Preparation method for thin flame-retardant non-woven fabric applied to vehicles
A technology of flame-retardant non-woven fabrics and manufacturing methods, which is applied in the direction of flame-retardant fibers, non-woven fabrics, fiber types, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve high-efficiency flame retardancy and flame-retardant effects, and achieve excellent adhesion Adhesion, good flame retardant effect, material saving effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The first step, the preparation of base cloth
[0023] Polyester fibers are formed by opening, carding, net laying, and needle punching, and then viscose fibers are laid on the upper layer and the two are needle punched to form a base fabric. , so that the polyester fibers are evenly and firmly connected together. The total weight of the base cloth is 100-120g / m 2 , and the weight percentage of polyester fiber is 80-95%, and the weight percentage of viscose fiber is 5-20%.
[0024] The second step, dipping
[0025] The flame retardant and the water-based glue are uniformly mixed to form the flame-retardant glue, wherein the weight percentage of the water-based glue is 40-60%, and the weight percentage of the flame retardant is 40-60%. The flame retardant glue is mixed with color paste and water to obtain an impregnating liquid, and the base cloth obtained by acupuncture is soaked in the impregnating liquid, and after impregnated, it is rolled by a hot roller to remov...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The first step, the preparation of base cloth
[0034] Polyester fibers are formed by opening, carding, net laying, and needle punching, and then viscose fibers are laid on the upper layer and the two are needle punched to form a base fabric. , so that the polyester fibers are evenly and firmly connected together. The total weight of the base cloth is 100-120g / m 2 , and the weight percentage of polyester fiber is 60-80%, and the weight percentage of viscose fiber is 20-40%.
[0035] The second step, dipping
[0036] The flame retardant and the water-based glue are uniformly mixed to form the flame-retardant glue, wherein the weight percentage of the water-based glue is 40-60%, and the weight percentage of the flame retardant is 40-60%. The flame retardant glue is mixed with color paste and water to obtain an impregnating liquid, and the base cloth obtained by acupuncture is soaked in the impregnating liquid, and after impregnated, it is rolled by a hot roller to remo...
Embodiment 1
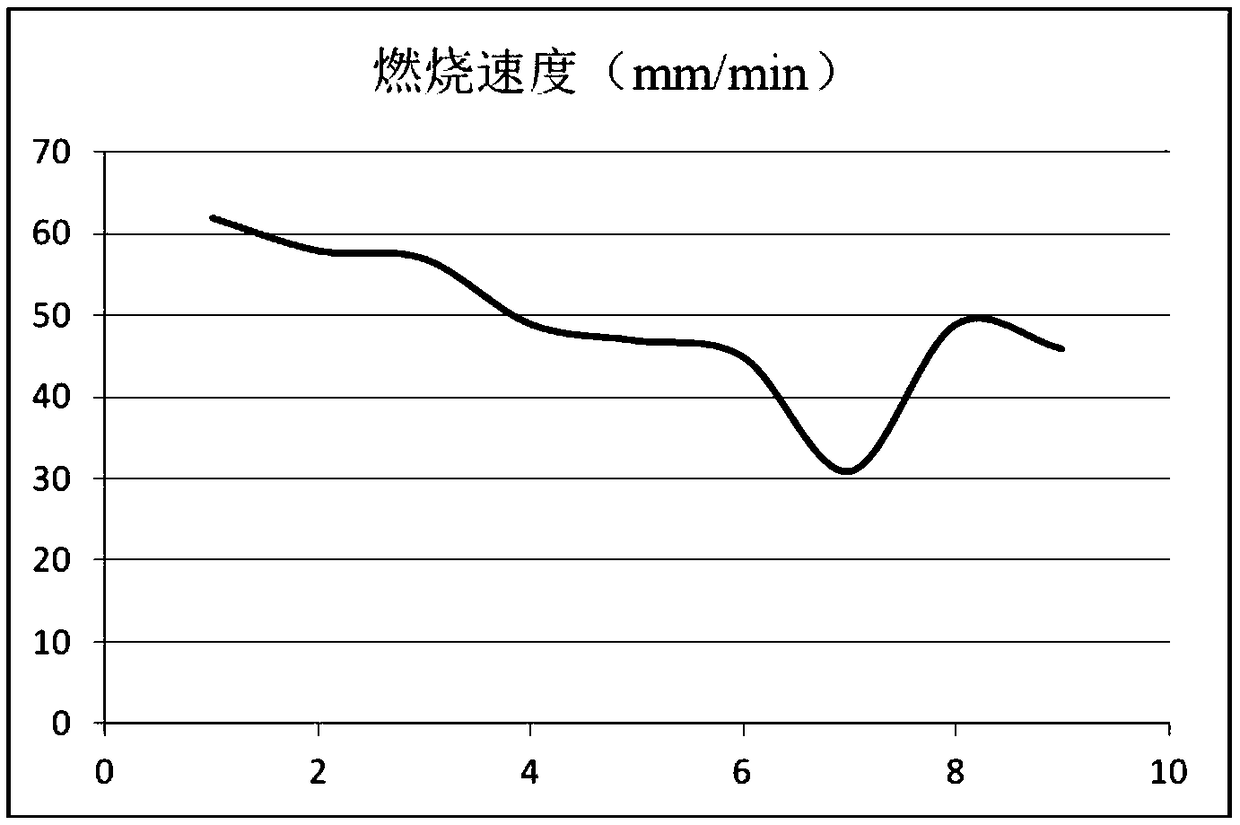
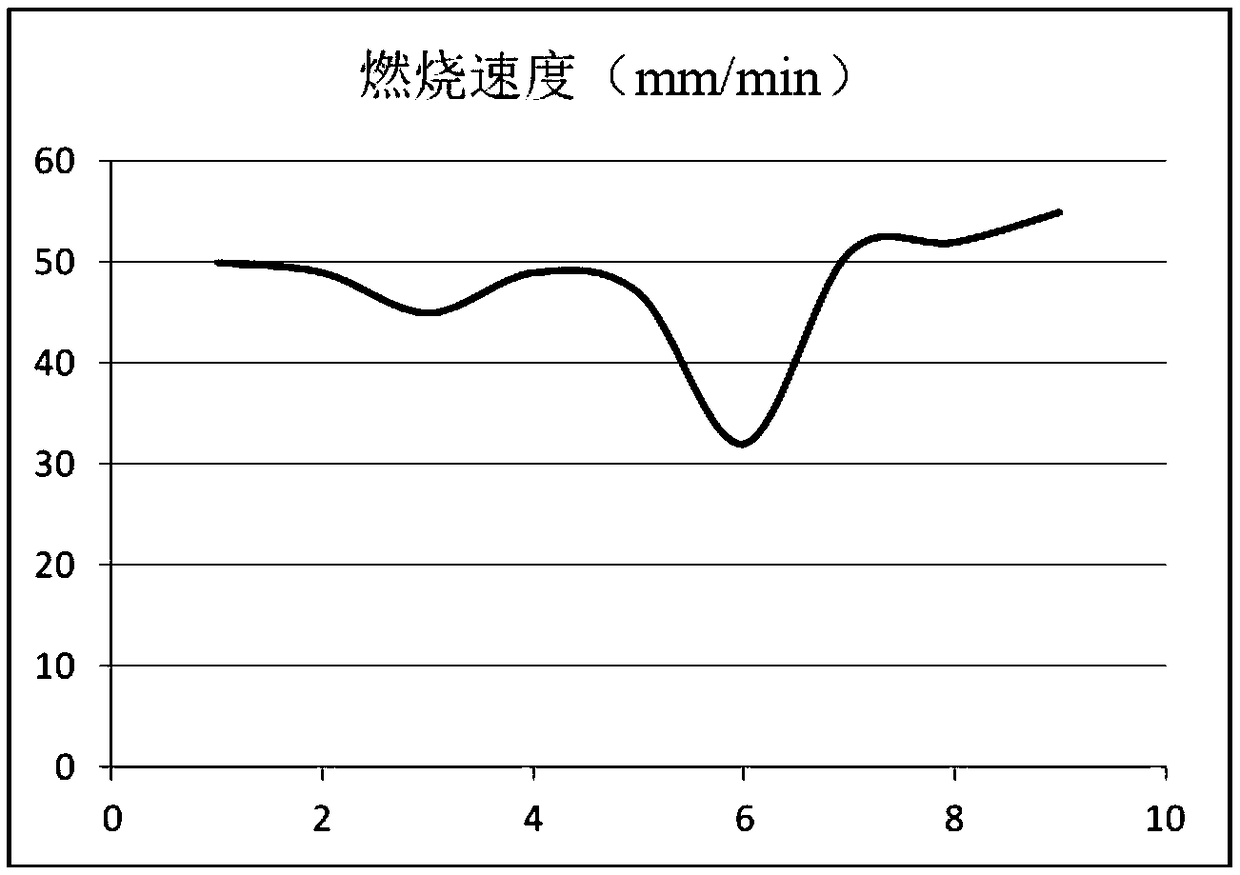
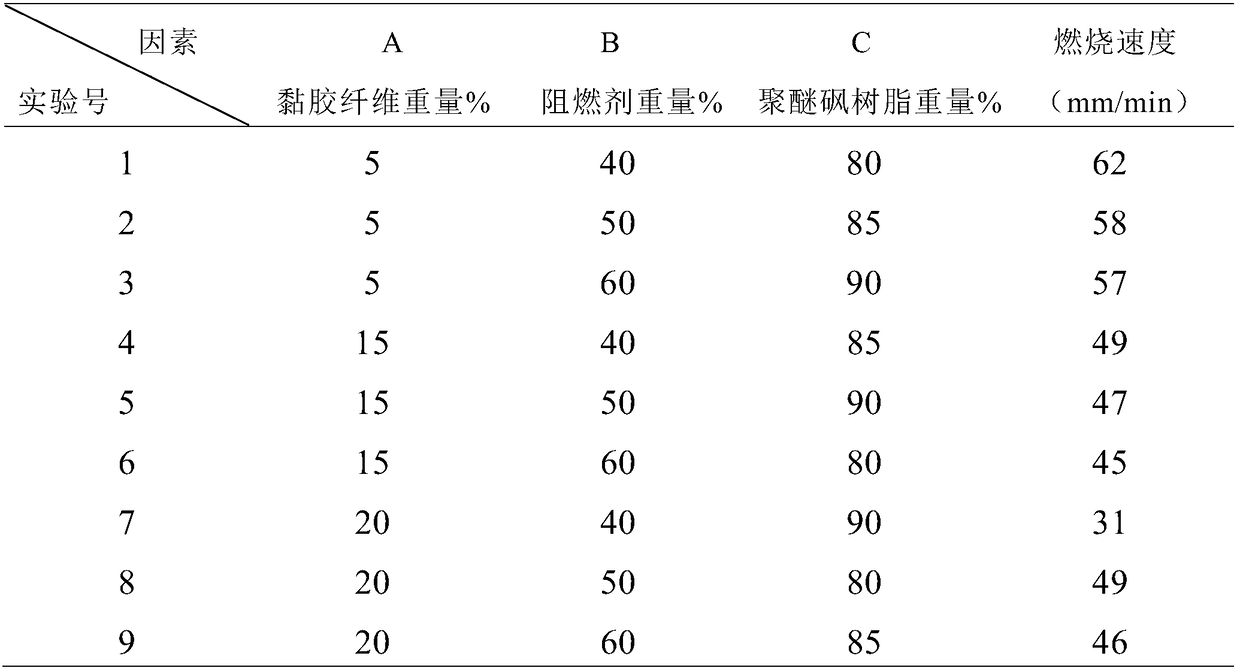
[0043] The comparison of the experimental results of the optimal process ratio of embodiment 1 and embodiment 2 shows that although the amount of flame retardant in the impregnation solution of experiment 7 of embodiment 1 is less than that of experiment 6 of embodiment 2, the mixed powder particles sprinkled The content of polyethersulfone resin is higher. Due to the good viscosity and internal cohesion of polyethersulfone resin, the powder particles of polyethersulfone resin are used to improve the bonding force between the base fabric and aluminum foil, glass fiber, and foam, and polyethersulfone resin is also self-extinguishing, without adding any Flame retardants have excellent flame retardancy, so the nonwoven fabric obtained in Example 1 has high flame retardancy. On the contrary, the content of polyethersulfone resin in the mixed powder particles in Experiment 7 of Example 2 is relatively low, but the content of flame retardant in the impregnation solution is relativel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Gram weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com