotube material as a comparison. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the new titanium (titanium alloy)-TiO 2 TiO on the surface of nanotube materials 2 The interlayer bond strength is greater than 2.5 MPa, close to level 1; while for ordinary titanium-TiO 2 As far as nanotube materials are concerned, the surface TiO 2 The bonding force between the layer and the substrate is only 1.4 MPa.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com