Contact graph routing algorithm based on stochastic linear network coding in deep space communication
A random linear, network coding technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of asymmetric forward and reverse link transmission rates, harsh deep space communication environment, few communication opportunities, etc., to improve the reliability of the first transmission, enhance the Network robustness, the effect of reducing the number of retransmissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
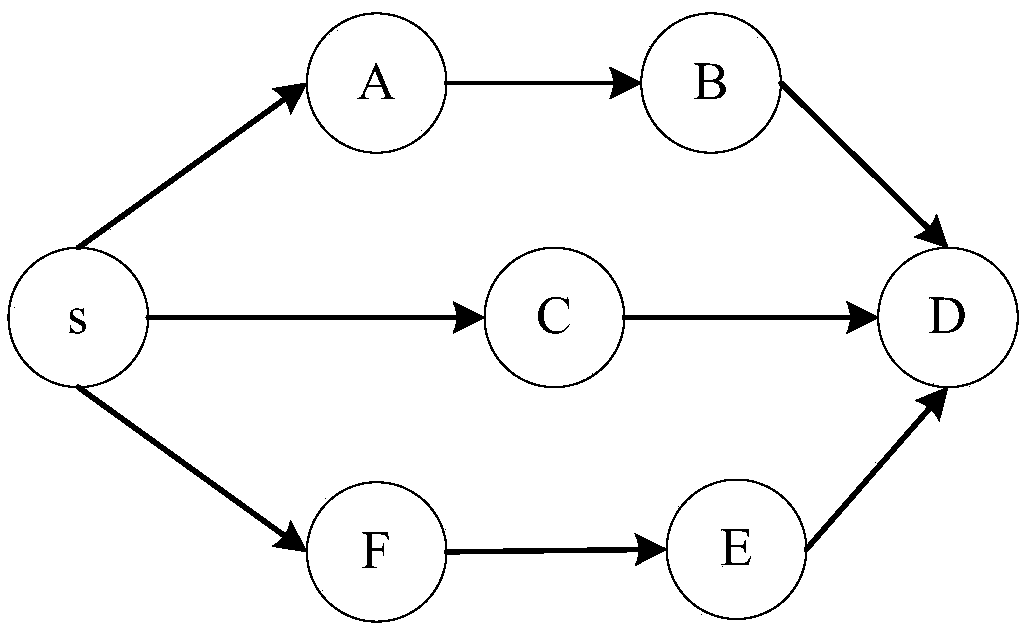
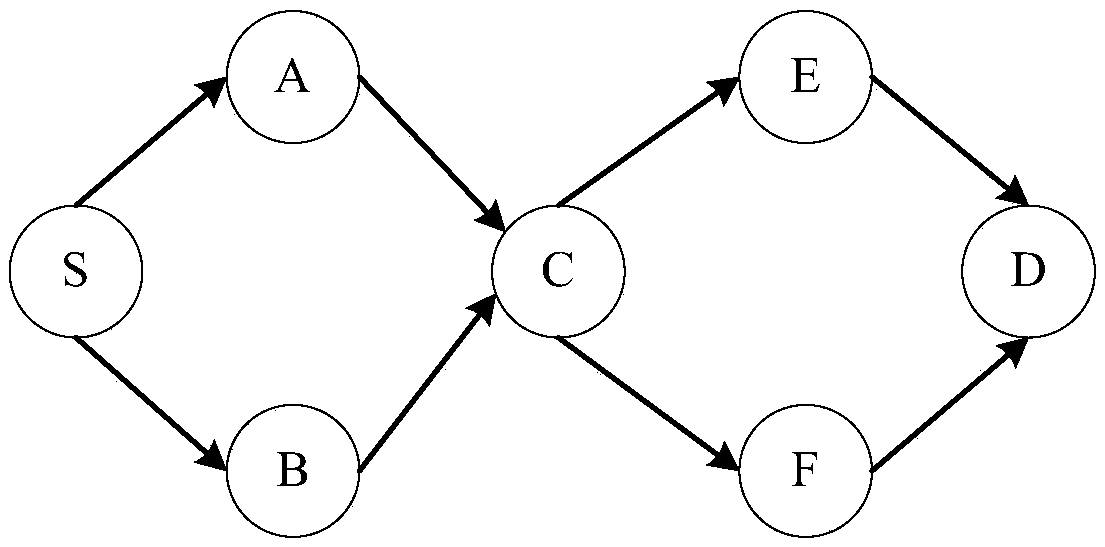
[0077] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1 to Figure 10 Shown; a contact graph routing algorithm based on stochastic linear network coding in deep space communication, which includes:
[0078] S1: The source node uses random linear network coding to process the data packets to be sent, and limits the number of coded packets sent according to the link state information;
[0079] S2: The source node selects multiple link disjoint paths according to the predicted contact graph, and transmits the encoded packets on multiple paths;
[0080] S3: Directly forward the received data packet at the intermediate node with an in-degree greater than 1, and re-encode it before forwarding;
[0081] S4: The destination node performs decoding prediction after receiving a certain number of data packets, and feeds back the data packets that cannot be successfully decoded to the previous hop node set, and the previous hop node set gives priority to sending encoded packets that are helpful for the destinat...
Embodiment 2
[0128] Embodiment 2: as Figure 1 to Figure 9 Shown; a contact graph routing algorithm based on stochastic linear network coding in deep space communication, which includes: multipath path finding, source node coding, partial intermediate node recoding and destination node decoding prediction.
[0129] First, the source node uses random linear network coding to process the data packets to be sent, and limits the number of coded packets sent according to the link state information, ensuring that the destination node can decode successfully and reduce the waste of network resources.
[0130] Secondly, the source node selects multiple link disjoint paths according to the predicted contact graph, and transmits the encoded packets on multiple paths, effectively utilizing the contact opportunities between nodes.
[0131] Thirdly, the received data packets are directly forwarded at the intermediate nodes with an in-degree greater than 1 to reduce the data processing amount of the int...
Embodiment 3
[0200] Embodiment 3, network coding is mainly divided into intra-stream coding and inter-stream coding. Intra-stream encoding mainly encodes the data generated by the same source node. By dividing the data packets of the same data stream into segments of the same size, and then dividing each segment into m data packets of the same size and performing encoding iterations on them, the receiving end only needs to It needs to receive more than m linearly independent coding packets to completely decode the original data packet of this segment with a high probability, improve the fault tolerance performance of the network, and exchange the reliability of data transmission through the computational complexity of the algorithm. Inter-stream coding refers to encoding multiple data packets generated by different data streams at the intermediate node, and multicasting the encoded packets, so that multiple receiving nodes can decode the data packets they need, reducing data traffic. The n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com