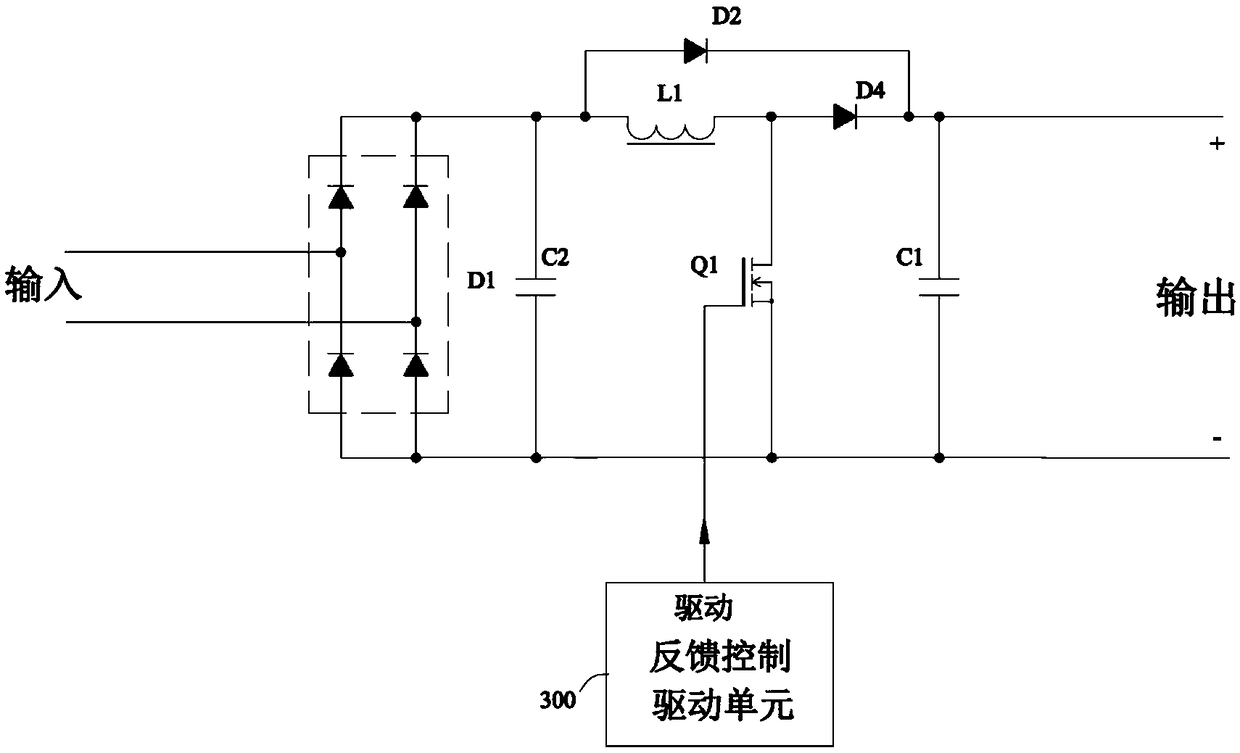
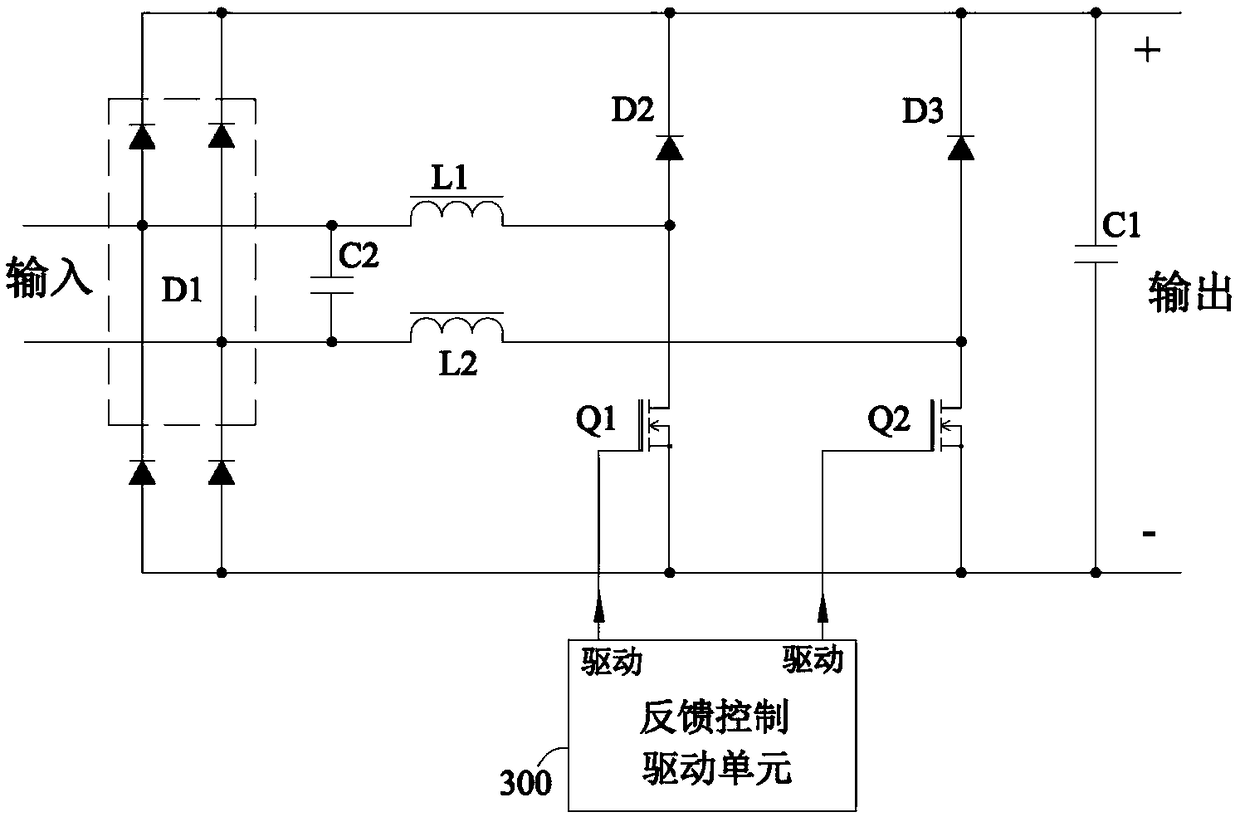
A bridgeless three-rectifier Boost power supply circuit
A power supply circuit and circuit technology, applied in the direction of high-efficiency power electronic conversion, electrical components, adjusting electrical variables, etc., can solve the problems of EMI noise, floating AC input line, complex control of bridgeless PFC circuit, etc., to achieve anti-surge capability Strong, strong anti-interference, to achieve the effect of active power factor correction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
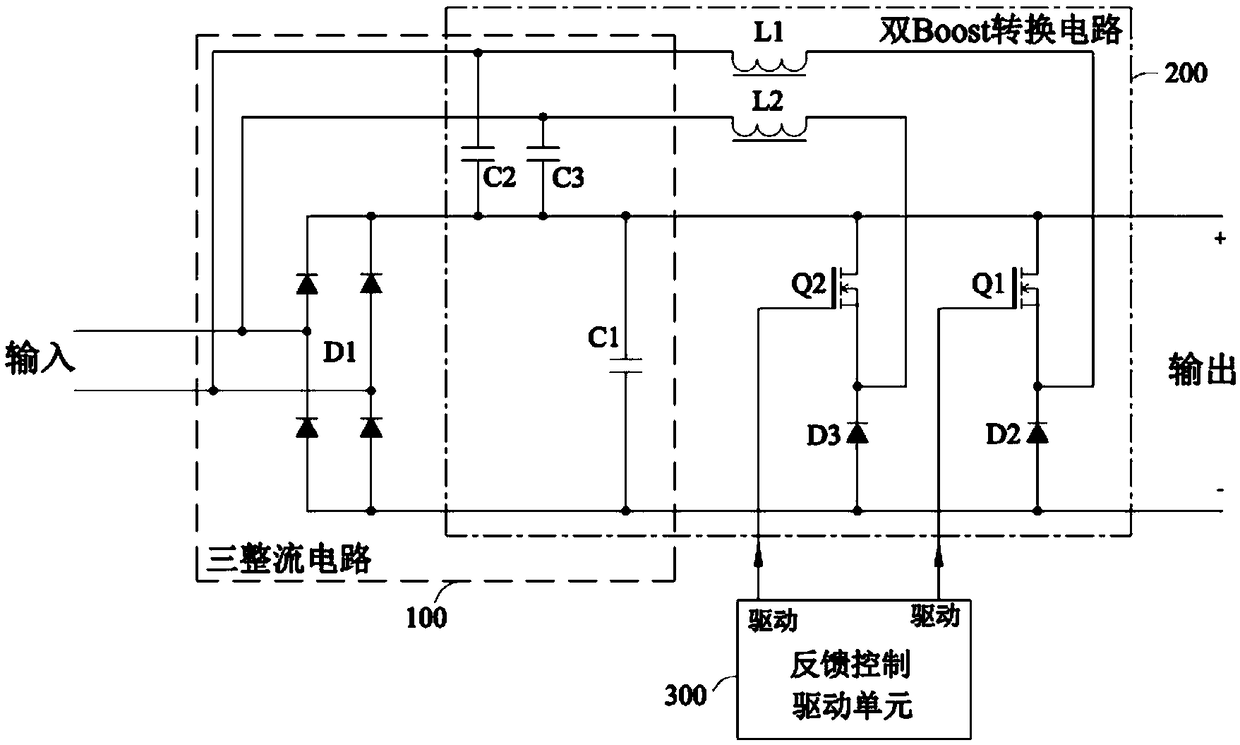
[0044] A bridgeless three-rectification Boost power supply circuit shown in this embodiment, see image 3 As shown, it includes three rectification circuits 100, a double Boost conversion circuit 200, a feedback control drive unit 300, and an energy storage capacitor C1.
[0045] The dual Boost conversion circuit includes a first Boost circuit and a second Boost circuit.
[0046] The first Boost circuit includes a first Boost capacitor C2, a first Boost inductor L1, a first Boost switch element Q1, and a first Boost rectifier element (diode D2 is selected). When the first Boost switch element Q1 is turned on, the first Boost inductor L1, the first Boost switching element Q1 and the first Boost capacitor C2 form a first Boost loop in which the voltage on the first Boost capacitor C2 charges the first Boost inductor L1; when the first Boost switching element is turned off, the first Boost inductor L1 , the first Boost rectifier element, the first Boost capacitor, and the energy...
Embodiment 2
[0073] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the first Boost rectifier element and the second Boost rectifier element use switching elements, which are respectively switching element Q3 and switching element Q4, see Figure 8 , the on and off of the switching element Q3 and the switching element Q4 are controlled by the feedback control driving unit.
[0074] The conduction loss of the switching element is Irms 2 *Rds(on), the conduction loss of the rectifier element is Vf*Iavg.
[0075] The current device technology, because the Rds(on) of the switching element FET, etc. is getting smaller and smaller, so in small and medium power applications, due to the low loss, it is used to replace the rectifier element to improve efficiency. The disadvantage is that it is expensive and requires additional drive control circuit. In high-power applications, since the Vf value of the rectifier element does not change too much with the increase of current, the lo...
Embodiment 3
[0078] In this embodiment, the first BUCK inductance Ls1, the second BUCK inductance Ls2 and the filter capacitor Cs1 are added on the basis of the first embodiment, and the first Boost switching element Q1 and the first Boost rectifying element (diode D2 is selected) form the first BUCK The bridge arm, the first BUCK bridge arm, the first BUCK inductance Ls1 and the filter capacitor Cs1 form the first BUCK converter, the first BUCK converter is used to perform BUCK conversion output on the voltage on the energy storage capacitor; the second Boost switching element Q2 and The second Boost rectifier element (diode D3 is selected) forms the second BUCK bridge arm, the second BUCK bridge arm, the second BUCK inductance and the filter capacitor Cs1 form the second BUCK converter, and the second BUCK converter is used for the energy storage capacitor voltage for BUCK conversion output, see Figure 9 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com