Biaxially oriented polypropylene film
A polypropylene film, biaxially oriented technology, used in synthetic resin layered products, chemical instruments and methods, layered products, etc., to achieve the effects of excellent film processability, strong orientation, and small molecular weight distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
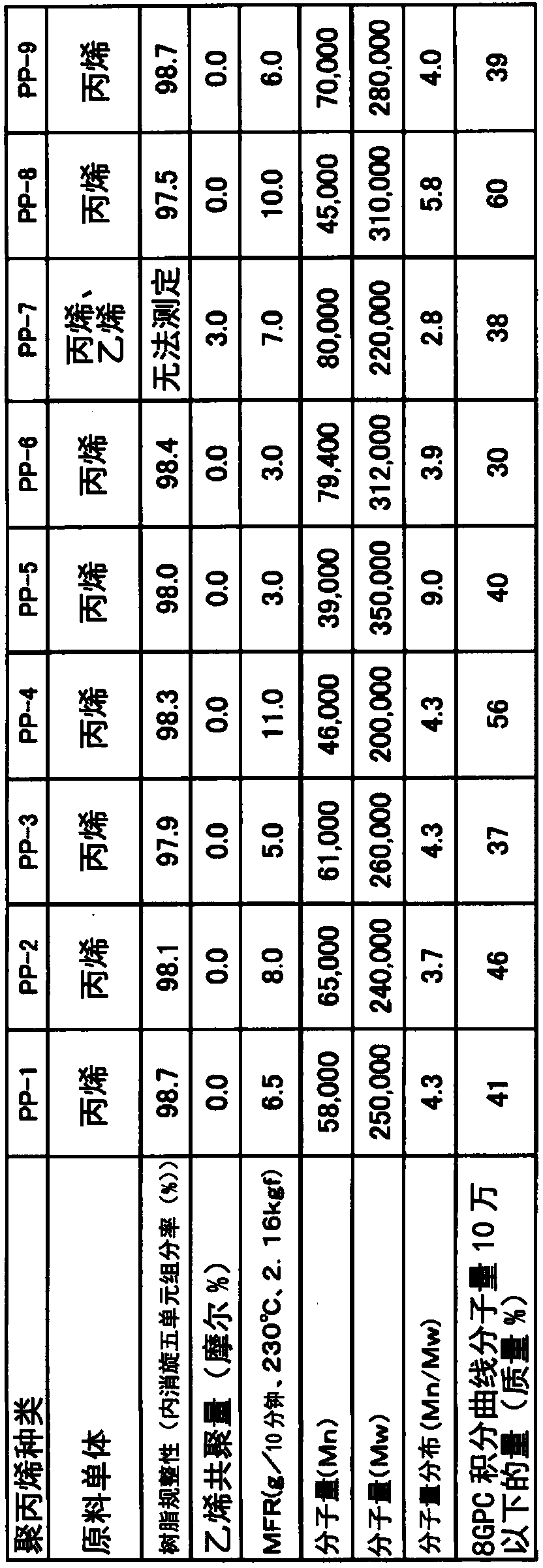
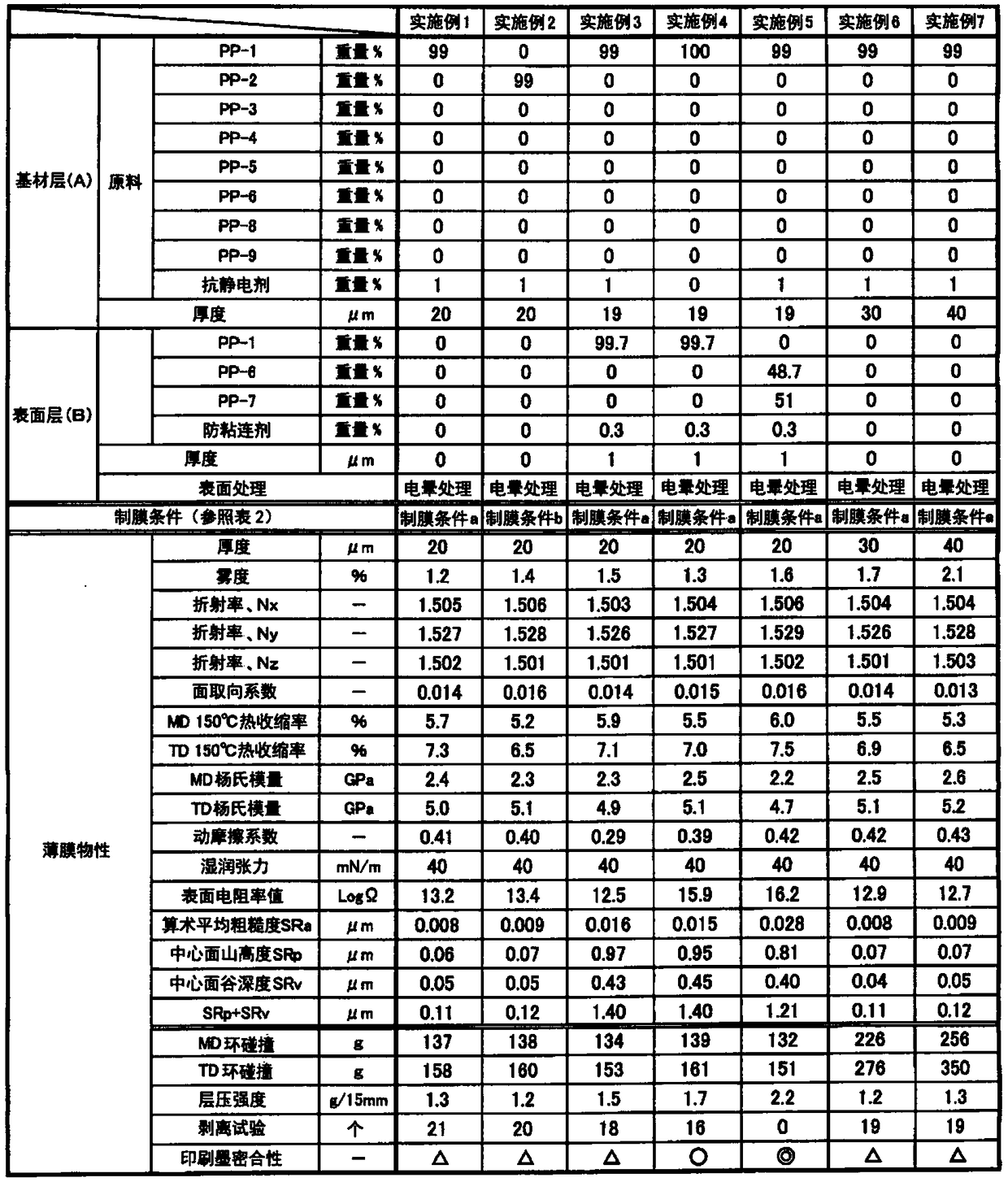
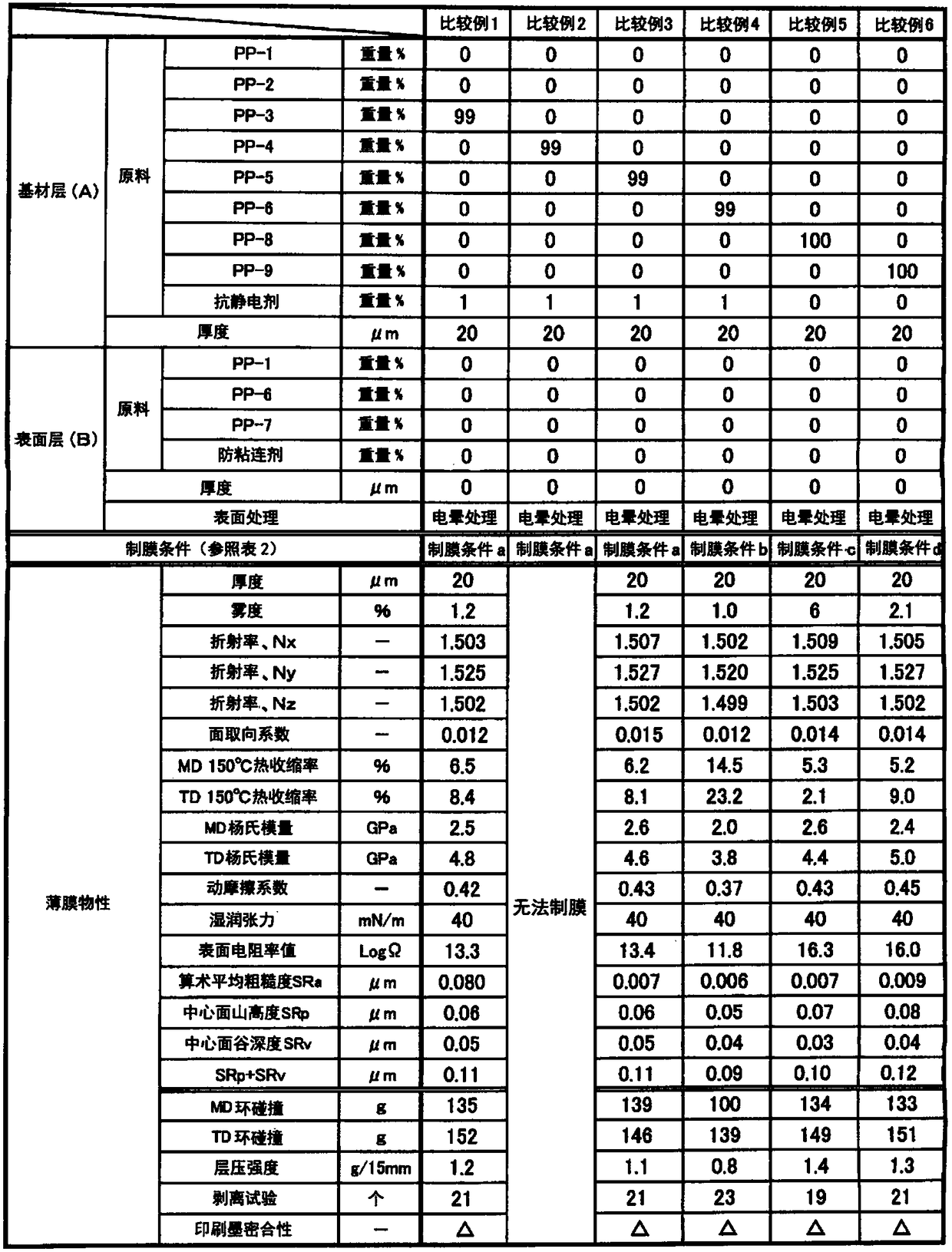
[0194] What is used is to mix 99% by weight of polypropylene homopolymer PP-1 shown in Table 1 and 1% by weight of antistatic agent (diethanolamine stearate stearate (Matsumoto Yushi Co., Ltd. KYM-4K)) resulting mixture.
[0195] This mixture was melted at 250°C using a 60mm extruder, co-extruded into a sheet form from a T-die, cooled and solidified on a cooling roll at 30°C, and machined at 135°C in the longitudinal direction (MD ) stretched to 4.5 times. Next, in the tenter, both ends of the film in the width direction are clamped with clamps, preheated at 175°C, stretched to 8.2 times in the width direction (TD) at 160°C, and relaxed in the width direction (TD) 6.7%, while heat-fixing at 170°C. The film forming conditions at this time are shown in Table 2 as film forming conditions a.
[0196] For the one-side surface side of the obtained biaxially oriented polypropylene film, use a corona treatment machine manufactured by SOFTAL Corona & Plasma GmbH, and apply a current...
Embodiment 2
[0198] The polypropylene homopolymer PP-1 shown in Table 1 was changed to polypropylene resin PP-2, and the mixed raw materials were melted at 250°C using a 60mm extruder, and co-extruded into a sheet form from a T-die. After being cooled and solidified on a cooling roll at 30°C, it was stretched to 4.5 times in the machine direction (MD) at 125°C. Next, in the tenter, both ends of the film in the width direction are clamped with clamps, preheated at 170°C, stretched to 8.2 times in the width direction (TD) at 158°C, and relaxed in the width direction (TD) A biaxially stretched single-layer polypropylene film was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the content was 6.7% and heat-set at 165°C. The film forming conditions at this time are shown in Table 2 as film forming conditions b. The physical properties of the obtained film are shown in Table 3.
Embodiment 3
[0200] In the base material layer (A), what is used is that the polypropylene homopolymer PP-1 shown in Table 1 99% by weight and an antistatic agent (diethanolamine stearate stearate (Matsumoto Yushi Co., Ltd. KYM- 4K)) A mixed raw material obtained by mixing 1% by weight. In addition, in the surface layer (B), 99.7% by weight of the polypropylene homopolymer PP-1 shown in Table 1, an antiblocking agent (commercially available silica particles (average particle diameter: 1.3 μm) ) 0.3% by mass of the mixed raw material blended.
[0201] Using a 60mm extruder for the mixed raw material used for the base layer (A) and a 65mm extruder for the mixed raw material used for the surface layer (B), melt the raw material resin at 250°C and co-extrude from a T-die It is formed into a sheet, cooled and solidified on a cooling roll at 30°C, and then stretched to 4.5 times in the longitudinal direction (MD) at 135°C. Next, in the tenter, both ends of the film in the width direction are c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com