Low-temperature preparation method of anti-cracking agent of concrete
An anti-cracking agent and concrete technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems of high energy consumption and complex process, and achieve the effects of low energy consumption, low calcination temperature and lower initial cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] A kind of low-temperature preparation method of concrete anti-cracking agent of the present invention, comprises the steps:
[0026] (1) Put the raw materials into a planetary ball mill, mix and grind them; wherein, the raw materials include aluminum-calcium raw materials, aluminum raw materials, calcium raw materials, and industrial gypsum; the mass ratio of raw materials is: aluminum-calcium raw materials: aluminum raw materials : Calcium raw materials: industrial gypsum = 15.73-29.05: 33.82-48.5: 27.62-40.13: 10.08-18.62; aluminum-calcium raw materials are high alumina cement, CaO-Al 2 o 3 One or more of base refining slag or waste refractory materials; aluminum raw material is bauxite; calcareous raw material is limestone; industrial gypsum is industrial waste gypsum such as desulfurized gypsum;
[0027] (2) Press the raw materials mixed in step (1) into a cake under a pressure of 2-6 MPa, place it in a high-temperature electric furnace and heat it up to 700°C-1200...
Embodiment 1
[0034] The ratio of raw materials is as shown in Table 2:
[0035] Table 2 Embodiment 1 raw material proportioning
[0036]
[0037] Specific steps are as follows:
[0038] 1) Mixing: Weigh the raw materials according to the ratio in Table 2, place them in a planetary mill, grind for 120min, and press them into cakes under a pressure of 2MPa;
[0039] 2) Calcination: put it in a high-temperature electric furnace and raise the temperature to 700°C, keep it warm for 3 hours, and then cool it rapidly;
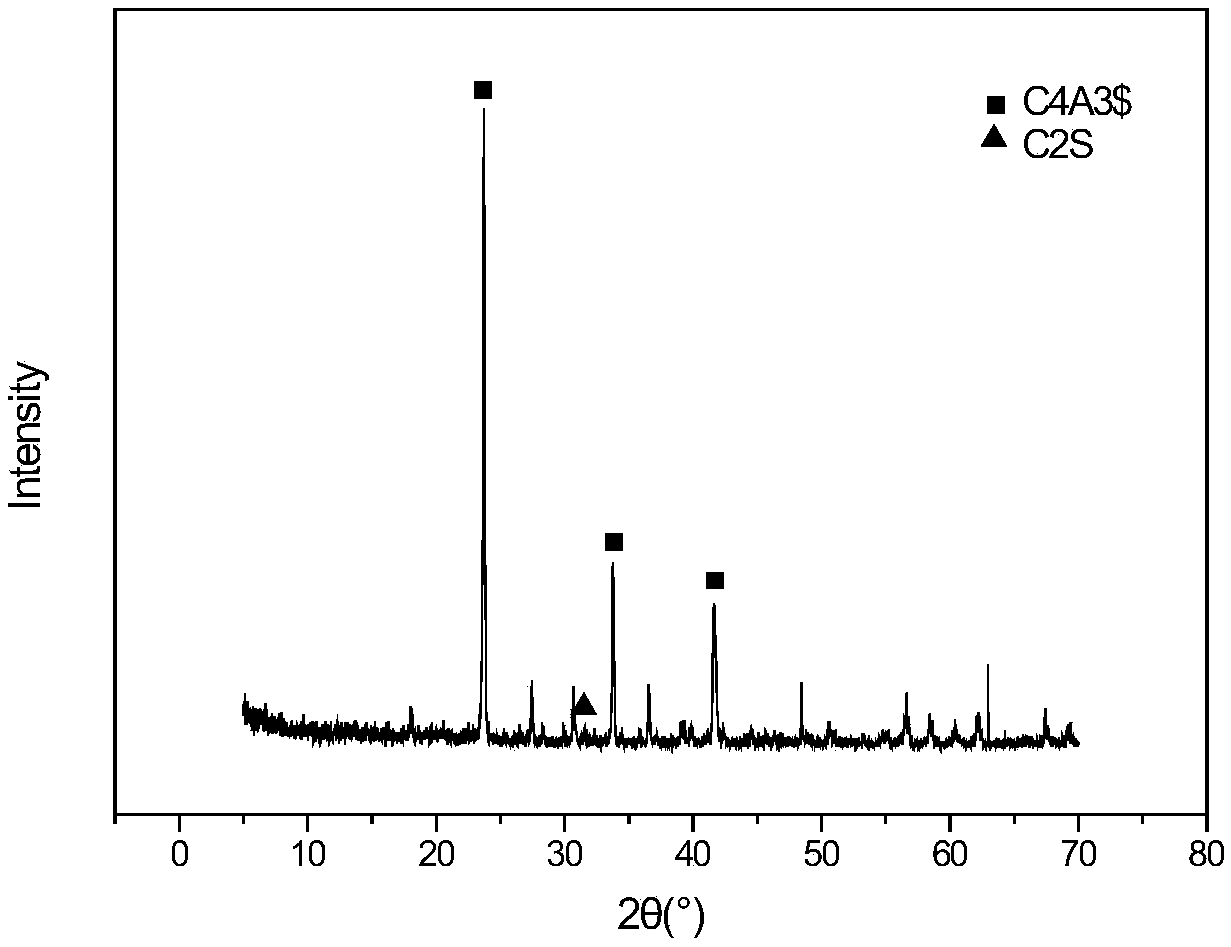
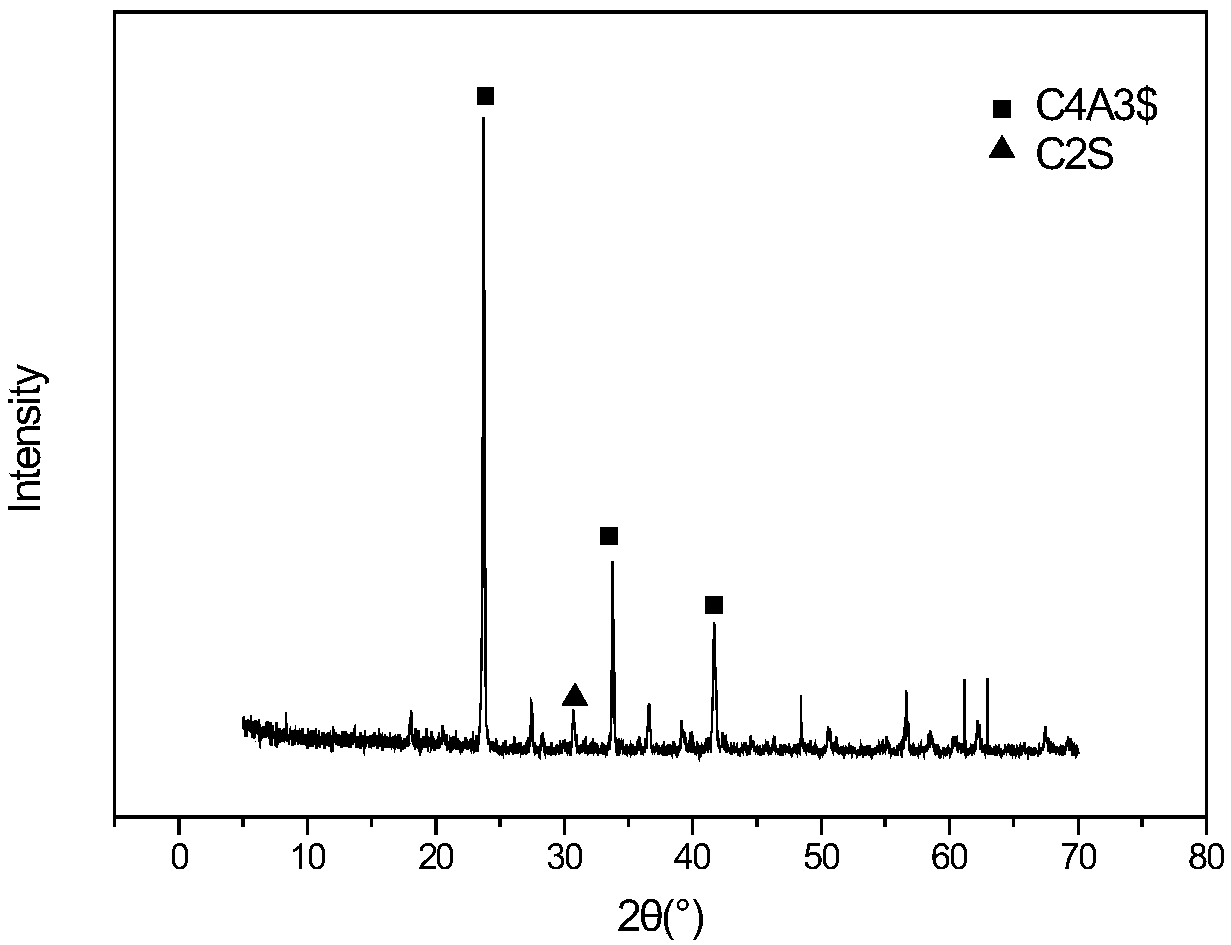
[0040] 3) Sieving: Grind until the particles can all pass through a square hole sieve with a pore size of 80 μm, and carry out XRD test and SEM analysis, such as figure 1 and figure 2 (CA, CA 2 , high alumina cement is mesophase).
Embodiment 2
[0042] Specific steps are as follows:
[0043] 1) Mixing: Weigh the raw materials according to the ratio in Table 2, place them in a planetary mill, grind for 120min, and press them into cakes under a pressure of 2MPa;
[0044] 2) Calcination: put it in a high-temperature electric furnace and raise the temperature to 700°C, keep it warm for 3 hours, and then cool it rapidly;
[0045] 3) Sieve: Grind until the particles can all pass through a square hole sieve with an aperture of 80 μm and a specific surface area of 350 m 2 / Kg, obtain anti-cracking agent;
[0046] 4) Strength test: the anti-cracking agent obtained in the step 3) of adding 5% of the cement mass into ordinary Portland cement, respectively carried out 3d, 28d bending resistance, compressive strength performance test and crack resistance performance test, as shown in Table 3 shown.
[0047] Table 3 Example 2 strength performance and crack resistance test
[0048]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com