A method for reusing ionic liquid from waste liquid for preparing cellulose nanofibers
A technology of nanofibers and ionic liquids, applied in the field of chemical waste liquid treatment, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory, and achieve the effect of simple operation, mild conditions, and efficient recycling and reuse
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
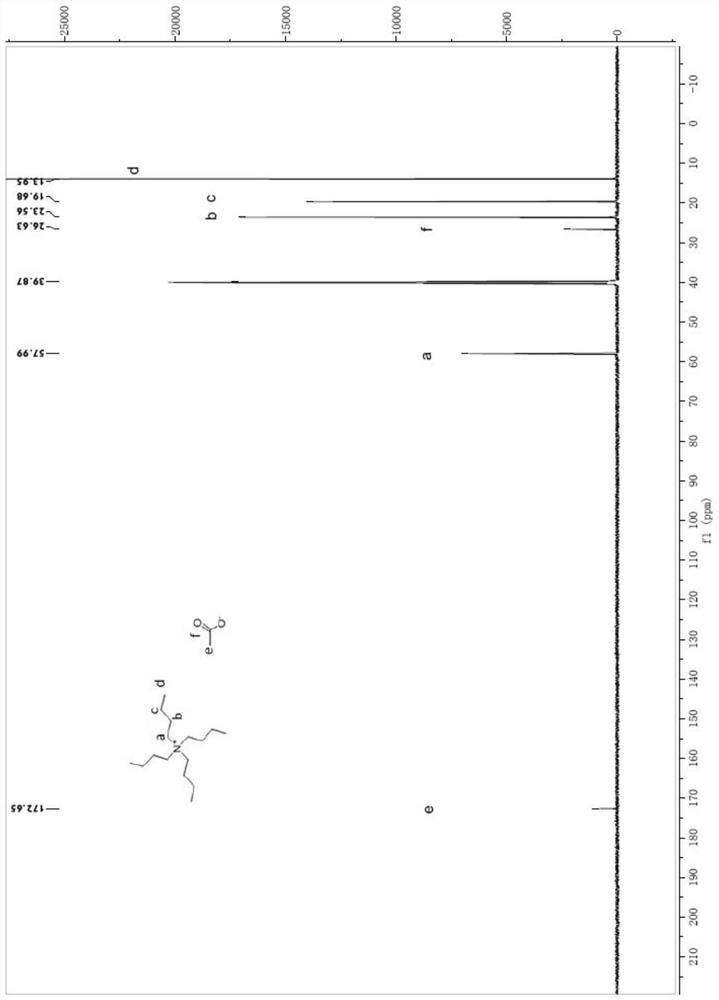
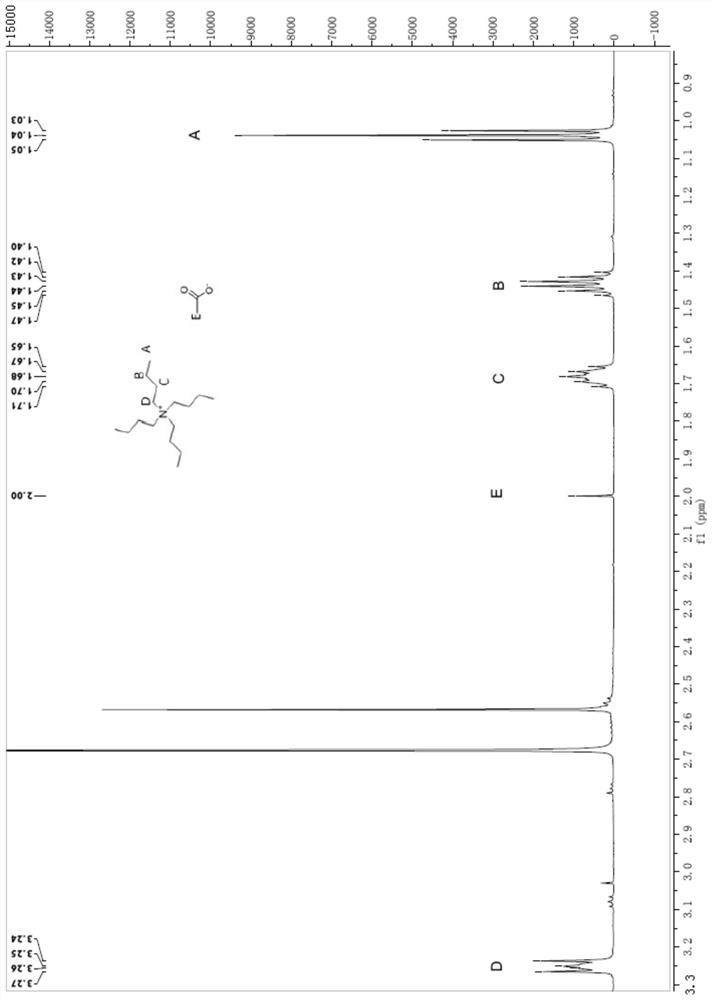
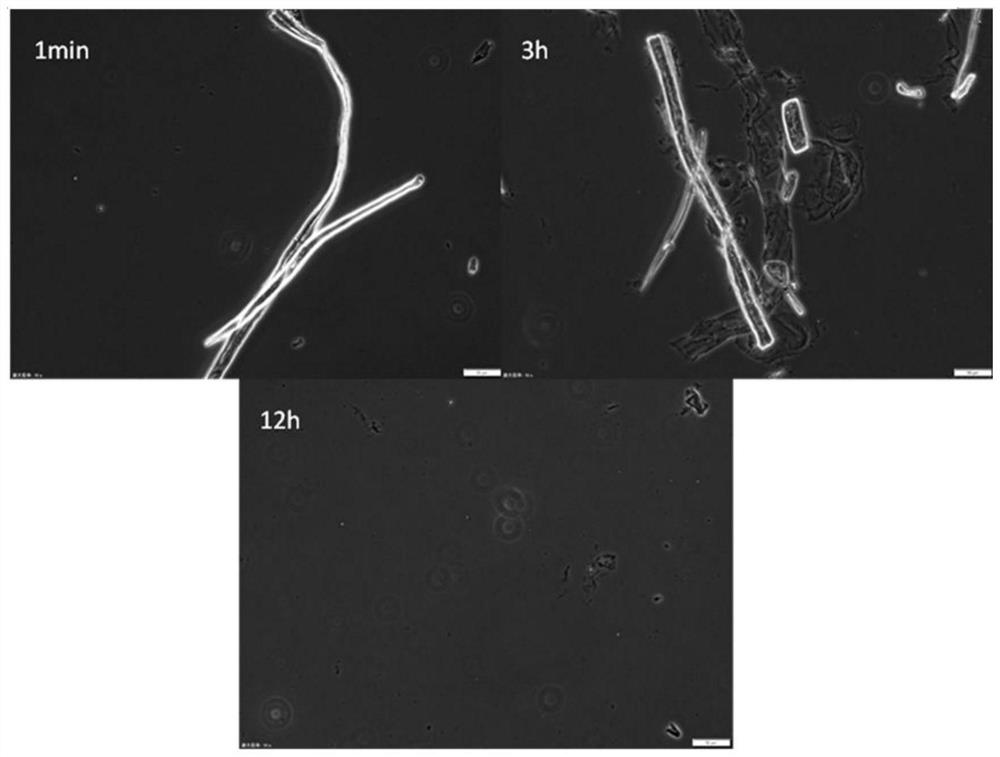
[0029] A method for reclaiming a quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid from waste liquid preparing cellulose nanofibers, the steps are as follows:
[0030] 1) Take 3 g of waste liquid from the preparation of cellulose nanofibers (containing a quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid with a mass percentage concentration of 5%), add dichloromethane and water in sequence, mix well, let stand for 10 minutes, and extract once. Most of the DMSO goes into the aqueous phase. Wherein, the mass of waste liquid accounts for 15% of the total mass of the system, and the mass concentration ratio of dichloromethane / water is 10:1.
[0031] 2) Collect the dichloromethane extraction phase in the lower layer, and rotate it at room temperature for 20 minutes. Observe that there is no more liquid distilled out, collect the residue, and use a vacuum freeze dryer with a temperature of -50 ° C and a vacuum of 20 Pa to dry it in a vacuum. Sample 12h.
[0032] 3) Add 5 times the mass of dichloromethane ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A method for reclaiming a quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid from waste liquid preparing cellulose nanofibers, the steps are as follows:
[0037] 1) Take 3 g of waste liquid from the preparation of cellulose nanofibers (containing a quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid with a mass percentage concentration of 5%), add dichloromethane and water in sequence, mix well, let stand for 10 minutes, and extract once. Most of the DMSO goes into the aqueous phase. Wherein, the mass of waste liquid accounts for 15% of the total mass of the system, and the mass concentration ratio of dichloromethane / water is 5:1.
[0038] 2) Collect the dichloromethane extraction phase in the lower layer, and rotate it at room temperature for 20 minutes. Observe that there is no more liquid distilled out, collect the residue, and use a vacuum freeze dryer with a temperature of -50 ° C and a vacuum of 20 Pa to dry it in a vacuum. Sample 12h.
[0039] 3) Add 5 times the mass of dichloromethane t...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A method for reclaiming a quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid from waste liquid preparing cellulose nanofibers, the steps are as follows:
[0044] 1) Take 3 g of waste liquid from the preparation of cellulose nanofibers (containing a quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid with a mass percentage concentration of 5%), add dichloromethane and water in sequence, mix well, let stand for 10 minutes, and extract once. Most of the DMSO goes into the aqueous phase. Wherein, the mass of waste liquid accounts for 15% of the total mass of the system, and the mass concentration ratio of dichloromethane / water is 1:1.
[0045]2) Collect the dichloromethane extraction phase in the lower layer, and rotate it at room temperature for 20 minutes. Observe that there is no more liquid distilled out, collect the residue, and use a vacuum freeze dryer with a temperature of -50 ° C and a vacuum of 20 Pa to dry it in a vacuum. Sample 12h.
[0046] 3) Add 5 times the mass of dichloromethane to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com