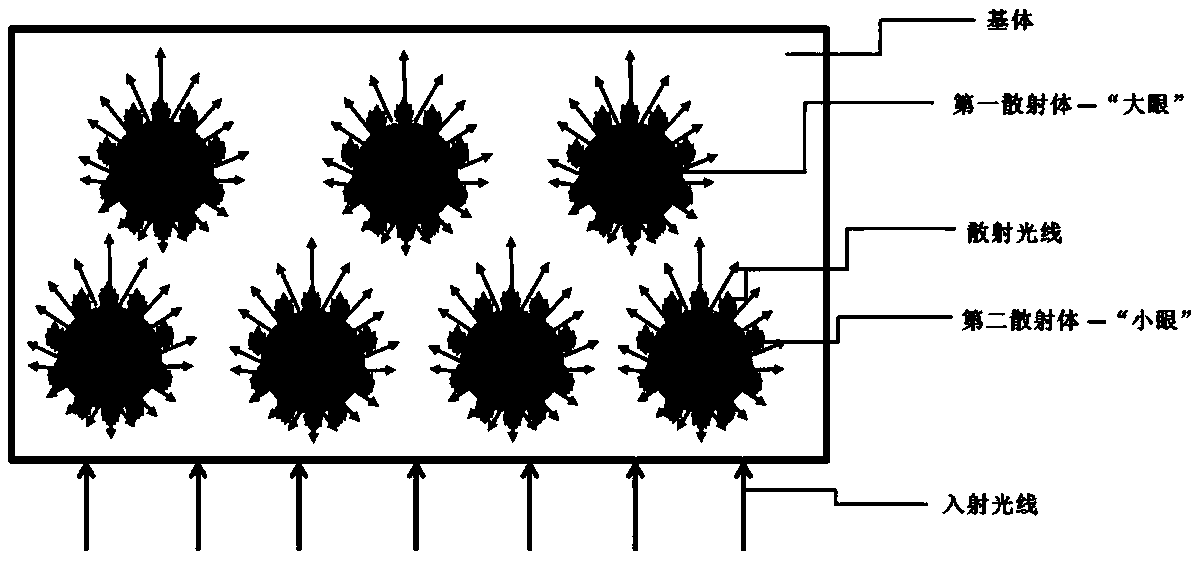
Light scattering material containing compound eye-like structure scatterer
A scatterer and light scattering technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenient optical performance, loss of scattering range, single scattering particles, etc., and achieve easy mold processing, low manufacturing cost, and large scattering range Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] 70 parts by mass of polycarbonate (PC), 30 parts by mass of acrylonitrile copolymer (SAN) and 3.3% of the total weight of SAN with a diameter of 2 μm silicon dioxide (SiO 2 ) were melt-blended by a torque rheometer and granulated to obtain polycarbonate composite particles, which were molded at 240°C to obtain an isotropic light-scattering sheet with a thickness of 0.6 mm. The measured transmittance is 73%, the haze is 87.5%, and the scattering angle is 30°.
Embodiment 2
[0034] 70 parts by mass of polycarbonate (PC), 30 parts by mass of acrylonitrile copolymer (SAN) and 3.3% of the total weight of SAN polymethylsilsesquioxane beads (OSB2) with a diameter of 5 μm were subjected to torque flow Polycarbonate composite particles were obtained by melting and blending with a variable instrument, and granulated. The composite particles were molded at 240° C. to obtain an isotropic light-scattering sheet with a thickness of 0.6 mm. The measured transmittance is 82.3%, the haze is 93.6%, and the scattering angle is 27°.
Embodiment 3
[0036] 70 parts by mass of polycarbonate (PC), 30 parts by mass of acrylonitrile copolymer (SAN) and polymethylsilsesquioxane beads (OSB3) with a diameter of 10 μm accounting for 6.7% of the total weight of SAN were subjected to torque flow Polycarbonate composite particles were obtained by melt blending and granulation, and the composite particles were molded at 240°C into a sample of 100.0 mm (length) × 30.0 mm (width) × 1 mm (thickness). Then the sample was fixed in a high-temperature universal tensile testing machine and thermally stretched at 190°C with a stretch ratio of 2. The scattering angle in the short-axis scattering direction is measured to be 22.0º, and the scattering angle in the long-axis scattering direction is 32.3º.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Scattering angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Scattering angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com