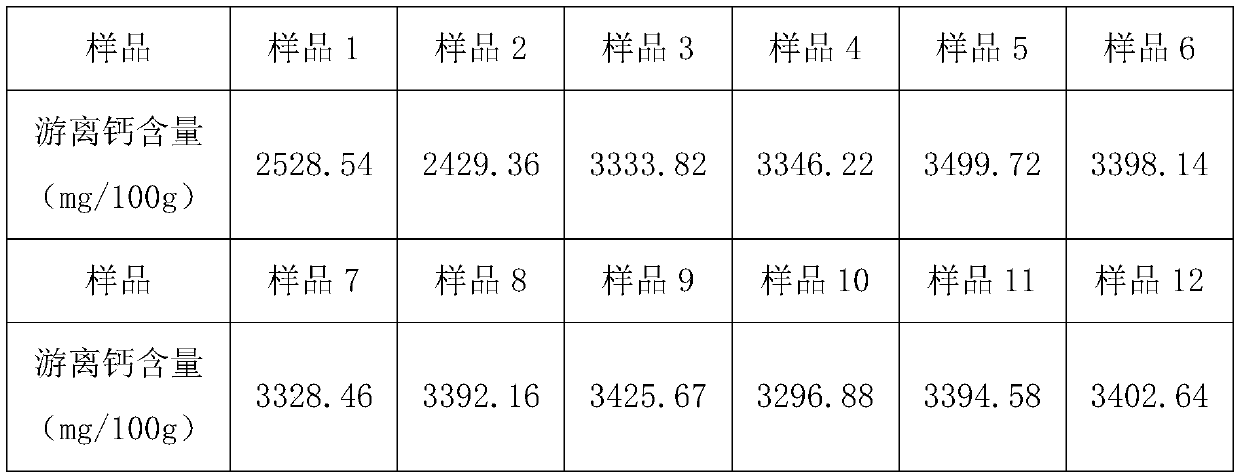
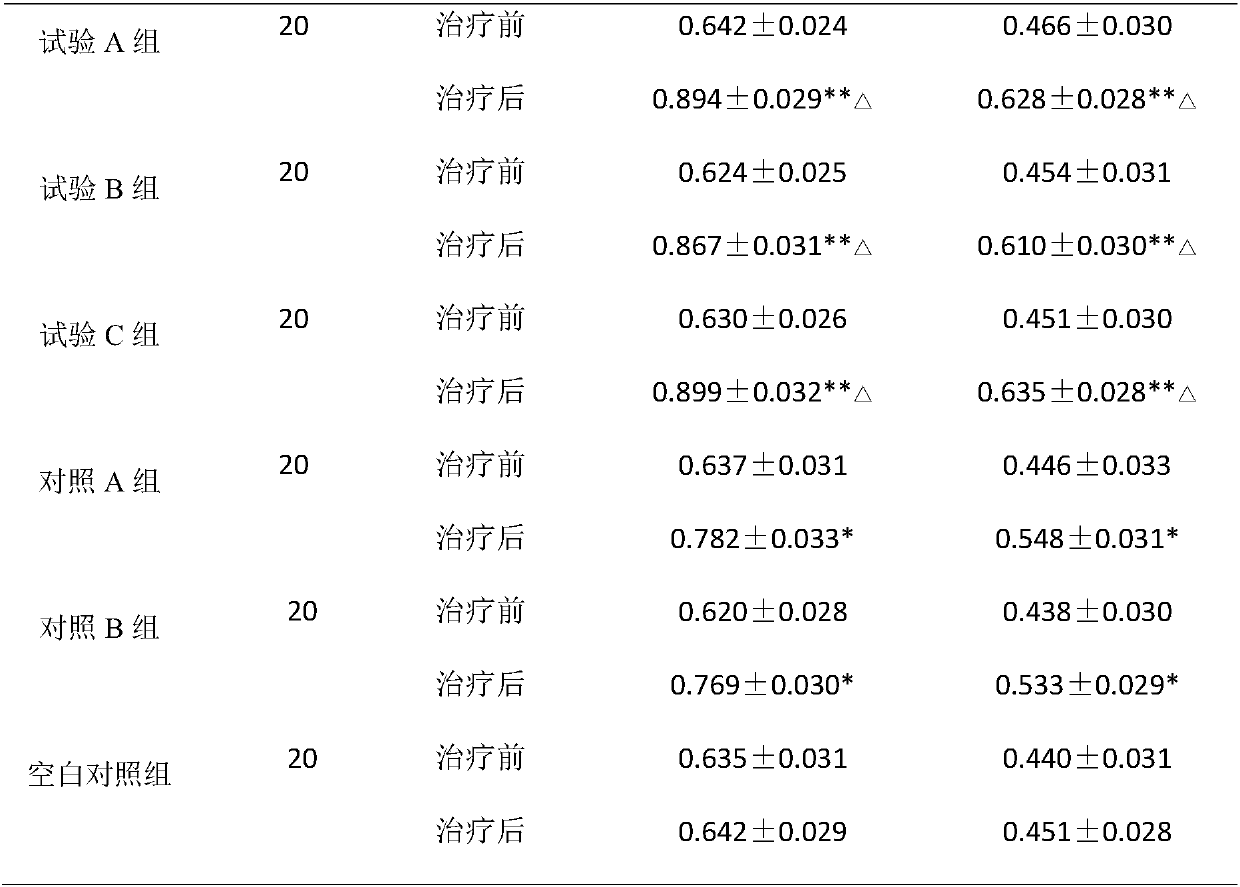
Method for extracting bone calcium and osteocalcin
A technology of osteocalcin and aggregates, which is applied in food extraction, pharmaceutical formulations, functions of food ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory calcium supplementation and insufficient free calcium content.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Preparation medium: MRS medium: peptone 1%, beef extract 1%, yeast extract 0.5%, glucose 2%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.2%, sodium acetate 0.5%, magnesium sulfate 0.02%, manganese sulfate 0.005%, Tween -80 0.1%, triammonium citrate 0.2%, pH 5.5~6.0, 115℃, sterilize for 30min.
Embodiment 2
[0055] (1) Bone crushing and sterilization;
[0056] (2) Take B. lactis (B. lactis), Lactobacillus bulgaricus (L. bulgaricus) and B. adolescentis (B. adolescentis), the weight ratio of three lactic acid bacteria is 1:2:2; the weight and volume of aggregate and water The ratio is 1:3, the weight ratio of lactic acid bacteria to the aggregate is 0.03%, 5% of the total weight of sucrose is added, and the fermentation is carried out at 40°C for 12 hours, and sterilized at 120°C for 30 minutes;
[0057] (3) Add hydrochloric acid to adjust pH value 1, add pepsin, the weight ratio of aggregate is 0.04%, hydrolysis temperature is 35℃, stir for 1h, add alkali to adjust the pH value to 6, add papain, weight ratio of aggregate is 0.04 %, 40℃, stirring for 1h, heating to kill the enzyme;
[0058] (4) Add 5% of the total weight of glucose, add Leuconostoc cristatum and citric acid, the weight ratio of Leuconostoc cristatum to the aggregate weight is 0.02%, the weight ratio of Leuconostoc lactis ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] (1) Bone crushing and sterilization;
[0061] (2) Take B. lactis (B. lactis), Lactobacillus bulgaricus (L. bulgaricus) and B. adolescentis (B. adolescentis), the weight ratio of three lactic acid bacteria is 1:2:2; the weight and volume of aggregate and water The ratio is 1:5, the weight ratio of lactic acid bacteria to the aggregate is 0.07%, 5% of the total weight of sucrose is added, fermentation is carried out at 50°C for 12 hours, and sterilized at 120°C for 30 minutes;
[0062] (3) Add hydrochloric acid to adjust pH value 3, add pepsin, the weight ratio of aggregate is 0.08%, hydrolysis temperature 40℃, stir for 2h, add alkali to adjust the pH value to 7, add papain, weight ratio of aggregate is 0.08 %, 50℃, stir for 2h, heat to kill the enzyme;
[0063] (4) Add 5% of the total weight of glucose, add Leuconostoc milk fat and citric acid, the weight ratio of Leuconostoc milk fat to aggregate is 0.06%, the weight ratio of Leuconostoc milk fat to citric acid is 1:30, and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com